Biology Notes for Chapter 14 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the fundamental difference between breathing and respiration for a quick summary?
Breathing is the physical process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide from the lungs. In contrast, cellular respiration is a biochemical process at the cellular level where food (like glucose) is broken down to produce energy (ATP), which requires oxygen and releases carbon dioxide as a waste product. Essentially, breathing facilitates cellular respiration.
2. How can I quickly revise the mechanism of human breathing?
The mechanism involves two main phases driven by pressure gradients created by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles:
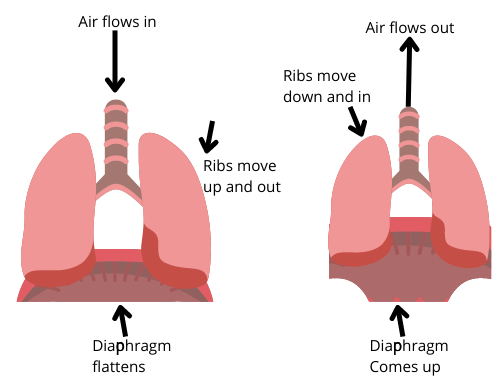
- Inspiration (Inhaling): The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract, expanding the chest cavity. This increases thoracic volume and decreases pressure inside the lungs, causing atmospheric air to rush in.
- Expiration (Exhaling): The muscles relax, returning the chest cavity to its original size. This decreases thoracic volume and increases pressure inside the lungs, forcing air out.
3. What are the most important respiratory volumes and capacities to remember from this chapter?
For a quick revision, focus on these key concepts as per the CBSE syllabus:
- Tidal Volume (TV): The volume of air breathed during a normal, relaxed breath (approx. 500 mL).
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): The additional volume of air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal inspiration (approx. 2500-3000 mL).
- Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): The additional volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal expiration (approx. 1000-1100 mL).
- Residual Volume (RV): The volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forceful expiration (approx. 1100-1200 mL).
- Vital Capacity (VC): The maximum volume of air a person can breathe out after a forced inhalation. It is calculated as TV + IRV + ERV.
