
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.
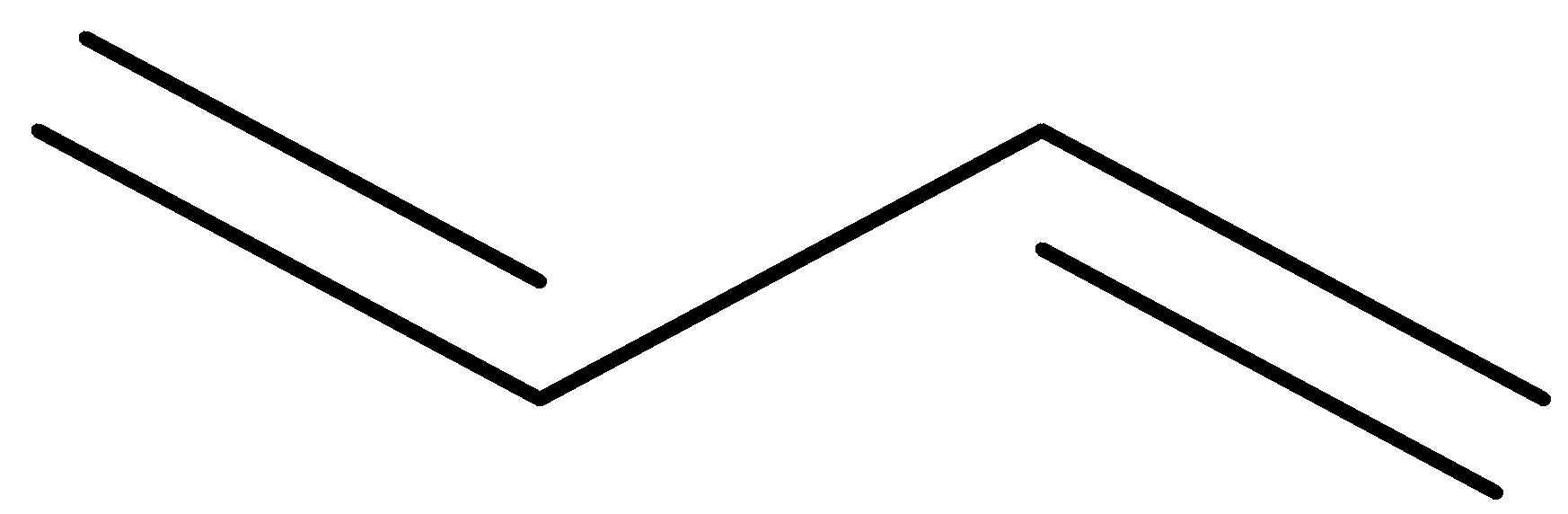

Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: For IUPAC nomenclature of unsubstituted alkenes, the longest continuous carbon chain having the carbon – carbon double bond is taken as the parent hydrocarbon and the name of the parent alkene is obtained by changing the suffix ‘ane’ to ‘ene’ in the name of the corresponding alkene.
Numbering is done from that end which gives the lowest possible number to the carbon atoms of the double bond. The position of the double bond is designated by the number of the first doubly bonded carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
-The compounds containing carbon – carbon double bonds or triple bonds in their molecules are known as unsaturated hydrocarbons.
-Those unsaturated hydrocarbons having carbon – carbon double bonds are called alkenes.
-In case of alkenes containing multiple bonds, i.e., double bonds and triple bonds, the rules are as follows.
-The first few rules are the same like those for simple alkenes till the numbering of the chain. -The locants should be placed just before the corresponding suffix.
-If the multiple double bond occurs two or more times, then the prefixes ‘di’, ‘tri’, etc. are used before the suffix ‘ene’.
Now, let us see the structure of the given compound.
