
Write the electronic structure of propene, but-1-ene and but-2-ene.
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: An electronic structure of given alkenes can be drawn from the molecular formula of the compound. The molecular formula of propene, but-1-ene and but-2-ene are${{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$,${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$and ${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecular formula of propene is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$.The electronic structure of Propene is given below:
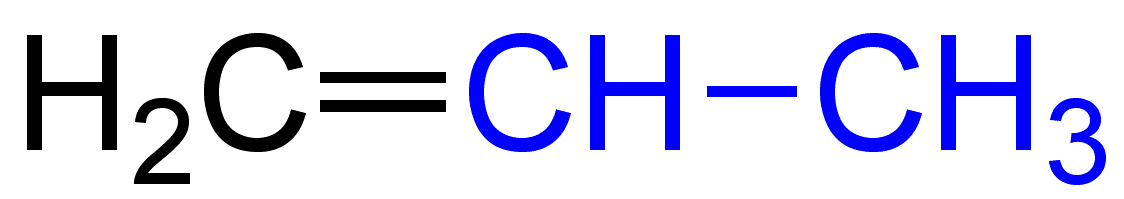
The molecular formula of But-1-ene is ${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$.The electronic structure of But-1-ene is given below:
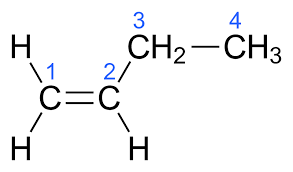
The molecular formula of But-2-ene is ${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$.The electronic structure of But-2-ene is given below:
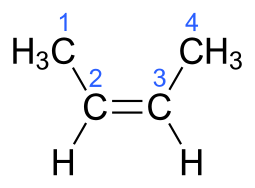
Additional Information:
-Following are steps to name an alkene following which we can draw the electronic structure of given alkenes.
-The ene suffix (ending) indicates an alkene or cycloalkene.
-The longest chain chosen for the root name must include both carbon atoms of the double bond.
-The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a double bond carbon atom. If the double bond is in the centre of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts.
-The smaller of the two numbers designating the carbon atoms of the double bond is used as the double bond locator.
-If more than one double bond is present the compound is named as a diene, triene or equivalent prefix indicating the number of double bonds, and each double bond is assigned a locator number.
Note:
But-1-ene and But-2-ene are structural isomers which differ in their structure but has same molecular formula. Since they differ in the position of double bond they are also known as position isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecular formula of propene is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$.The electronic structure of Propene is given below:

The molecular formula of But-1-ene is ${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$.The electronic structure of But-1-ene is given below:

The molecular formula of But-2-ene is ${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$.The electronic structure of But-2-ene is given below:
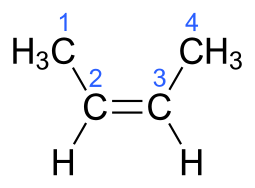
Additional Information:
-Following are steps to name an alkene following which we can draw the electronic structure of given alkenes.
-The ene suffix (ending) indicates an alkene or cycloalkene.
-The longest chain chosen for the root name must include both carbon atoms of the double bond.
-The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a double bond carbon atom. If the double bond is in the centre of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts.
-The smaller of the two numbers designating the carbon atoms of the double bond is used as the double bond locator.
-If more than one double bond is present the compound is named as a diene, triene or equivalent prefix indicating the number of double bonds, and each double bond is assigned a locator number.
Note:
But-1-ene and But-2-ene are structural isomers which differ in their structure but has same molecular formula. Since they differ in the position of double bond they are also known as position isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




