
Write down the chemical equation for the preparation of Bakelite from formaldehyde?
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction between formaldehyde (HCHO) and phenol $$\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}} \right)$$ leads to the formation of intermediates which undergo reaction with each other to form a Novolac resin. This resin is further heated with formaldehyde to produce a cross linked polymer, i.e., Bakelite.
Complete step by step solution:
The molecular formula of formaldehyde is HCHO. When formaldehyde reacts with phenol having molecular formula of $${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}$$ in the presence of any acid or base catalyst, this leads to the formation of o-hydroxymethyl phenol and/ or p-hydroxymethyl phenol derivatives (monoethylol phenols) which act as intermediates.
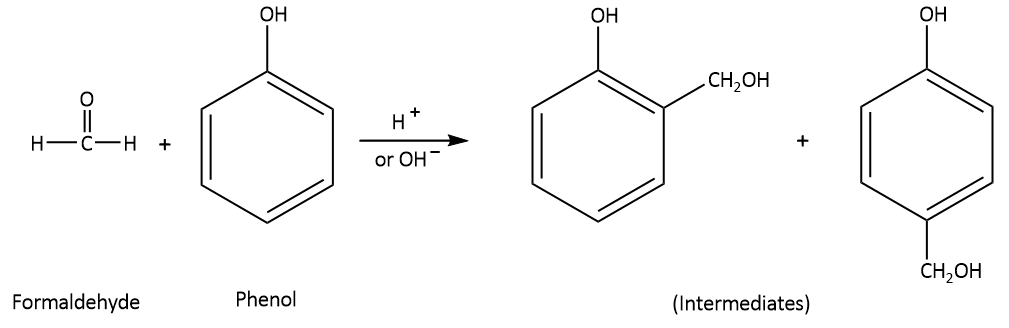
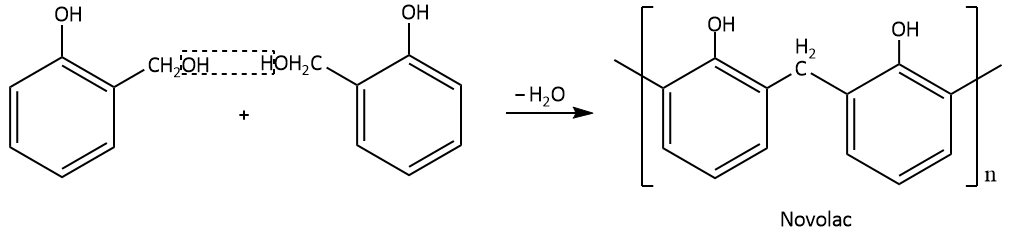
When two monoethylol phenols react with each other, Novolac resin is produced by the elimination of a water molecule. Novolac resin is also referred to as phenol-formaldehyde resin.
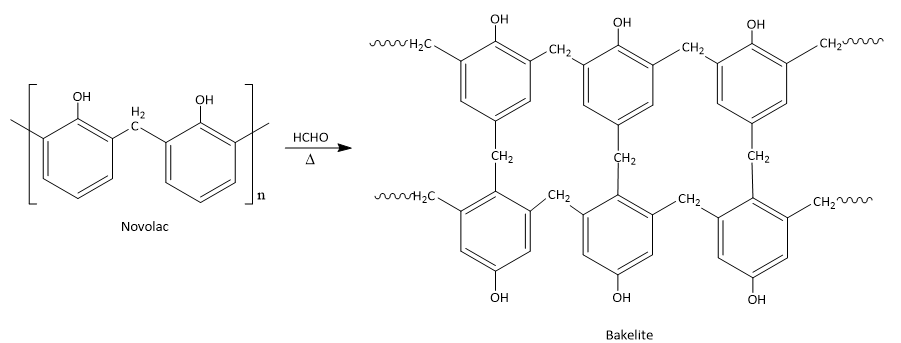
The Novolac resin is further heated in the availability of formaldehyde which leads to the formation of a cross linked polymer which is referred to as Bakelite.
Additional Information: Bakelite is an infusibe solid mass. It is a non-conductive material and hence acts as a good insulator. Therefore it is utilized for the formation of a number of daily used products such as combs, switches, handles of different utensils. It is a thermosetting plastic.
Note: Sometimes, you can get confused between Novolac and Bakelite. Thus the difference between Bakelite and Novolac is that Bakelite is a cross linked polymer or a branched structure which is produced by formaldehyde cross linking to produce an infusible solid mass whereas Novolac is a linear structure produced by the condensation reaction between phenol $$\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}} \right)$$ and formaldehyde (HCHO).
Complete step by step solution:
The molecular formula of formaldehyde is HCHO. When formaldehyde reacts with phenol having molecular formula of $${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}$$ in the presence of any acid or base catalyst, this leads to the formation of o-hydroxymethyl phenol and/ or p-hydroxymethyl phenol derivatives (monoethylol phenols) which act as intermediates.

When two monoethylol phenols react with each other, Novolac resin is produced by the elimination of a water molecule. Novolac resin is also referred to as phenol-formaldehyde resin.

The Novolac resin is further heated in the availability of formaldehyde which leads to the formation of a cross linked polymer which is referred to as Bakelite.

Additional Information: Bakelite is an infusibe solid mass. It is a non-conductive material and hence acts as a good insulator. Therefore it is utilized for the formation of a number of daily used products such as combs, switches, handles of different utensils. It is a thermosetting plastic.
Note: Sometimes, you can get confused between Novolac and Bakelite. Thus the difference between Bakelite and Novolac is that Bakelite is a cross linked polymer or a branched structure which is produced by formaldehyde cross linking to produce an infusible solid mass whereas Novolac is a linear structure produced by the condensation reaction between phenol $$\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}} \right)$$ and formaldehyde (HCHO).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