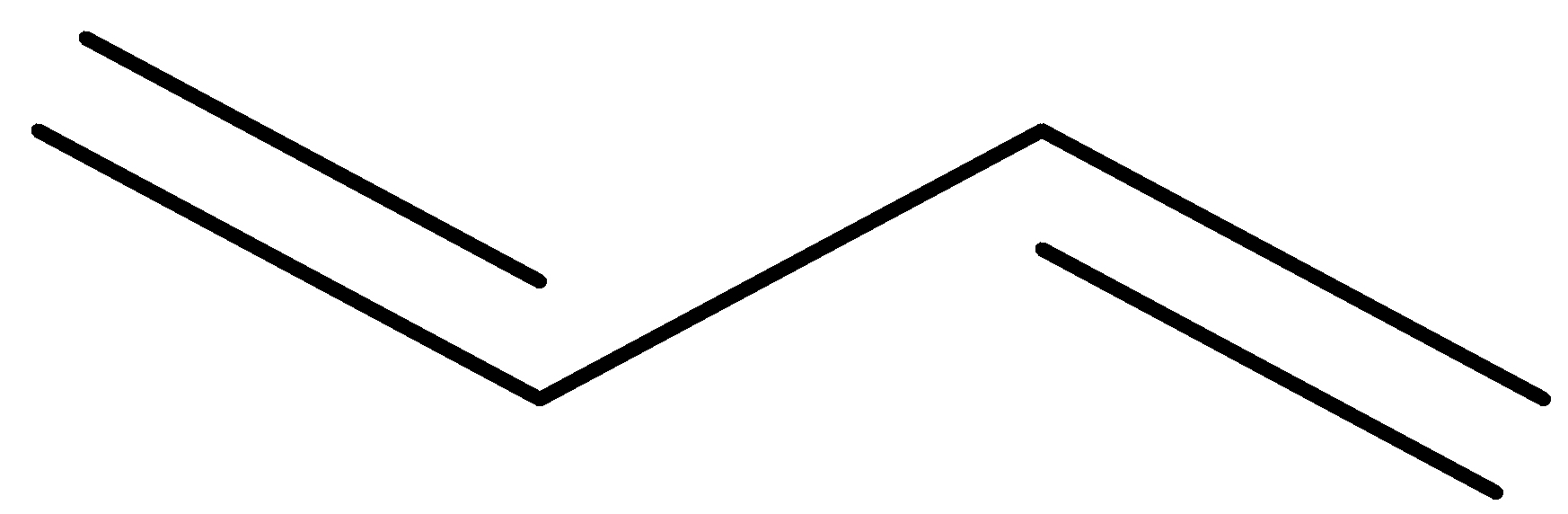 or
or
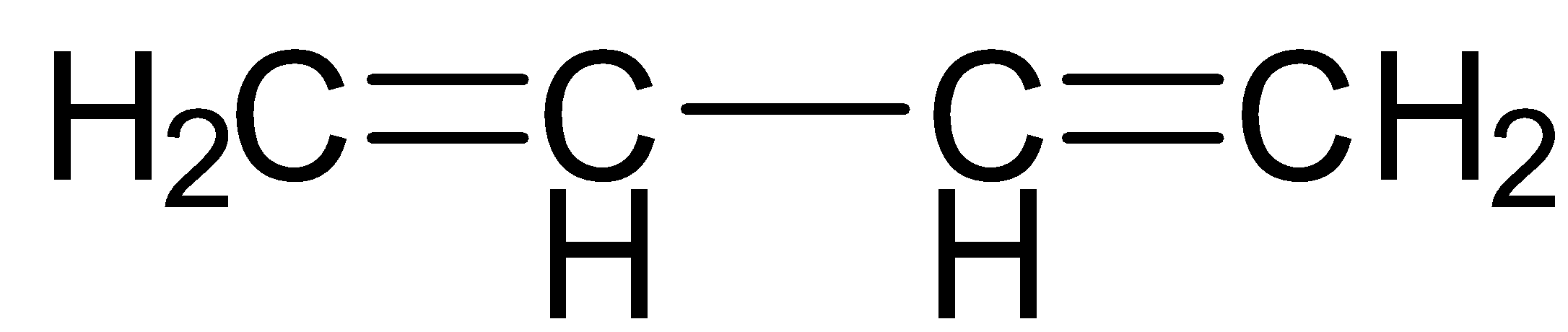
It contains two double bonds.
