
Write structure of (i) isohexane (ii) Neopentane
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: Isohexane is also known as $\text{2-methylpentane}$ which is a non-cyclic compound.
Neopentane is also known as $\text{2,2-dimethylpropane}$, which is a branched chain alkane.
Complete answer:
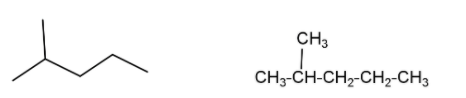
(i) Isohexane – is a saturated alkane molecule with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{14}}}$. This is a six carbon compound in which five carbon atoms are arranged in a leaner form while one carbon atom is attached with a second carbon as a side chain. The IUPAC name of isohexane is $\text{2-methylpentane}$ which shows chain isomerism (same molecular formula and parent chain but differ in arrangement of carbon chain) with $\text{n-hexane}$ and \[\text{2,3-dimethyl butane}\]. Isohexane also shows positional isomerism (compounds which have the same molecular formula, same functional group, same parental carbon chain but they differ in the position of the functional group) with $\text{3-methyl pentane}$.
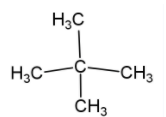
(ii) Neopentane – this is five carbon compound with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}$ in which three carbon compound attached linearly while two carbon compound attached with second carbon as a side chain. This compound shows chain isomerism with $\text{n-pentane}$ and $\text{2-methyl}\,\,\text{butane}$ (iso-pentane). Neopentane is an alkane with quaternary carbon which has tetrahedral geometry. Neopentane is found in gaseous state while its isomers are found in liquid state.
Note:
Neopentane have only one type $\text{(}{{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}\text{H)}$ of hydrogen atom, on reacting with chlorine in the presence of sunlight it gives only one type of monochlorinated product. Due to high branching it has low boiling and melting point and is found in gaseous state at room temperature.
When carbon atoms are branched in a straight chain, the carbon atoms are numbered from that end which is nearest from the branching carbon.
Neopentane is also known as $\text{2,2-dimethylpropane}$, which is a branched chain alkane.
Complete answer:
(i) Isohexane – is a saturated alkane molecule with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{14}}}$. This is a six carbon compound in which five carbon atoms are arranged in a leaner form while one carbon atom is attached with a second carbon as a side chain. The IUPAC name of isohexane is $\text{2-methylpentane}$ which shows chain isomerism (same molecular formula and parent chain but differ in arrangement of carbon chain) with $\text{n-hexane}$ and \[\text{2,3-dimethyl butane}\]. Isohexane also shows positional isomerism (compounds which have the same molecular formula, same functional group, same parental carbon chain but they differ in the position of the functional group) with $\text{3-methyl pentane}$.

(ii) Neopentane – this is five carbon compound with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}$ in which three carbon compound attached linearly while two carbon compound attached with second carbon as a side chain. This compound shows chain isomerism with $\text{n-pentane}$ and $\text{2-methyl}\,\,\text{butane}$ (iso-pentane). Neopentane is an alkane with quaternary carbon which has tetrahedral geometry. Neopentane is found in gaseous state while its isomers are found in liquid state.

Note:
Neopentane have only one type $\text{(}{{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}\text{H)}$ of hydrogen atom, on reacting with chlorine in the presence of sunlight it gives only one type of monochlorinated product. Due to high branching it has low boiling and melting point and is found in gaseous state at room temperature.
When carbon atoms are branched in a straight chain, the carbon atoms are numbered from that end which is nearest from the branching carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




