
Write the definition of figure of merit of Galvanometer.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: The figure of merit in general is defined as the numerical value representing the degree of effectiveness or efficiency of an instrument approximated by different estimation techniques. Galvanometer is a device which is used to measure small electric current. When current passes through the coil of the galvanometer, a deflection is observed. Use this information to find the definition of figure of merit of Galvanometer.
Complete answer:
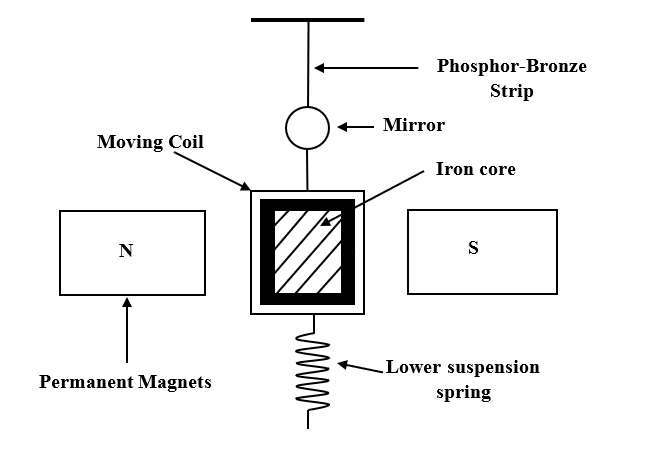
Galvanometer is a device used to detect feeble electric voltage and current in a circuit. The figure of merit of a galvanometer can be defined as a current required to produce unit deflection in the galvanometer scale. The figure of merit is denoted by the symbol k. It is given by,
$k= \dfrac {I}{\theta}$ …(1)
Where, I is the current through the coil
$\theta$ is the angle of deflection
At equilibrium,
$I= \left(\dfrac {K}{NAB}\right)\theta$ …(2)
Where, K is the restoring torque per unit twist of spring constant
N is the number of turns in the coil
A is the area of the galvanometer coil
B is the magnetic flux density of the radial magnetic field of galvanometer magnet
Substituting equation. (2) in equation. (1) we get,
$k= \dfrac {\left(\dfrac {K}{NAB}\right)\theta }{\theta}$
$\Rightarrow k= \dfrac {K}{NAB}$ …(3)
But, $G= \dfrac {k}{NAB}$ ...(4)
Where, G is the galvanometer constant
From the equation. (2) and (3) we get,
$k=G$
Note:
Galvanometer has a moderate resistance of about $100 \Omega$ and the galvanometer itself has a small current carrying capacity of 1 mA. The deflection in the galvanometer is directly proportional to the current passed through it. Students must remember that a galvanometer can be used as an ammeter as well as a voltmeter. If we want to use it as an ammeter then it should be connected along the element. Whereas if we have to use a galvanometer as a voltmeter then it should be connected across the element.
Complete answer:

Galvanometer is a device used to detect feeble electric voltage and current in a circuit. The figure of merit of a galvanometer can be defined as a current required to produce unit deflection in the galvanometer scale. The figure of merit is denoted by the symbol k. It is given by,
$k= \dfrac {I}{\theta}$ …(1)
Where, I is the current through the coil
$\theta$ is the angle of deflection
At equilibrium,
$I= \left(\dfrac {K}{NAB}\right)\theta$ …(2)
Where, K is the restoring torque per unit twist of spring constant
N is the number of turns in the coil
A is the area of the galvanometer coil
B is the magnetic flux density of the radial magnetic field of galvanometer magnet
Substituting equation. (2) in equation. (1) we get,
$k= \dfrac {\left(\dfrac {K}{NAB}\right)\theta }{\theta}$
$\Rightarrow k= \dfrac {K}{NAB}$ …(3)
But, $G= \dfrac {k}{NAB}$ ...(4)
Where, G is the galvanometer constant
From the equation. (2) and (3) we get,
$k=G$
Note:
Galvanometer has a moderate resistance of about $100 \Omega$ and the galvanometer itself has a small current carrying capacity of 1 mA. The deflection in the galvanometer is directly proportional to the current passed through it. Students must remember that a galvanometer can be used as an ammeter as well as a voltmeter. If we want to use it as an ammeter then it should be connected along the element. Whereas if we have to use a galvanometer as a voltmeter then it should be connected across the element.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