4. What is the main function of the conducting part versus the exchange part of the respiratory system?
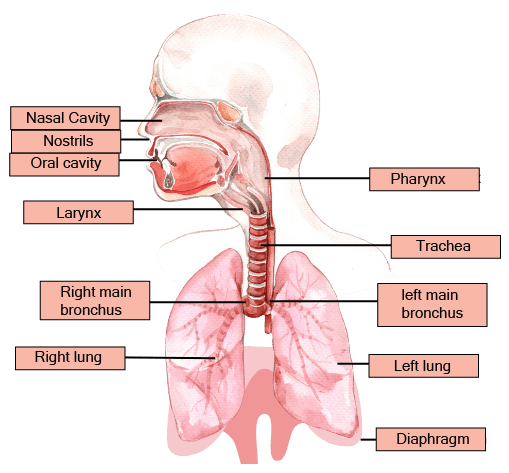
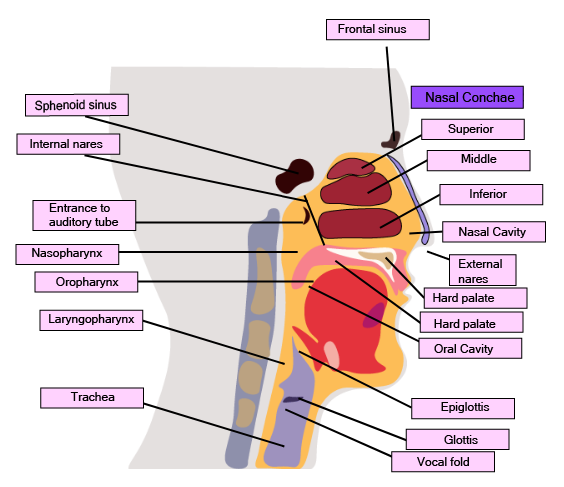
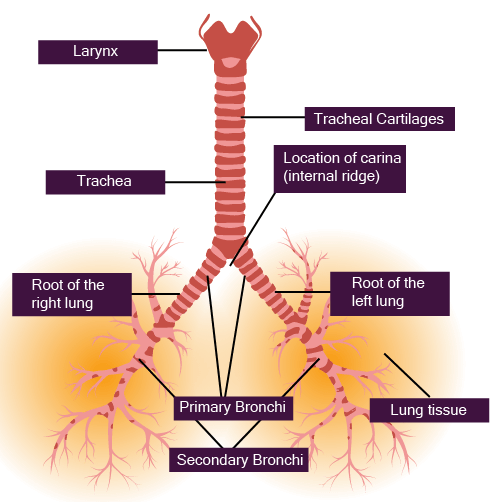
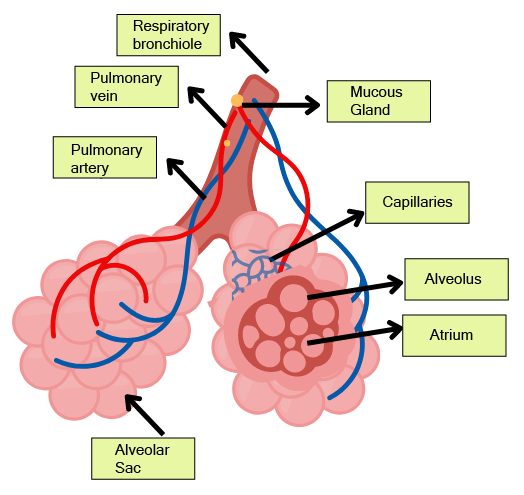
The conducting part, which includes the nostrils, pharynx, trachea, and bronchi, serves to transport atmospheric air to the alveoli. It also cleans the air of foreign particles, humidifies it, and brings it to body temperature. The exchange part, consisting of the alveoli and their ducts, is the actual site where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs between the blood and the inhaled air.
5. Why is the oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve sigmoidal (S-shaped)?
The S-shaped curve reflects the cooperative binding of oxygen to haemoglobin. When the first oxygen molecule binds to a haemoglobin subunit, it causes a change in the protein's shape. This change increases the affinity of the other three subunits for oxygen, making it progressively easier for them to bind. This cooperative effect results in a steep slope on the curve, allowing for rapid oxygen loading in the lungs. The plateau at the top indicates saturation.
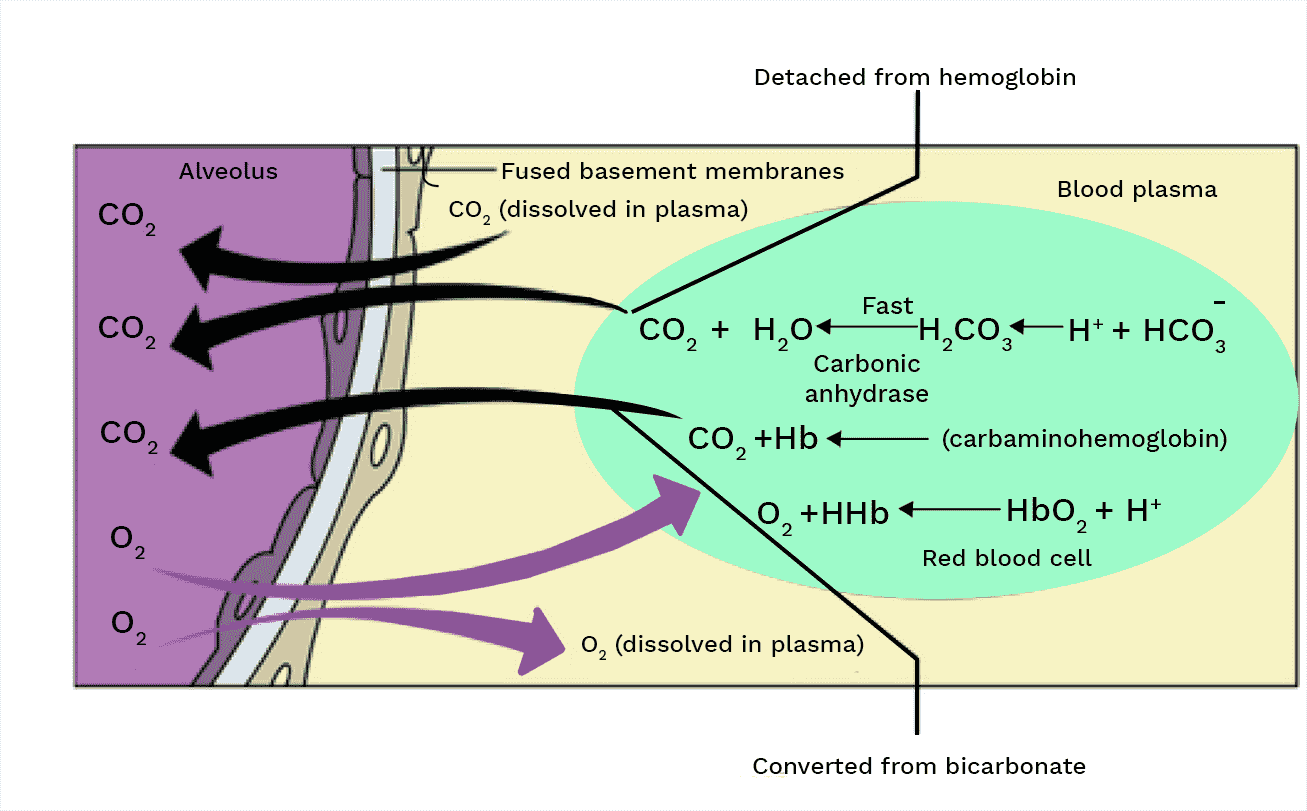
6. How is the majority of carbon dioxide transported in the blood, and why is this method so effective?
Approximately 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻) in the blood plasma. This method is highly effective because it allows large quantities of CO₂ to be transported from tissues to the lungs with minimal change in blood pH. The conversion of CO₂ to bicarbonate is a reversible reaction rapidly catalysed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which is abundant in red blood cells.
7. What key factors influence the binding of oxygen with haemoglobin in the lungs and its release in the tissues?
The binding and release of oxygen are primarily governed by several factors:
- Partial Pressure of O₂ (pO₂): High pO₂ in the lungs promotes the formation of oxyhaemoglobin, while low pO₂ in tissues facilitates its dissociation.
