
Write the molecular formula of the \[{2^{nd}}\] and \[{3^{rd}}\] number of the homologous series whose first member is ethene.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Alkanes are aliphatic organic compounds which have a minimum of 1 and maximum ‘n’ number of carbon atoms. Also, only sigma bonds are present in alkanes. This means that alkanes are formed only with single bonds, and not double or triple bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkane is a homologous series with the general formula of \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}\].
Now, from the very first and simplest alkane methane, the molecular formula is different from the \[ - C{H_2}\] unit.
Now from ethane the molecular formula of the \[{2^{nd}}\] and \[{3^{rd}}\] number of the homologous series are, \[{C_3}{H_6},{C_4}{H_8}\].
Additional information:
If organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having that functional group is selected. Functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
The IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a system of organic chemical compounds in the nomenclature of chemicals as stated by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Informally we call it Blue Book. The book mentions certain rules for the naming of compounds having functional groups.
As per IUPAC rules, the first thing is to select the longest continuous chain. Then this chain is numbered and the numbering should begin from the end which is close to the substituent groups. Each substituent group has a certain assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon it has been attached to. These groups are generally arranged alphabetically.
For example, 5-(2-ethylbutyl)-3,3-dimethyldecane has a parent carbon chain called decade I.e. have 10 carbons in the chain. On its third carbon, two methyl groups are attached as mentioned \[\left( {3,3} \right)\]. And on its fifth carbon, a butyl chain is bonded to which another ethyl chain is attached at the second position of the butyl chain. From all this, we get the structure of the compound as
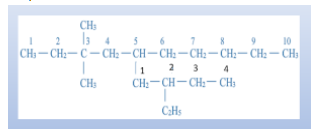
Note: IUPAC names are combined with the primary prefix, root word, and primary suffix. By this, each compound can be named unique. Primary prefixes are used to indicate the origin of the compound in IUPAC nomenclature. Prefixes are used to differentiate the cyclic and acyclic molecules in IUPAC nomenclature.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkane is a homologous series with the general formula of \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}\].
Now, from the very first and simplest alkane methane, the molecular formula is different from the \[ - C{H_2}\] unit.
Now from ethane the molecular formula of the \[{2^{nd}}\] and \[{3^{rd}}\] number of the homologous series are, \[{C_3}{H_6},{C_4}{H_8}\].
Additional information:
If organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having that functional group is selected. Functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
The IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a system of organic chemical compounds in the nomenclature of chemicals as stated by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Informally we call it Blue Book. The book mentions certain rules for the naming of compounds having functional groups.
As per IUPAC rules, the first thing is to select the longest continuous chain. Then this chain is numbered and the numbering should begin from the end which is close to the substituent groups. Each substituent group has a certain assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon it has been attached to. These groups are generally arranged alphabetically.
For example, 5-(2-ethylbutyl)-3,3-dimethyldecane has a parent carbon chain called decade I.e. have 10 carbons in the chain. On its third carbon, two methyl groups are attached as mentioned \[\left( {3,3} \right)\]. And on its fifth carbon, a butyl chain is bonded to which another ethyl chain is attached at the second position of the butyl chain. From all this, we get the structure of the compound as

Note: IUPAC names are combined with the primary prefix, root word, and primary suffix. By this, each compound can be named unique. Primary prefixes are used to indicate the origin of the compound in IUPAC nomenclature. Prefixes are used to differentiate the cyclic and acyclic molecules in IUPAC nomenclature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




