
Write structure and function of hair found on the skin.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Mammals are characterized by the presence of hairs on the body. Both the dermal as well as epidermal layers of skin contain follicles necessary for growth of hairs.
Complete answer:
Structure:
The structure of hair is simple. Keratin is a tough protein found in hairs. A hair is anchored onto the skin via hair follicle. Following are the parts of the hair follicle: papilla, matrix, hair bulb. Papilla which is the base of the hair is also known as the root hair. These are found rooted in the connective tissue. These are interconnected with the blood vessel which provides nourishment to the cell and also provides hormones for modifying the structure as well as the growth of the hairs at different stages of life. Inside the papilla or the root hairs, a fluid known as a hair matrix is present. The hair bulbs are the follicles of hair that come out of the surface of the skin. Also, the sebaceous gland and the sweat glands are present along the follicular skin.
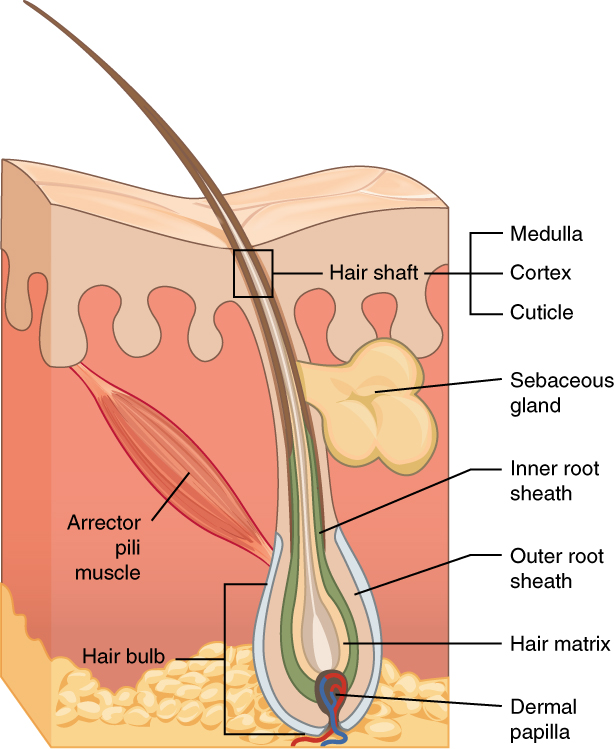
Function:
The presence of hair on the scalp provides protection to the underlying skin from the harmful UV rays as well as help in enhancing the aesthetic beauty of an organism. These hairs are also responsible for maintaining the body temperature. As compared to animals, humans have got very sparse hairs on the body. In case of very high temperatures, the pores of the sweat glands which exist along the follicles of hair start releasing sweat. While in conditions of very low temperature, erection of hairs present over the skin occurs, that is the goose bumps are seen which helps in maintaining the temperature of the body. Also the hairs of the eyebrows that are found above the eyes protect the eyes against the harmful radiations.
Note: The rate of hair growth varies in different people with average rate being approximately one-half inch per month. Also, the pigment cells present in the hair follicles that are responsible for production of melanin creates the hair color. Pigment cells reduce with age thus turning the hairs gray.
Complete answer:
Structure:
The structure of hair is simple. Keratin is a tough protein found in hairs. A hair is anchored onto the skin via hair follicle. Following are the parts of the hair follicle: papilla, matrix, hair bulb. Papilla which is the base of the hair is also known as the root hair. These are found rooted in the connective tissue. These are interconnected with the blood vessel which provides nourishment to the cell and also provides hormones for modifying the structure as well as the growth of the hairs at different stages of life. Inside the papilla or the root hairs, a fluid known as a hair matrix is present. The hair bulbs are the follicles of hair that come out of the surface of the skin. Also, the sebaceous gland and the sweat glands are present along the follicular skin.

Function:
The presence of hair on the scalp provides protection to the underlying skin from the harmful UV rays as well as help in enhancing the aesthetic beauty of an organism. These hairs are also responsible for maintaining the body temperature. As compared to animals, humans have got very sparse hairs on the body. In case of very high temperatures, the pores of the sweat glands which exist along the follicles of hair start releasing sweat. While in conditions of very low temperature, erection of hairs present over the skin occurs, that is the goose bumps are seen which helps in maintaining the temperature of the body. Also the hairs of the eyebrows that are found above the eyes protect the eyes against the harmful radiations.
Note: The rate of hair growth varies in different people with average rate being approximately one-half inch per month. Also, the pigment cells present in the hair follicles that are responsible for production of melanin creates the hair color. Pigment cells reduce with age thus turning the hairs gray.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