- Partial Pressure of CO₂ (pCO₂): High pCO₂ in tissues lowers haemoglobin's affinity for O₂, causing oxygen release (the Bohr effect).
- H+ Concentration (pH): An increase in H+ ions (lower pH) in active tissues also decreases oxygen affinity, aiding its delivery.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures in metabolically active tissues promote the release of oxygen from haemoglobin.
8. How do the different respiratory centres in the brain work together to regulate breathing?
Breathing regulation is a coordinated effort by centres in the medulla and pons:
- The Respiratory Rhythm Centre in the medulla oblongata generates the primary rhythm for inspiration and expiration.
- The Pneumotaxic Centre in the pons modulates the signals from the rhythm centre, helping to fine-tune the breathing rate and depth.
- A Chemosensitive Area near the rhythm centre is highly sensitive to changes in blood CO₂ and H+ ion levels, signalling the rhythm centre to adjust breathing to maintain homeostasis.
9. What are the critical differences between asthma and emphysema to note for revision?
For quick revision, remember these key distinctions:
- Asthma is an inflammatory condition causing spasms in the bronchi and bronchioles, which leads to wheezing and difficulty breathing. It is often triggered by allergens.
- Emphysema is a chronic disease characterized by the damage and breakdown of alveolar walls. This reduces the surface area available for gas exchange and is most commonly caused by long-term cigarette smoking.
10. What is vital capacity, and what is its physiological significance?
Vital Capacity (VC) is the maximum volume of air a person can exhale after a maximum, forceful inhalation. Its physiological significance lies in indicating the total usable volume of the lungs for gas exchange. A higher vital capacity suggests a stronger respiratory system and better physical fitness, as it allows for a greater volume of air to be exchanged with each breath, which is particularly important during exercise.