
How can I write the Lewis dot structure for ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$?
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Lewis dot structure shows the valence electrons/ outermost shell electrons of the entire molecule or electrons which are involved in the formation of bonds inside the molecule.
Complete Solution :
As we know that in ethane (${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$) single bond is present in between two carbon atoms and its structure is shown as follow:
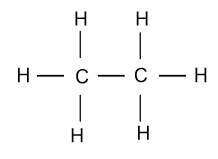
-For drawing the Lewis structure of ethane, first we calculate the valence electrons of each atom present in the molecule.
-Atomic number of carbon is 6 and its electronic configuration is written as $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2}$ and from this it is clear that in carbon four valence electrons are present.
-Atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is written as $1{s^1}$ and from this it is clear that in hydrogen one valence electron is present.
-In ethane two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms are present,
So total valence electrons in ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$$ = (2 \times 4) + (6 \times 1)$
${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$$ = 8 + 6 = 14$
-Lewis dot structure of ethane (${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$) is as follow:
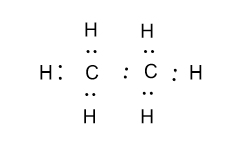
-In the above figure a total seven pairs of electrons are present which further makes bonds in the structure. Out of seven pairs of electrons, in six pairs one electron of that pair belongs from the one hydrogen atom and another one belongs from the carbon atom. And in one pair each electron belongs from the single carbon atom.
Note: During the formation of Lewis dot structure some of you may get confused in between the total number of valence electrons of the entire molecule and valence electrons of each atom involved in that molecule. So, always keep in mind that never calculate the number of valence electrons of each atom from the total number of valence electrons of the molecule. In Spite of this, first write the valence electrons of each present atom and then calculate total valence electrons for the molecule.
Complete Solution :
As we know that in ethane (${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$) single bond is present in between two carbon atoms and its structure is shown as follow:

-For drawing the Lewis structure of ethane, first we calculate the valence electrons of each atom present in the molecule.
-Atomic number of carbon is 6 and its electronic configuration is written as $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2}$ and from this it is clear that in carbon four valence electrons are present.
-Atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is written as $1{s^1}$ and from this it is clear that in hydrogen one valence electron is present.
-In ethane two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms are present,
So total valence electrons in ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$$ = (2 \times 4) + (6 \times 1)$
${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$$ = 8 + 6 = 14$
-Lewis dot structure of ethane (${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$) is as follow:
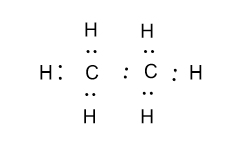
-In the above figure a total seven pairs of electrons are present which further makes bonds in the structure. Out of seven pairs of electrons, in six pairs one electron of that pair belongs from the one hydrogen atom and another one belongs from the carbon atom. And in one pair each electron belongs from the single carbon atom.
Note: During the formation of Lewis dot structure some of you may get confused in between the total number of valence electrons of the entire molecule and valence electrons of each atom involved in that molecule. So, always keep in mind that never calculate the number of valence electrons of each atom from the total number of valence electrons of the molecule. In Spite of this, first write the valence electrons of each present atom and then calculate total valence electrons for the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




