
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:
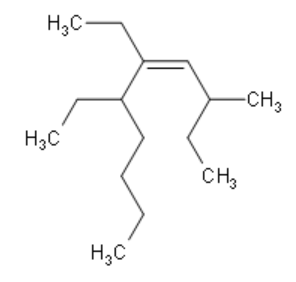

Answer
606k+ views
Hint: The above-stated compound contains 15 carbon atoms and 30 hydrogen atoms. For determining the IUPAC name, we need to follow some steps which are defined step-by-step.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Firstly, we need to identify the functional group here, which is Alkene. This determines that the prefix is –ene. Secondly, we need to determine the longest carbon chain that includes the double bond $\left( \text{C=C} \right)$. In the given diagram, we can see that the longest carbon chain contains a total of 10 carbon atoms. Therefore, we can determine that the suffix is dec- since 10 carbon atoms are present in the decane group of organic compounds.
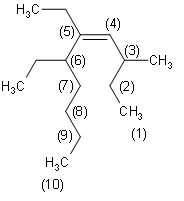
Now that we know the suffix and prefix, we need to number the chain properly such that the Alkene is connected to the carbon atom of the lowest possible number. Then, we identify the branches. Here, the branches are methyl at position 3 and ethyl at positions 5 and 6. Since there are 2 ethyl groups present, the nomenclature contains ${\text{5,6}-\text{diethyl}}$. Alkane is at position 4. Hence the nomenclature contains ${\text{dec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$. Hence, we can write the correct IUPAC name as
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Additional Information: Here are some properties of Alkene that we should be knowing:
The alkenes are insoluble in water because of the non polar characteristics.
The boiling points of the compounds increase as the number of carbon atoms in the compound increases.
Alkenes are more reactive than the alkanes.
Almost all the chemical reactions of alkene occur at the double bond.
Note: We should be having an idea about the lowest sum rule. The lowest sum rule is used whenever there are moreNow that we know the suffix and prefix, we need to number the chain properly such that the Alkene is connected to the carbon atom of the lowest possible number. Then, we identify the branches. Here, the branches are methyl at position 3 and ethyl at positions 5 and 6. Since there are 2 ethyl groups present, the nomenclature contains ${\text{5,6}-\text{diethyl}}$. Alkane is at position 4. Hence the nomenclature contains ${\text{dec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$. Hence, we can write the correct IUPAC name as
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Additional Information: Here are some properties of Alkene that we should be knowing:
The alkenes are insoluble in water because of the non polar characteristics.
The boiling points of the compounds increase as the number of carbon atoms in the compound increases.
Alkenes are more reactive than the alkanes.
Almost all the chemical reactions of alkene occur at the double bond.
Note: We should be having an idea about the lowest sum rule. The lowest sum rule is used whenever there are more than one substitutes present on the carbon chain. This rule states that, substituent should get the lowest possible number.
The numbering of the ring carbons then continues in a direction (clockwise or anti clockwise) that affords the second substituent the lowest possible location number.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Firstly, we need to identify the functional group here, which is Alkene. This determines that the prefix is –ene. Secondly, we need to determine the longest carbon chain that includes the double bond $\left( \text{C=C} \right)$. In the given diagram, we can see that the longest carbon chain contains a total of 10 carbon atoms. Therefore, we can determine that the suffix is dec- since 10 carbon atoms are present in the decane group of organic compounds.

Now that we know the suffix and prefix, we need to number the chain properly such that the Alkene is connected to the carbon atom of the lowest possible number. Then, we identify the branches. Here, the branches are methyl at position 3 and ethyl at positions 5 and 6. Since there are 2 ethyl groups present, the nomenclature contains ${\text{5,6}-\text{diethyl}}$. Alkane is at position 4. Hence the nomenclature contains ${\text{dec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$. Hence, we can write the correct IUPAC name as
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Additional Information: Here are some properties of Alkene that we should be knowing:
The alkenes are insoluble in water because of the non polar characteristics.
The boiling points of the compounds increase as the number of carbon atoms in the compound increases.
Alkenes are more reactive than the alkanes.
Almost all the chemical reactions of alkene occur at the double bond.
Note: We should be having an idea about the lowest sum rule. The lowest sum rule is used whenever there are moreNow that we know the suffix and prefix, we need to number the chain properly such that the Alkene is connected to the carbon atom of the lowest possible number. Then, we identify the branches. Here, the branches are methyl at position 3 and ethyl at positions 5 and 6. Since there are 2 ethyl groups present, the nomenclature contains ${\text{5,6}-\text{diethyl}}$. Alkane is at position 4. Hence the nomenclature contains ${\text{dec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$. Hence, we can write the correct IUPAC name as
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is
${\text{3}-\text{methyl}-\text{5,6}-\text{diethyldec}-\text{4}-\text{ene}}$.
Additional Information: Here are some properties of Alkene that we should be knowing:
The alkenes are insoluble in water because of the non polar characteristics.
The boiling points of the compounds increase as the number of carbon atoms in the compound increases.
Alkenes are more reactive than the alkanes.
Almost all the chemical reactions of alkene occur at the double bond.
Note: We should be having an idea about the lowest sum rule. The lowest sum rule is used whenever there are more than one substitutes present on the carbon chain. This rule states that, substituent should get the lowest possible number.
The numbering of the ring carbons then continues in a direction (clockwise or anti clockwise) that affords the second substituent the lowest possible location number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




