
X-rays obtained by Coolidge tube are:-
A. Mono-chromatic
B. Of all wavelengths below a maximum wavelength
C. Of all wave length above a minimum wavelength
D. Of all wave length between a maximum and a minimum wavelength
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: A device that is used to produce X-rays is called X-ray tube. Coolidge tube is an example of an X-ray producing tube. A Coolidge tube consists of an evacuated glass bulb containing an anode and a cathode. A tungsten filament is used as the anode in the Coolidge tube. When current passes through the tungsten filament, the filament gets heated due to the heating effect of current and will emit electrons due to thermionic emission.
Complete step by step answer:
A tungsten filament is used as the tube cathode, and during the operation, the filament is heated by passing a current through it. This causes the filament to emit electrons at a rate which depends on the temperature of the filament. The electrons are then accelerated towards the tube anode by the strong tube voltage. Upon hitting the anode, the electrons are then decelerated very rapidly, and shed their excess kinetic energy mostly as heat, and partly as X-ray radiation. To prevent the electron beam from dispersing due to repulsive forces between the electrons, the cathode filament is surrounded by a metal focusing cup at a high negative potential that has the effect of converging the beam to a relatively small area on the anode.
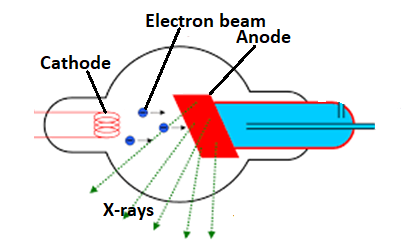
X-ray tubes previous to the Coolidge tube which are used for their electron source. In these tubes, the tube voltage is very strong and 'pulls' electrons from the cathode. These electrons were accelerated towards the anode and collided with residual gas molecules purposefully left in the tube, ionizing the molecules and causing the ejection of more electrons. In this way, the specified beam was built up with a sort of 'avalanche effect'. However, the number of electrons in a beam produced this way, and their energy upon collision with the anode were both dependent on the gas pressure within the tube, which was rarely stable, and difficult to control. Besides, the number of electrons produced in this way was, by today's standards extremely small, and hence the intensity of the produced X-rays very low, leading to very long exposure times.
The Coolidge tube uses thermionic emission to obtain a source of electrons, removing the dependency on residual gas for the number and energy of the electrons in the. As the number of electrons produced depended on the current applied across the cathode filament and the energy of the electrons on the tube voltage. The Coolidge tube made it possible to easily and independently vary the number of electrons (and hence the intensity of X-rays produced), and their energy (and hence the frequency of produced X-rays). The X - rays beam which is produced by the Coolidge tube has a wavelength greater than a minimum wavelength known as cut-off wavelength. As the maximum energy that can be possessed by the ray of photon has a certain maximum wavelength. But energy and wavelength are inversely related so for lower energy, the wavelength should be higher than the wavelength which corresponds to maximum energy should be lower. So in Coolidge tube X-rays have a minimum wavelength.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The modern X-ray tubes use the principle of thermionic emission. Thermionic emission is the process of removal of an electron from the surface of some metals due to heating. Don’t get confused between thermionic emission and photoelectric emission. In photoelectric emission, lights were used to excite electrons. The minimum heat or energy required to remove an electron from the surface of a metal is known as work function.
Complete step by step answer:
A tungsten filament is used as the tube cathode, and during the operation, the filament is heated by passing a current through it. This causes the filament to emit electrons at a rate which depends on the temperature of the filament. The electrons are then accelerated towards the tube anode by the strong tube voltage. Upon hitting the anode, the electrons are then decelerated very rapidly, and shed their excess kinetic energy mostly as heat, and partly as X-ray radiation. To prevent the electron beam from dispersing due to repulsive forces between the electrons, the cathode filament is surrounded by a metal focusing cup at a high negative potential that has the effect of converging the beam to a relatively small area on the anode.

X-ray tubes previous to the Coolidge tube which are used for their electron source. In these tubes, the tube voltage is very strong and 'pulls' electrons from the cathode. These electrons were accelerated towards the anode and collided with residual gas molecules purposefully left in the tube, ionizing the molecules and causing the ejection of more electrons. In this way, the specified beam was built up with a sort of 'avalanche effect'. However, the number of electrons in a beam produced this way, and their energy upon collision with the anode were both dependent on the gas pressure within the tube, which was rarely stable, and difficult to control. Besides, the number of electrons produced in this way was, by today's standards extremely small, and hence the intensity of the produced X-rays very low, leading to very long exposure times.
The Coolidge tube uses thermionic emission to obtain a source of electrons, removing the dependency on residual gas for the number and energy of the electrons in the. As the number of electrons produced depended on the current applied across the cathode filament and the energy of the electrons on the tube voltage. The Coolidge tube made it possible to easily and independently vary the number of electrons (and hence the intensity of X-rays produced), and their energy (and hence the frequency of produced X-rays). The X - rays beam which is produced by the Coolidge tube has a wavelength greater than a minimum wavelength known as cut-off wavelength. As the maximum energy that can be possessed by the ray of photon has a certain maximum wavelength. But energy and wavelength are inversely related so for lower energy, the wavelength should be higher than the wavelength which corresponds to maximum energy should be lower. So in Coolidge tube X-rays have a minimum wavelength.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The modern X-ray tubes use the principle of thermionic emission. Thermionic emission is the process of removal of an electron from the surface of some metals due to heating. Don’t get confused between thermionic emission and photoelectric emission. In photoelectric emission, lights were used to excite electrons. The minimum heat or energy required to remove an electron from the surface of a metal is known as work function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




