
Write the laws of refraction of light. Explain the same with the help of a ray diagram, when a ray of light passes through a rectangular slab.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:We know that when a light ray moves from one medium to another medium, its direction of propagation is bent. It generally occurs due to the change in density of the two media. Each of the medium is characterised with the help of refractive index.
Complete answer:
In the given question, it is talked about the refraction of light. We are required to write the laws associated with it and explain the phenomenon of refraction, when a ray of light passes through a rectangular slab, with a net diagram.
To begin with, we must know what the phenomenon of refraction is. Refraction in physics is the change in the direction of a wave travelling from one medium to another or from a slow shift in the medium. The most frequently observed effect is the refraction of light, but other waves also undergo refraction, such as sound waves and water waves.
We can frequently observe the phenomenon of refraction in our day to day life. On summer days, we observe mirages on the roads, which give the illusion of water. Again, when we place a coin in the bottom of a jar filled with water. The coin appears to be present above the actual position.
The laws of refraction are as follows:
1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal, all lie in the same plane, at the interface which joins the two media.
2. The ratio of the sine of the incident angle and the refracted angle is always a constant for a particular medium, which we call it as refractive index.
Now, let us take a glass slab, which is placed on a horizontal plane.
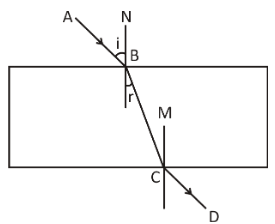
The light ray \[AB\] enters glass slab from the upper direction, which hits the glass at the point \[B\] , as it enters from rarer medium to denser medium. The normal present at the upper part is \[N\] . The angle of incidence is designated as \[i\] . As the ray enters the glass slab, it gets closer to the normal and forms the refracted angle designated as \[r\] . The light ray then hits the opposite side of the slab and suffers refraction again as it exits from denser to rarer medium.
Note: It is important to remember that when a ray of light suffers refraction, it moves closer to the normal when it enters a denser medium from a rarer medium. The angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence if the light rays moves from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
Complete answer:
In the given question, it is talked about the refraction of light. We are required to write the laws associated with it and explain the phenomenon of refraction, when a ray of light passes through a rectangular slab, with a net diagram.
To begin with, we must know what the phenomenon of refraction is. Refraction in physics is the change in the direction of a wave travelling from one medium to another or from a slow shift in the medium. The most frequently observed effect is the refraction of light, but other waves also undergo refraction, such as sound waves and water waves.
We can frequently observe the phenomenon of refraction in our day to day life. On summer days, we observe mirages on the roads, which give the illusion of water. Again, when we place a coin in the bottom of a jar filled with water. The coin appears to be present above the actual position.
The laws of refraction are as follows:
1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal, all lie in the same plane, at the interface which joins the two media.
2. The ratio of the sine of the incident angle and the refracted angle is always a constant for a particular medium, which we call it as refractive index.
Now, let us take a glass slab, which is placed on a horizontal plane.

The light ray \[AB\] enters glass slab from the upper direction, which hits the glass at the point \[B\] , as it enters from rarer medium to denser medium. The normal present at the upper part is \[N\] . The angle of incidence is designated as \[i\] . As the ray enters the glass slab, it gets closer to the normal and forms the refracted angle designated as \[r\] . The light ray then hits the opposite side of the slab and suffers refraction again as it exits from denser to rarer medium.
Note: It is important to remember that when a ray of light suffers refraction, it moves closer to the normal when it enters a denser medium from a rarer medium. The angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence if the light rays moves from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




