
Write the names of reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis.
A.1-propoxypropane
B.Ethoxy benzene
C.2-methoxy-2-methyl propane
D.1-methoxy ethane
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Williamson synthesis is the general method for the synthesis of ether. It involves the nucleophilic displacement of a halide ion or other leaving group by an alkoxide ion. To solve this question, we need to know the reaction mechanism of Williamson synthesis.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically, the name of this reaction was coined after the scientist named Alexander William Williamson. It is a reaction that uses deprotonated alcohol and an organohalide to form an ether. In this reaction, the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide and forms an ether from the back. This response takes place in the single step, which is both cleavage and bond formation. The products are then formed by elimination. The general reaction is as shown:
$RX + R'ONa \to R - O - R' + NaX$
Now, let’s discuss the name of reagents and their respective equations for the preparation of ethers by Williamson’s synthesis.
1)1-propoxypropane- It is formed by the reaction of sodium prop oxide and 1-bromopropane. The reaction is as shown:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CHONa + C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br \to {C_2}{H_5}C{H_2} - O - C{H_2}{C_2}{H_5} + NaBr$
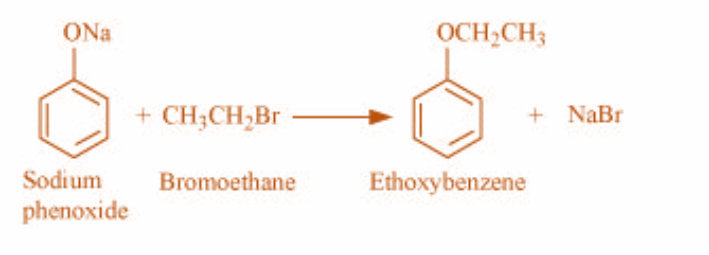
2)Sodium phenoxide and bromoethane react to give ethoxy benzene. The reaction is as shown:
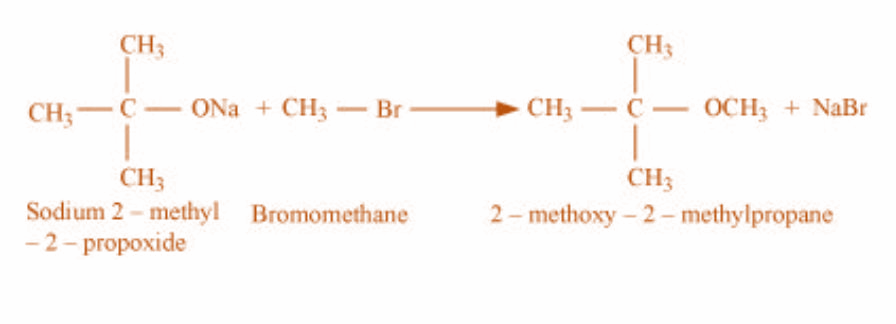
3)In the third case, the reactants are sodium-2-methyl 2 prop oxide and bromoethane and the product obtained is 2-methoxy- 2-methylpropane. The reaction is as shown:
4)In the last case, sodium ethoxide and bromoethane react together to form 1-methoxyethane. The reaction is as shown:
$C{H_3}C{H_2} - ONa + C{H_3} - Br \to C{H_3}C{H_2} - O - C{H_3} + NaBr$
Note: There are few limitations of Williamson’s synthesis reaction. The tertiary alkyl halides or primary or secondary alkyl halides that are sterically impeded continue to undergo ${E_2}$ removal in the presence of alkoxide, which serves as a base in addition to being a nucleophile. Moreover, this reaction is significant in the organic chemistry history as it has helped to prove the ether structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically, the name of this reaction was coined after the scientist named Alexander William Williamson. It is a reaction that uses deprotonated alcohol and an organohalide to form an ether. In this reaction, the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide and forms an ether from the back. This response takes place in the single step, which is both cleavage and bond formation. The products are then formed by elimination. The general reaction is as shown:
$RX + R'ONa \to R - O - R' + NaX$
Now, let’s discuss the name of reagents and their respective equations for the preparation of ethers by Williamson’s synthesis.
1)1-propoxypropane- It is formed by the reaction of sodium prop oxide and 1-bromopropane. The reaction is as shown:
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CHONa + C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br \to {C_2}{H_5}C{H_2} - O - C{H_2}{C_2}{H_5} + NaBr$
2)Sodium phenoxide and bromoethane react to give ethoxy benzene. The reaction is as shown:

3)In the third case, the reactants are sodium-2-methyl 2 prop oxide and bromoethane and the product obtained is 2-methoxy- 2-methylpropane. The reaction is as shown:

4)In the last case, sodium ethoxide and bromoethane react together to form 1-methoxyethane. The reaction is as shown:
$C{H_3}C{H_2} - ONa + C{H_3} - Br \to C{H_3}C{H_2} - O - C{H_3} + NaBr$
Note: There are few limitations of Williamson’s synthesis reaction. The tertiary alkyl halides or primary or secondary alkyl halides that are sterically impeded continue to undergo ${E_2}$ removal in the presence of alkoxide, which serves as a base in addition to being a nucleophile. Moreover, this reaction is significant in the organic chemistry history as it has helped to prove the ether structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




