
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms and ions:
A.S and \[{S^{2 - }}\]
B.Al and \[A{l^{3 + }}\]
C.H and \[{H^ - }\]
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Lewis structures are simplified diagrammatic representations of the valence shell electrons in a molecule. These symbols display how the electrons are arranged around the individual atom in a molecule. We represent electrons as dots and for bonding electrons, a line between two atoms is drawn.
Complete step by step answer:
A Lewis symbol can be drawn for a single atom, ions or a covalent compound as well. Typically, we represent only valence electrons in Lewis structures and avoid depicting non-valence electrons. Its main purpose is to fulfil the octet rule. It is denoted by an atomic symbol with the dots that represent the valence electrons around it.
Sulphur has an atomic symbol S and atomic number 16. Its electronic configuration is \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^4}\]. So, it has 6 valence electrons. If we add two more electrons to it, \[{S^{2 - }}\] will be formed having 8 valence electrons. We can represent them as:

Aluminium has an atomic symbol of Al and atomic number 13. Its electronic configuration is \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1}\]. So, it has three valence electrons. If we remove these three electrons, \[A{l^{3 + }}\] will be formed having no valence electrons. We can represent them as:

A Hydrogen atom has an atomic symbol H and its atomic number is 1. Its electronic configuration is \[1{s^1}\]. So, it has just one valence electron. If we add one more electron to it, \[{H^ - }\] will be formed having two valence electrons. We can represent them as:
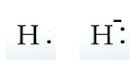
Note:
The Lewis dot structures do not interpret the geometry of the atoms or molecules and do not tell us how bonds are formed between two atoms or how the sharing of electrons results in covalent bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
A Lewis symbol can be drawn for a single atom, ions or a covalent compound as well. Typically, we represent only valence electrons in Lewis structures and avoid depicting non-valence electrons. Its main purpose is to fulfil the octet rule. It is denoted by an atomic symbol with the dots that represent the valence electrons around it.
Sulphur has an atomic symbol S and atomic number 16. Its electronic configuration is \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^4}\]. So, it has 6 valence electrons. If we add two more electrons to it, \[{S^{2 - }}\] will be formed having 8 valence electrons. We can represent them as:

Aluminium has an atomic symbol of Al and atomic number 13. Its electronic configuration is \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1}\]. So, it has three valence electrons. If we remove these three electrons, \[A{l^{3 + }}\] will be formed having no valence electrons. We can represent them as:

A Hydrogen atom has an atomic symbol H and its atomic number is 1. Its electronic configuration is \[1{s^1}\]. So, it has just one valence electron. If we add one more electron to it, \[{H^ - }\] will be formed having two valence electrons. We can represent them as:
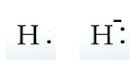
Note:
The Lewis dot structures do not interpret the geometry of the atoms or molecules and do not tell us how bonds are formed between two atoms or how the sharing of electrons results in covalent bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




