
Write structure of compounds A and B in each of the following reaction:
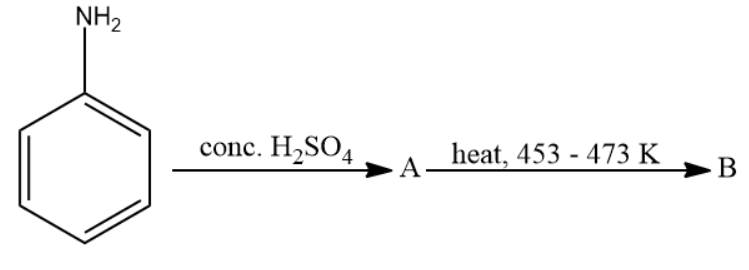

Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: Identify the set of reagents used in the above series of chemical reactions. Concentrated sulfuric acid acts as an acid in the reaction as it has replaceable hydrogen atoms. Identify the basic atom in aniline. Now when heat is supplied to the intermediate, hydrogen ion is eliminated.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The initial reactant in the above series of reactions is aniline.
The nitrogen atom present in the amine group is considered to be basic in nature. So, the concentrated sulfuric acid protonated the nitrogen atom as the lone pair of electrons accepted it. The reaction leading to compound A is given below:
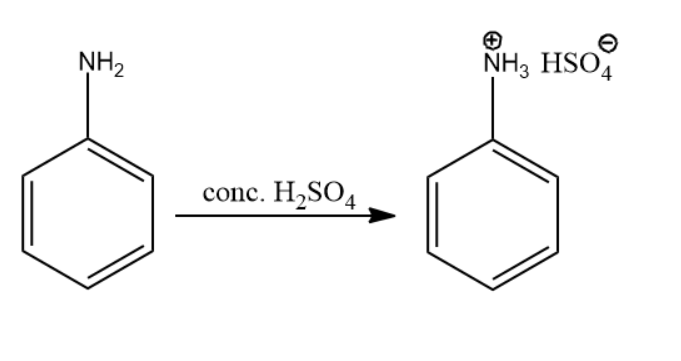
Thus, the product of the above reaction is compound (A).
Now this compound when subjected to heat the following set of reactions take place:
- Hydrogen ion is eliminated from ammonium ion.
- Sulphonyl electrophile attacks the para position of the compound.
Due to the above actions, we arrive at the final compound i.e. p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid. The reaction leading to compound (B) is given below:
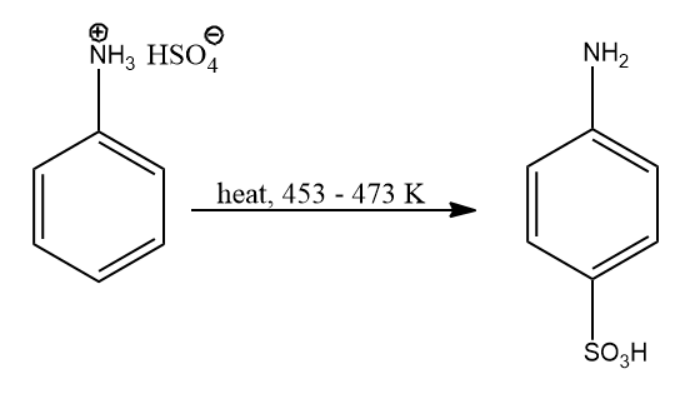
Thus, the product of the above reaction is compound (B).
Note: It is important to understand that sulfuric acid is used for two purposes. Sulfuric acid when accompanied with heat is used as a dehydrating agent for e.g. in dehydration reaction of alkane to give alkene as a product. However, in the above reaction sulfuric acid is seen as a protonating agent. This is because the solution is concentrated and no heat is supplied in the initial stage. Remember this before proceeding with the reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The initial reactant in the above series of reactions is aniline.
The nitrogen atom present in the amine group is considered to be basic in nature. So, the concentrated sulfuric acid protonated the nitrogen atom as the lone pair of electrons accepted it. The reaction leading to compound A is given below:

Thus, the product of the above reaction is compound (A).
Now this compound when subjected to heat the following set of reactions take place:
- Hydrogen ion is eliminated from ammonium ion.
- Sulphonyl electrophile attacks the para position of the compound.
Due to the above actions, we arrive at the final compound i.e. p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid. The reaction leading to compound (B) is given below:

Thus, the product of the above reaction is compound (B).
Note: It is important to understand that sulfuric acid is used for two purposes. Sulfuric acid when accompanied with heat is used as a dehydrating agent for e.g. in dehydration reaction of alkane to give alkene as a product. However, in the above reaction sulfuric acid is seen as a protonating agent. This is because the solution is concentrated and no heat is supplied in the initial stage. Remember this before proceeding with the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




