
Write the structure of oleum (${H_2}{S_2}{O_7}$)
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Oleum is also known as pyrosulfuric acid and disulfuric acid. The IUPAC name of oleum is sulfo hydrogen sulphate.
Complete step by step answer:
Oleum is the main constituent of fuming sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is a stronger acid than pyrosulfuric acid. Salts such as sodium and potassium pyrosulfate are obtained by reacting them with the bases.
This acid can also be synthesised by reacting excess $S{O_3}\;$ with sulfuric acid.
You can see the structure of oleum in the below diagram:
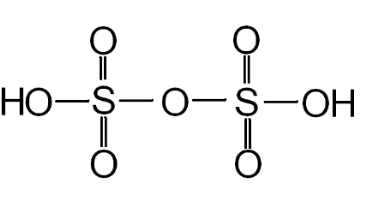
The number of S-S bonds present in pyrosulphuric acid is zero. There are a total of 4 double bonds in the structure. We can see that four oxygen atoms are linked to S by a double bond and the rest by a single bond.
Properties of oleum:
- The property value of hydrogen bond donor is 2 and that of the hydrogen bond acceptor is 7. The rotatable bond count is 7.
- The molecular weight of oleum is $178.129 g/mol$.
- It has a melting point of ${36^ \circ }C$.
- Disulfate is the conjugate base of oleum.
- The chemical formula of oleum is ${H_2}{S_2}{O_7}$
We have seen the structure and properties of oleum; now let us see where it is used.
Applications of Oleum
- Oleum is used in the manufacture of explosives and dyes.
- It is also used as a sulfating agent.
- It is used in petroleum refining applications.
It can cause severe eyes irritation when exposed to it and permanent tissue damage when swallowed.
Note: Do not confuse pyrosulfuric acid (${H_2}{S_2}{O_7}$) with peroxymonosulfuric acid. The chemical formula for peroxymonosulfuric acid is ${H_2}{S_2}{O_5}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Oleum is the main constituent of fuming sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is a stronger acid than pyrosulfuric acid. Salts such as sodium and potassium pyrosulfate are obtained by reacting them with the bases.
This acid can also be synthesised by reacting excess $S{O_3}\;$ with sulfuric acid.
You can see the structure of oleum in the below diagram:

The number of S-S bonds present in pyrosulphuric acid is zero. There are a total of 4 double bonds in the structure. We can see that four oxygen atoms are linked to S by a double bond and the rest by a single bond.
Properties of oleum:
- The property value of hydrogen bond donor is 2 and that of the hydrogen bond acceptor is 7. The rotatable bond count is 7.
- The molecular weight of oleum is $178.129 g/mol$.
- It has a melting point of ${36^ \circ }C$.
- Disulfate is the conjugate base of oleum.
- The chemical formula of oleum is ${H_2}{S_2}{O_7}$
We have seen the structure and properties of oleum; now let us see where it is used.
Applications of Oleum
- Oleum is used in the manufacture of explosives and dyes.
- It is also used as a sulfating agent.
- It is used in petroleum refining applications.
It can cause severe eyes irritation when exposed to it and permanent tissue damage when swallowed.
Note: Do not confuse pyrosulfuric acid (${H_2}{S_2}{O_7}$) with peroxymonosulfuric acid. The chemical formula for peroxymonosulfuric acid is ${H_2}{S_2}{O_5}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