-Now, following the IUPAC rule, we will see that the longest continuous carbon chain having the carbon – carbon double bond involves 4 carbon atoms and so the parent hydrocarbon is butane.
-The suffix ane is changed to ene and thus the name of parent alkene is butene.
The numbering of double bonds from both ends gives the same position 1.
-After that, moving across the chain, we have the position of the second double bond as 3. So, the double bonds are present at 1 and 3 positions.
Since double bond occurs twice, the prefix di will be used before the suffix ene.
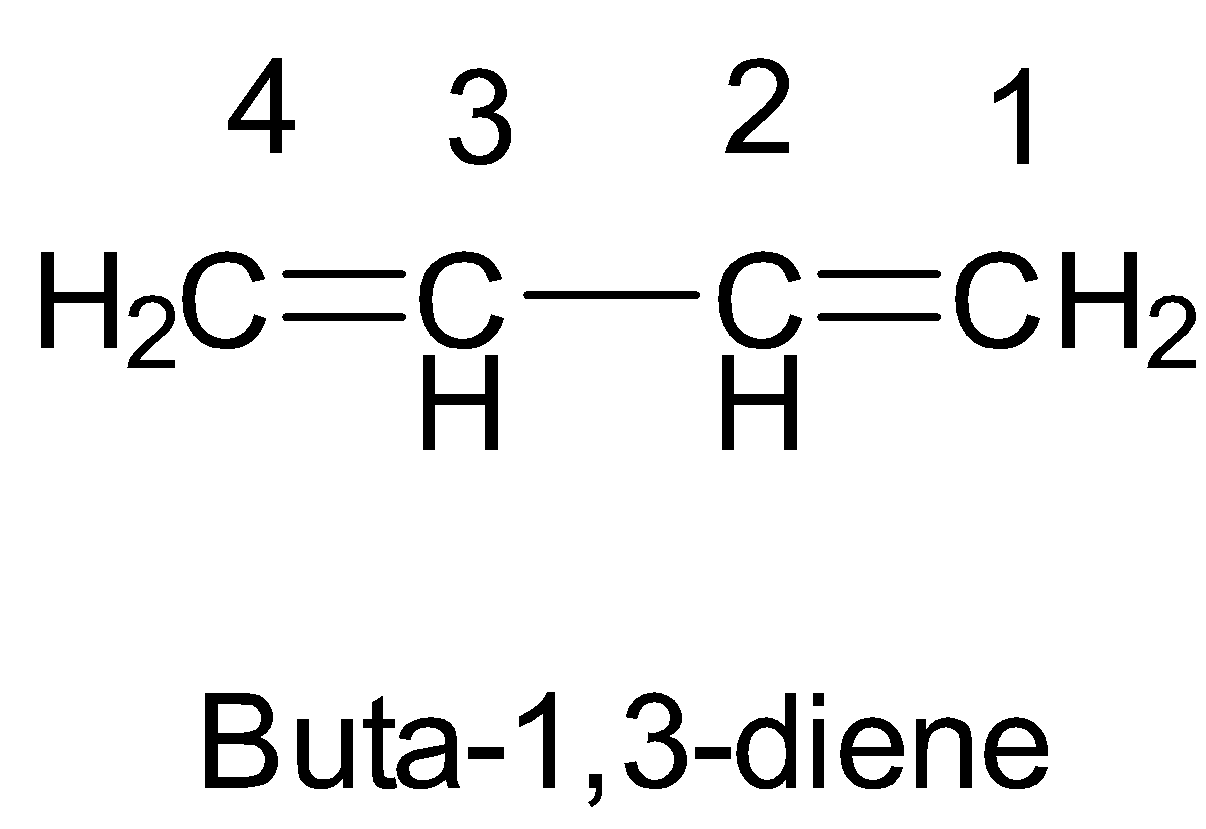
So, finally we will have the IUPAC name of the given compound as buta-1,3-diene.
