
Write the differences between P-wave and T-wave
Answer
589.2k+ views
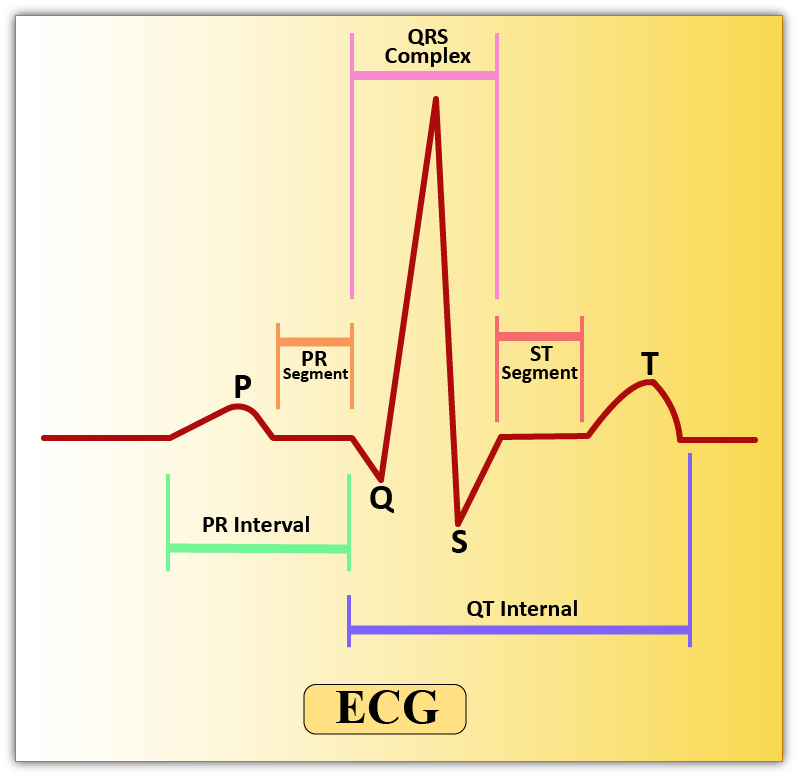
Hint: A normal ECG consists of different waves and complexes. An ECG or the electrocardiogram is the graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It is recorded using different leads. In a normal ECG different waves like P-wave, the QRS complex, and the T-wave are seen.
Complete answer:
Additional Information: -The pacemaker region of the heart (SA Node) exhibits spontaneous depolarization that causes action potentials, resulting in the automatic beating of the heart.
-The QRS wave represents the depolarization of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction of the ventricles starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
-QR wave is elevated in myocardial infarction.
- T wave is elevated in hyperkalemia and depressed in hypokalemia.
-PR is elevated in bradycardia and declines in tachycardia.
-Insufficient oxygen received by heart muscles is indicated by a flat T-wave.
Note: P-wave and T-wave have diagnostic importance as the enlargement of the waves or smaller waves indicate different problems.
For example- In the case of Atrial fibrillation ‘P’ wave is absent or in the case of hyperkalemia, the P-wave is absent or small.
In the case of hyperkalemia, the T-wave is tall and tented.
Complete answer:
| P-Wave | T-Wave |
| ‘P’ wave is the first wave in an ECG and is a positive wave. It indicates the activation of the SA nodes. | ‘T’ wave too is a positive wave and is the final wave in an ECG though sometimes an additional U wave may be seen. It represents ventricular relaxation. |
| The p wave is also called the atrial complex. | It is also called as the Ventricular complex |
| The normal duration of the P-wave is 0.1 seconds. | The normal duration of the T-wave is 0.2 seconds. |
| The normal amplitude of P-wave is 0.1 to 0.12 mV. | The normal amplitude of T-wave is 0.3 mV |
| A P-wave is produced due to the depolarization of the atrial musculature | A T-wave is produced due to the repolarization of ventricular musculature. |
Additional Information: -The pacemaker region of the heart (SA Node) exhibits spontaneous depolarization that causes action potentials, resulting in the automatic beating of the heart.
-The QRS wave represents the depolarization of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction of the ventricles starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
-QR wave is elevated in myocardial infarction.
- T wave is elevated in hyperkalemia and depressed in hypokalemia.
-PR is elevated in bradycardia and declines in tachycardia.
-Insufficient oxygen received by heart muscles is indicated by a flat T-wave.

Note: P-wave and T-wave have diagnostic importance as the enlargement of the waves or smaller waves indicate different problems.
For example- In the case of Atrial fibrillation ‘P’ wave is absent or in the case of hyperkalemia, the P-wave is absent or small.
In the case of hyperkalemia, the T-wave is tall and tented.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




