
Youngest layer of secondary xylem is located
(a) In the center of the stem
(b) Just outside pith
(c) Just outside the vascular cambium
(d) Just inside the vascular cambium
Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: It is composed of tracheary elements, rays, fibers, and interspersed axial parenchyma cells. The tracheary components comprise of just tracheids, as in a couple of vesselless angiosperms (e.g., Winteraceae), or of the two tracheids and vessel components, as in by far most of the angiosperms.
Complete answer
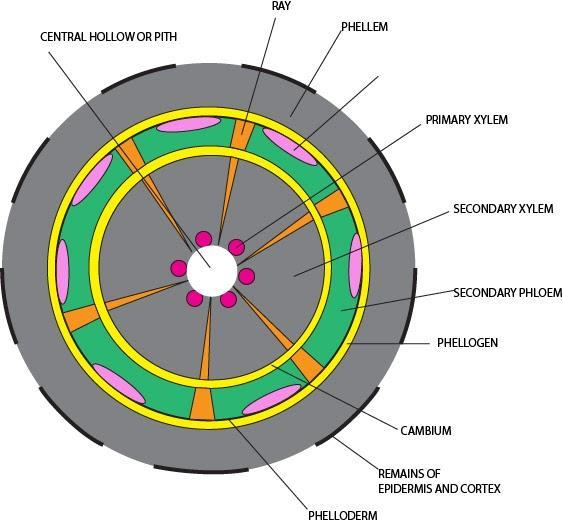
The arrangement of the vascular cambium is started when cells between the sections of vascular tissue interface the cambia inside the segments of vascular tissue to frame a total chamber around the stem. The cells formed toward the within are called secondary xylem or wood and people formed toward the surface of the cambium are called secondary phloem.
Xylem formation begins when the actively dividing cells of growing root and shoot tips produce primary xylem. The secondary xylem comprises the fundamental aspect of a developed stem or root in woody plants and is made in light of the fact that the plant grows in circumference and fabricates a loop of new xylem around the first essential xylem tissues.
At the point when this occurs, the primary xylem cells pass on and lose their leading capacity, framing an extreme skeleton that serves just to help the plant. Hence, inside the storage compartment and more established parts of an outsized tree, just the external secondary xylem (sapwood) serves in water conduction, while the internal part (heartwood) comprises dead yet basically solid essential xylem. In this way, the most youthful layer of secondary xylem is found simply inside the vascular cambium and not in the focal point of the stem, outside essence, or outside vascular cambium.
Additional information
Secondary xylem is missing in non-woody plants yet is available in trees and bushes. Its cell walls are thickened by the deposition of lignin, subsequently, delivering mechanical help to such plants. Secondary xylem comprises tracheids and vessels that are more limited and more extensive than those of primary xylem. It is additionally more extravagant in xylem filaments than in primary xylem.
So the correct answer is ‘Just inside vascular cambium’.
Note:
Secondary xylem is the type of xylem formed from secondary growth. In comparison, the first xylem forms during primary growth. Because of this, the secondary xylem is related to lateral growth instead of vertical growth as within the primary xylem. Another difference lies in the type of cambium that gives rise to them. The primary xylem originates from the procambium while the secondary xylem develops from the vascular cambium.
Complete answer
The arrangement of the vascular cambium is started when cells between the sections of vascular tissue interface the cambia inside the segments of vascular tissue to frame a total chamber around the stem. The cells formed toward the within are called secondary xylem or wood and people formed toward the surface of the cambium are called secondary phloem.
Xylem formation begins when the actively dividing cells of growing root and shoot tips produce primary xylem. The secondary xylem comprises the fundamental aspect of a developed stem or root in woody plants and is made in light of the fact that the plant grows in circumference and fabricates a loop of new xylem around the first essential xylem tissues.
At the point when this occurs, the primary xylem cells pass on and lose their leading capacity, framing an extreme skeleton that serves just to help the plant. Hence, inside the storage compartment and more established parts of an outsized tree, just the external secondary xylem (sapwood) serves in water conduction, while the internal part (heartwood) comprises dead yet basically solid essential xylem. In this way, the most youthful layer of secondary xylem is found simply inside the vascular cambium and not in the focal point of the stem, outside essence, or outside vascular cambium.
Additional information
Secondary xylem is missing in non-woody plants yet is available in trees and bushes. Its cell walls are thickened by the deposition of lignin, subsequently, delivering mechanical help to such plants. Secondary xylem comprises tracheids and vessels that are more limited and more extensive than those of primary xylem. It is additionally more extravagant in xylem filaments than in primary xylem.
So the correct answer is ‘Just inside vascular cambium’.
Note:
Secondary xylem is the type of xylem formed from secondary growth. In comparison, the first xylem forms during primary growth. Because of this, the secondary xylem is related to lateral growth instead of vertical growth as within the primary xylem. Another difference lies in the type of cambium that gives rise to them. The primary xylem originates from the procambium while the secondary xylem develops from the vascular cambium.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




