Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Summary Notes PDF Download



FAQs on Atoms Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the main points to remember when revising the atomic models discussed in Class 12 Physics Chapter 12?
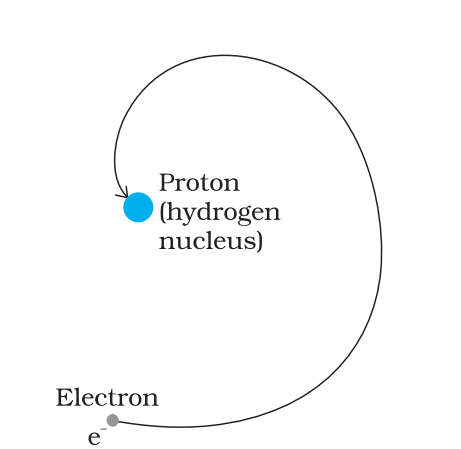
The main points include the Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr models. Thomson's model describes the atom as a 'plum pudding', Rutherford introduced the concept of a dense nucleus, while Bohr explained fixed orbits and quantized energy levels. Focus on how each model improved upon the last and their limitations.
2. How does the concept of energy quantization help explain atomic stability in Bohr's model?
Energy quantization means electrons can only occupy certain orbits with specific energies. This prevents them from spiraling into the nucleus, as predicted by classical physics, ensuring atomic stability. Only discrete energy jumps are allowed, which matches the observed line spectra.
3. What is the significance of the negative total energy of an electron in the hydrogen atom?
The negative total energy indicates that the electron is bound to the nucleus and energy must be provided to remove it. This binding energy reflects the stability of the atom's configuration and the attraction between the electron and nucleus.
