
What is the zero error as shown in the figure?
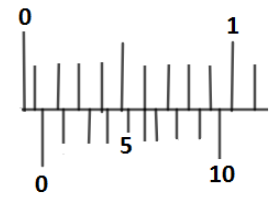
A. $0.6\,mm$
B. $0.06\,mm$
C. $6\,mm$
D. $60\,mm$

Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: In the given figure, we have a main scale which is $1mm$ in length and the Vernier scale has $10$ divisions. Since, least count is the smallest and accurate magnitude of any measuring physical quantity and zero error means when the zero of main scale and measuring scale like Vernier calliper do not coincide and there is lag of some value is called zero error. We will use the general concept of zero error to find its magnitude.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the formula used to determine the zero error is given by
Zero error $ = n \times L.C$
Where, $L.C$ stands for least count and it’s calculated as,
Number of divisions on Vernier scale is $10$
Unit of main scale division denoted as $M.S.D$ is $1mm$
So, least count is given as $\dfrac{{1M.S.D}}{{10}}$
$L.C = 0.1mm$
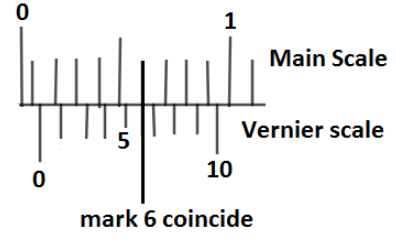
And, $n$ denotes the number of count to which the marks of both Vernier scale division and the main scale division coincide, and according to the given diagram we have it’s the ${6^{th}}$ mark which coincide, so
$n = 6$
Using the formula, Zero error $ = n \times L.C$ we have,
Zero error $ = 6 \times 0.1$
Zero error $ = 0.6mm$
So, the zero error of the given scale is Zero error $ = 0.6\,mm$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: It should be remembered that, generally Vernier callipers are used to determine the radius or diameter of given circular bodies very accurately. If one needs to determine the zero error in suitable units we can use general conversion units as $1mm = 0.1cm$ and $1mm = 0.001m$ and always carefully observe the exact point mark which coincide on bath scales while performing the experiment in the laboratory.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the formula used to determine the zero error is given by
Zero error $ = n \times L.C$
Where, $L.C$ stands for least count and it’s calculated as,
Number of divisions on Vernier scale is $10$
Unit of main scale division denoted as $M.S.D$ is $1mm$
So, least count is given as $\dfrac{{1M.S.D}}{{10}}$
$L.C = 0.1mm$

And, $n$ denotes the number of count to which the marks of both Vernier scale division and the main scale division coincide, and according to the given diagram we have it’s the ${6^{th}}$ mark which coincide, so
$n = 6$
Using the formula, Zero error $ = n \times L.C$ we have,
Zero error $ = 6 \times 0.1$
Zero error $ = 0.6mm$
So, the zero error of the given scale is Zero error $ = 0.6\,mm$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: It should be remembered that, generally Vernier callipers are used to determine the radius or diameter of given circular bodies very accurately. If one needs to determine the zero error in suitable units we can use general conversion units as $1mm = 0.1cm$ and $1mm = 0.001m$ and always carefully observe the exact point mark which coincide on bath scales while performing the experiment in the laboratory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




