
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+3x-6y+9=0$, How can you find the centre, radius, and intercepts?
Answer
552.6k+ views
Hint: In this problem we have given the equation of the circle and asked to find the centre, radius and the intercepts of the circle. From this we will convert the given equation in form of ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$, where $\left( h,k \right)$ is the centre of the circle and $r$ is the radius of the circle. To convert the given equation, we will first rearrange the terms so that all the $x$ variables are at one place and all the $y$ variables are at one place. Now we will follow the method of completing squares and simplify the equation to convert it into required form. After converting the equation, we can write the centre and radius of the circle. Now we will calculate the intercepts by substituting $x=0$, $y=0$ in the circle equation and calculate the intercepts.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation of the circle is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+3x-6y+9=0$.
Rearranging the terms in the above equation, so that all the $x$ variable are at one place and all the $y$ variables are at one place. Hence the above equation is modified as
$\Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-6y \right)+9=0$
Performing the completing squares method in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{3}{2}x \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-2\times 3y \right)+9=0$
Adding and subtracting the terms ${{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}$, ${{3}^{2}}$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{3}{2}x \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-2\times 3y \right)+9+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{3}{2}x+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-2\times 3y+{{3}^{2}} \right)+9-\dfrac{9}{4}-9=0 \\
\end{align}$
Applying the algebraic formulas ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
Comparing the above equation with ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& -h=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow h=-\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$ , $\begin{align}
& -k=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow k=3 \\
\end{align}$ , $\begin{align}
& {{r}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the centre of the circle is $\left( h,k \right)=\left( -\dfrac{3}{2},3 \right)$, radius is $r=\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Calculating the intercepts of the circle.
For $y$-intercept substituting $x=0$, in the equation of the circle, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 0+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}+{{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{9}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=3 \\
\end{align}$
We have only one $y$-intercept value that means the circle do not intercept the $y-axis$. It only touches the $y-axis$.
For $x$- intercept substituting $y=0$, in the equation of the circle, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-3 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+3x+\dfrac{9}{4}+9=\dfrac{9}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+3x+9=0 \\
\end{align}$
Discriminant of the above quadratic equation is
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 9 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}=\sqrt{9-36} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}=\sqrt{-27} \\
\end{align}$
From the above value we can say that the quadratic equation has no real solution, so there is no $x-$intercept for the circle. Now the graph of the circle will be
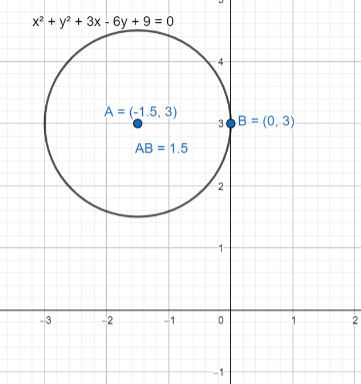
Note: We can also calculate the centre of the circle which is in form of $a{{x}^{2}}+b{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ is given by $\left( -\dfrac{g}{a},-\dfrac{f}{b} \right)$. So, we will compare the given equation with the $a{{x}^{2}}+b{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ and then write the centre of the circle.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation of the circle is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+3x-6y+9=0$.
Rearranging the terms in the above equation, so that all the $x$ variable are at one place and all the $y$ variables are at one place. Hence the above equation is modified as
$\Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-6y \right)+9=0$
Performing the completing squares method in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{3}{2}x \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-2\times 3y \right)+9=0$
Adding and subtracting the terms ${{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}$, ${{3}^{2}}$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{3}{2}x \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-2\times 3y \right)+9+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( {{x}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{3}{2}x+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \right)+\left( {{y}^{2}}-2\times 3y+{{3}^{2}} \right)+9-\dfrac{9}{4}-9=0 \\
\end{align}$
Applying the algebraic formulas ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
Comparing the above equation with ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& -h=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow h=-\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$ , $\begin{align}
& -k=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow k=3 \\
\end{align}$ , $\begin{align}
& {{r}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the centre of the circle is $\left( h,k \right)=\left( -\dfrac{3}{2},3 \right)$, radius is $r=\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Calculating the intercepts of the circle.
For $y$-intercept substituting $x=0$, in the equation of the circle, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 0+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}+{{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{9}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( y-3 \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=3 \\
\end{align}$
We have only one $y$-intercept value that means the circle do not intercept the $y-axis$. It only touches the $y-axis$.
For $x$- intercept substituting $y=0$, in the equation of the circle, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-3 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+3x+\dfrac{9}{4}+9=\dfrac{9}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+3x+9=0 \\
\end{align}$
Discriminant of the above quadratic equation is
$\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 9 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}=\sqrt{9-36} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}=\sqrt{-27} \\
\end{align}$
From the above value we can say that the quadratic equation has no real solution, so there is no $x-$intercept for the circle. Now the graph of the circle will be

Note: We can also calculate the centre of the circle which is in form of $a{{x}^{2}}+b{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ is given by $\left( -\dfrac{g}{a},-\dfrac{f}{b} \right)$. So, we will compare the given equation with the $a{{x}^{2}}+b{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ and then write the centre of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