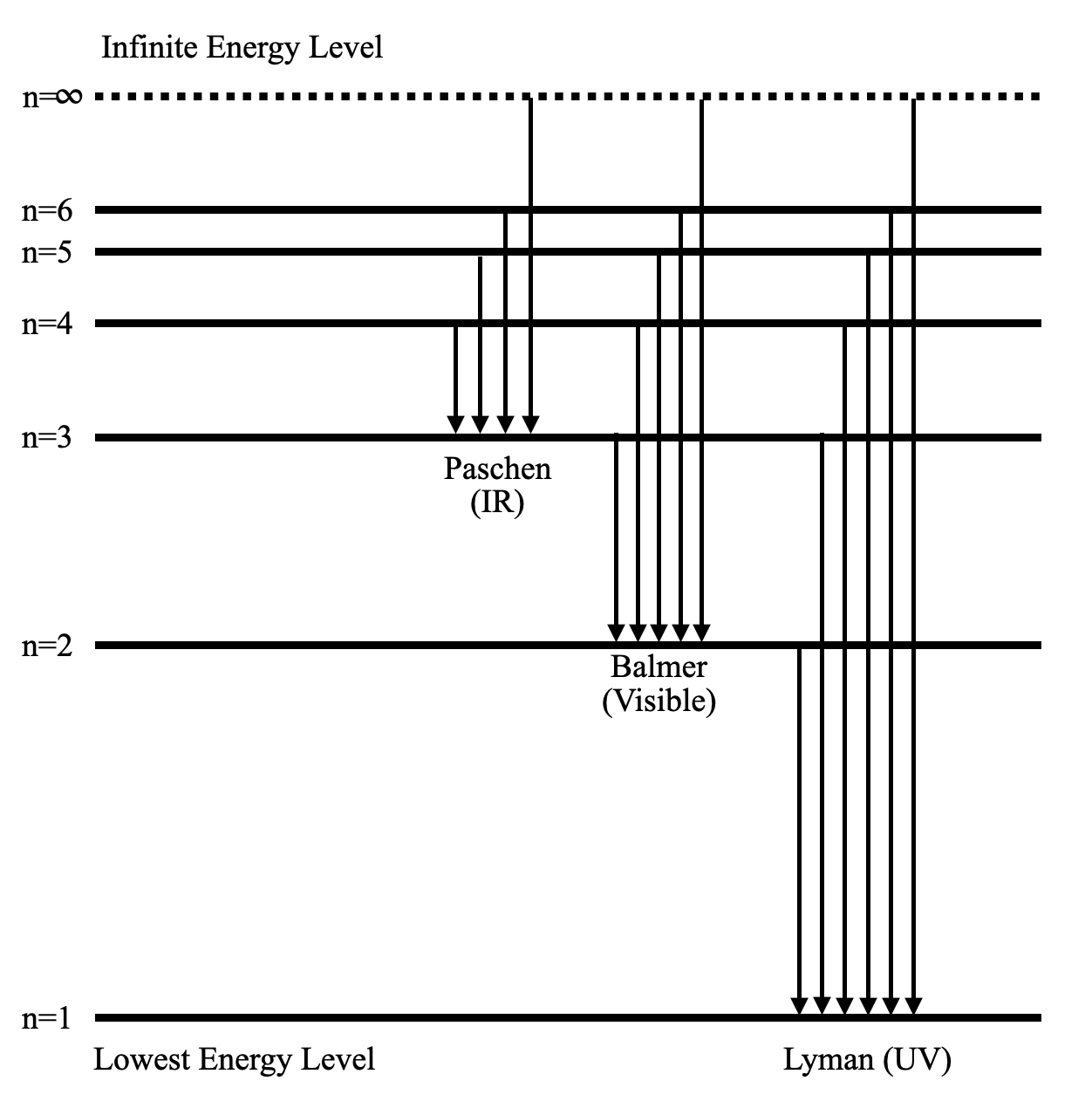
4. When revising atomic spectra, which formulas should you focus on for quick calculations?
Prioritize the Rydberg formula for spectral lines, Bohr's formulas for energy of orbits $E_n = -13.6 \frac{1}{n^2}$ eV for hydrogen, and Bohr radius $a_0 = 0.53$ Å. Knowing these allows you to swiftly solve most spectral line and energy level questions.
5. What revision strategies make it easier to distinguish between emission and absorption spectra?
Remember that emission spectra consist of bright lines produced when electrons fall to lower energy levels, while absorption spectra display dark lines where specific wavelengths are absorbed as electrons move up. Use diagrams and associate each with the direction of electron transition.
6. Which common misconceptions should be avoided when revising the Bohr model?
Do not assume the Bohr model applies to all atoms; it is valid for hydrogen-like (single-electron) species only. Another misconception is that electrons lose energy while in stable orbits; according to Bohr, they do not. Remember, actual atoms require quantum mechanics for complete explanation.
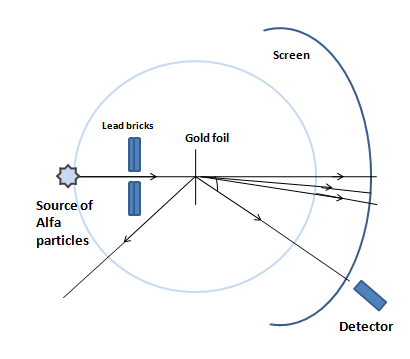
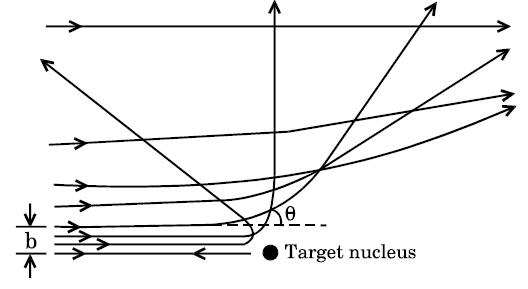
7. How can understanding the impact parameter improve your grasp of Rutherford's experiment during quick revision?
The impact parameter determines how close an alpha particle comes to the nucleus and thus the deflection angle. Recognizing this helps you visualize why most alpha particles pass straight and only a few are scattered sharply, confirming the presence of a small nucleus.
8. What is the best order to revise the concepts in Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 for maximum retention?
Start with historical atomic models, then study Bohr's model and postulates. Next, review quantization and energy levels, followed by atomic spectra (emission and absorption), and end with modern quantum concepts such as de Broglie wavelength and model limitations.
9. How does the de Broglie hypothesis connect with quantization in the Bohr model?
The de Broglie hypothesis suggests electrons have wave-like properties. In Bohr's model, orbits are stable only where the electron's circumference is an integer multiple of its wavelength, leading to quantized angular momentum. This explained why only certain orbits are allowed.
10. Which real-life phenomena can you relate to the topics covered in the atom chapter to reinforce your revision?
The working of neon lights and fireworks can be explained by electron transitions and emission spectra. The distinct colors in each case are due to specific atomic transitions in gases or compounds, directly linking to the chapter concepts.
11. What are the practical advantages of concise revision notes for Class 12 Physics Atoms?
Concise notes save time, clarify key formulas and concepts, reduce exam stress, and ensure you focus on high-weightage topics. Well-structured notes make it easy to quickly revise major themes like atomic models, energy levels, and spectra before exams.
12. How should you approach the mathematical aspects of the Atoms chapter during last-minute revision?
Focus on understanding rather than memorizing derivations. Practice using core formulas (energy levels, orbit radius, spectral lines) with quick examples. Pay attention to unit conversions and steps in calculation, as these often appear in board questions.