Note:
The IUPAC nomenclature for alkynes is similar, only the suffix ane is changed to ‘yne’.
If a compound has double as well as triple bonds, then the two are considered at par applying the lowest sum rule. But if the position of both double and triple bonds are the same, then the double bond gets the preference in numbering, but the compound is named as a derivative of alkyne in both cases.
Numbering is done from that end which gives the lowest possible number to the carbon atoms of the double bond. The position of the double bond is designated by the number of the first doubly bonded carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
-The compounds containing carbon – carbon double bonds or triple bonds in their molecules are known as unsaturated hydrocarbons.
-Those unsaturated hydrocarbons having carbon – carbon double bonds are called alkenes.
-In case of alkenes containing multiple bonds, i.e., double bonds and triple bonds, the rules are as follows.
-The first few rules are the same like those for simple alkenes till the numbering of the chain. -The locants should be placed just before the corresponding suffix.
-If the multiple double bond occurs two or more times, then the prefixes ‘di’, ‘tri’, etc. are used before the suffix ‘ene’.
Now, let us see the structure of the given compound.

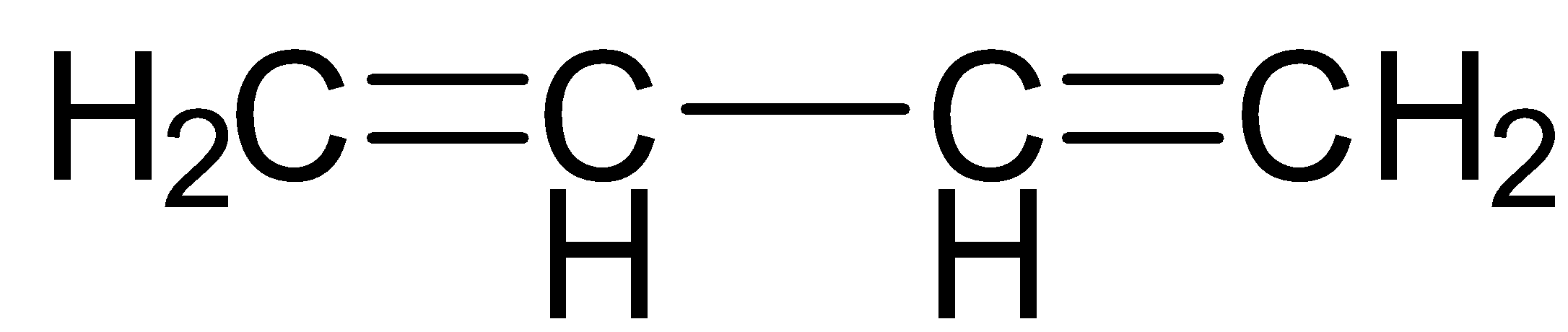
It contains two double bonds.
-Now, following the IUPAC rule, we will see that the longest continuous carbon chain having the carbon – carbon double bond involves 4 carbon atoms and so the parent hydrocarbon is butane.
-The suffix ane is changed to ene and thus the name of parent alkene is butene.
The numbering of double bonds from both ends gives the same position 1.
-After that, moving across the chain, we have the position of the second double bond as 3. So, the double bonds are present at 1 and 3 positions.
Since double bond occurs twice, the prefix di will be used before the suffix ene.

So, finally we will have the IUPAC name of the given compound as buta-1,3-diene.
Note:
The IUPAC nomenclature for alkynes is similar, only the suffix ane is changed to ‘yne’.
If a compound has double as well as triple bonds, then the two are considered at par applying the lowest sum rule. But if the position of both double and triple bonds are the same, then the double bond gets the preference in numbering, but the compound is named as a derivative of alkyne in both cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




