Physics Notes for Chapter 7 Alternating Current Class 12 - FREE PDF Download



FAQs on Alternating Current Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts that students should focus on when revising the Alternating Current chapter in Class 12 Physics?
Focus on understanding alternating current (AC) basics, including its mathematical representation, impedance in AC circuits, resonance, reactance (inductive and capacitive), transformers, and the concept of Power Factor. Being clear on the phase difference between current and voltage, and practicing numericals on power calculations and resonant frequency, is essential for revision.
2. How should students structure their revision to cover all important topics in the Class 12 Physics Alternating Current chapter?
Begin with core definitions like alternating current, mean value, and rms value. Proceed to study the properties of AC in resistive, inductive, and capacitive circuits. Revise phasor diagrams, derivations for resonance and LCR circuits, and end with practical applications such as transformers. Review key formulas and practice corresponding numericals to consolidate understanding.
3. Why is the concept of resonance critical to understand in the context of AC circuits in revision notes?
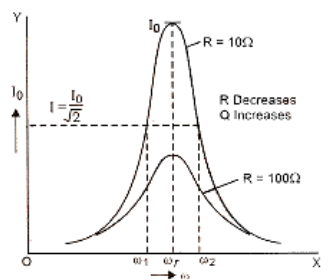
Resonance occurs in an AC circuit when inductive reactance and capacitive reactance are equal, resulting in a minimum circuit impedance and maximum current flow. Understanding resonance is crucial as it explains the conditions for efficient energy transfer, power maximization, and its applications in filtering and tuning electrical circuits.
4. What makes revision notes valuable compared to the full textbook for Alternating Current in Class 12 Physics?
Revision notes condense the most important concepts for rapid review, presenting them in a structured and student-friendly manner. They skip less relevant details, focus on frequently tested topics like impedance and transformers, and include essential formulas and diagrams that boost quick retention before exams.
5. How does understanding phasor diagrams enhance revision for the Alternating Current chapter?
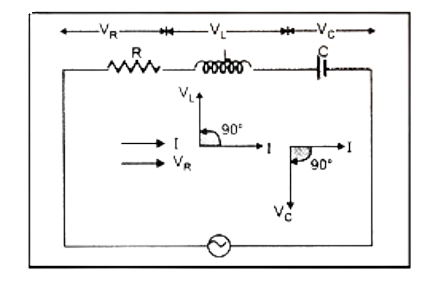
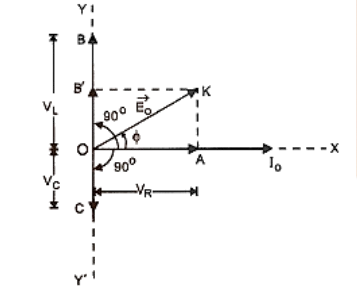
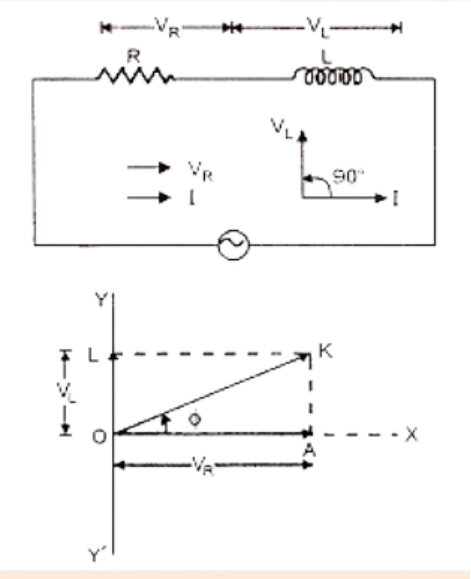
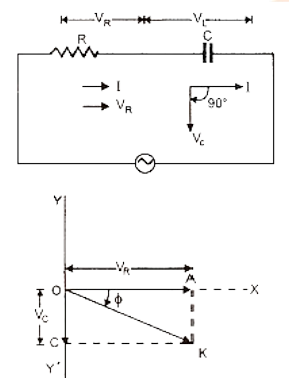
Phasor diagrams visually represent the phase relationship between current and voltage in various AC circuit elements (R, L, and C). Mastering these diagrams helps students solve complex problems and facilitates better retention of phase differences and their effect on circuit behavior.
6. What are effective tips for memorizing key formulas in Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 during revision?
Create a formula sheet summarizing essential equations, such as those for rms value (Irms = I₀/√2), power in AC circuits (P = VrmsIrmscosφ), impedance of LCR circuits, and resonant frequency. Understanding the physical meaning and application of each formula, then practicing related questions, improves recall for exams.
7. What is the importance of the power factor in AC circuits, and how should students revise this concept?
The power factor (cosφ) determines the efficiency of power usage in AC circuits. A power factor of 1 means all power is used effectively. Revision should involve understanding how phase difference affects power factor and its calculation using impedance and resistance values in the circuit.
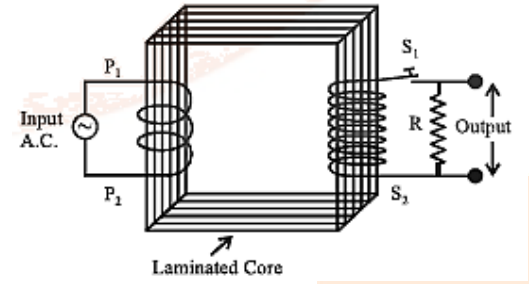
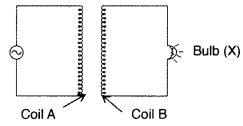
8. How can students apply theoretical concepts of transformers learned in revision notes to solve exam problems?
By reviewing revision notes, students learn the principle of mutual induction, turns ratio equations, and efficiency calculations for transformers. Applying these principles to solve numerical and conceptual problems in exams demonstrates a solid grasp of both theoretical and practical aspects.
9. In quick revision, what misconceptions should students avoid regarding alternating current and its applications?
Students should avoid thinking that AC supplies a constant current like DC or that all the energy is consumed in pure inductors and capacitors. It's essential to grasp that in pure inductive or capacitive circuits, average power consumed is zero, and wattless current is present.
10. How do revision notes make it easier to understand the practical applications of AC circuit concepts introduced in Chapter 7?
Revision notes highlight real-life uses such as power transmission, transformers in electrical grids, and resonance in radios and filters, connecting theoretical understanding with practical engineering, which is critical for higher-order learning and application-based questions.
11. What is the best way to revise problem-solving strategies for alternating current numericals from notes?
Review solved examples included in the notes, pay special attention to steps for calculating current, voltage, impedance, and phase angle in various circuits. Practice similar questions, breaking down each step as shown in the revision material to internalize the procedure.
12. Why is it important to differentiate between rms value and mean value of alternating current during revision?
The rms value gives the equivalent DC value for AC in terms of heating effect, while the mean value is the average over a half cycle. Revising the differences and applications ensures accuracy when answering exam questions about measurement and calculation in AC circuits.
13. How do revision notes aid in connecting different topics within the Alternating Current chapter for holistic understanding?
Well-structured notes link concepts such as resonance, power factor, transformer operation, and phasor analysis, helping students see how each topic builds upon and relates to others, which is essential for comprehensive exam preparation.
14. How can students efficiently use revision notes to prepare for higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) questions in Class 12 Physics?
By thoroughly understanding the underlying principles, derivations, and applications highlighted in revision notes, students can tackle HOTS questions requiring analysis, synthesis, and problem-solving, instead of just memorization.