
Write the chemical formula using the criss-cross method:
Magnesium bicarbonate:
Answer
551.1k+ views
Hint Write down the name of the element and its valency below. Now, interchange the valencies with the other element. This interchanged valency numbers represent the atomicity of the element in the final chemical formula.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about the chemical formula and how it can be found out using the criss-cross method. Now, every compound has a chemical formula. The chemical formula helps us to identify what elements are present in a particular compound, and how many (means the atomicity of each element). For example, ${{H}_{2}}O$ and ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ represent two different but very similar chemical formula of water and hydrogen peroxide respectively, where hydrogen peroxide has an extra oxygen atom.
Now, we have been given with the compounds name as magnesium bicarbonate. By seeing the compound name, we can see that the compound consists of magnesium and the bicarbonate. However, we will consider them as the magnesium cation and the bicarbonate cation. In order to find the chemical formula using the criss-cross method, we have to know the valencies of the cation and anion. Magnesium has a valency of +2 and bicarbonate anion has a valency of -1. So, we write them as:
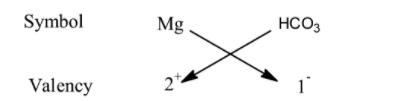
Now, we just interchange the valencies and arrange the compound. As Magnesium corresponds to 1 and $HC{{O}_{3}}$ corresponds to 2, we can write the final chemical formula of the compound as $Mg{{(HC{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}$, which is the required answer for the question.
NOTE: It is to be noted that although the valency of bicarbonate is -1, during the criss-cross method, it is treated as +1 because atomicity cannot be negative in a chemical formula.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about the chemical formula and how it can be found out using the criss-cross method. Now, every compound has a chemical formula. The chemical formula helps us to identify what elements are present in a particular compound, and how many (means the atomicity of each element). For example, ${{H}_{2}}O$ and ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ represent two different but very similar chemical formula of water and hydrogen peroxide respectively, where hydrogen peroxide has an extra oxygen atom.
Now, we have been given with the compounds name as magnesium bicarbonate. By seeing the compound name, we can see that the compound consists of magnesium and the bicarbonate. However, we will consider them as the magnesium cation and the bicarbonate cation. In order to find the chemical formula using the criss-cross method, we have to know the valencies of the cation and anion. Magnesium has a valency of +2 and bicarbonate anion has a valency of -1. So, we write them as:

Now, we just interchange the valencies and arrange the compound. As Magnesium corresponds to 1 and $HC{{O}_{3}}$ corresponds to 2, we can write the final chemical formula of the compound as $Mg{{(HC{{O}_{3}})}_{2}}$, which is the required answer for the question.
NOTE: It is to be noted that although the valency of bicarbonate is -1, during the criss-cross method, it is treated as +1 because atomicity cannot be negative in a chemical formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




