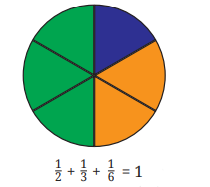Maths Notes for Chapter 7 Fractions Class 6 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Fractions Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts covered in the Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Revision Notes?
The Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Revision Notes provide a summary of core concepts such as the definition of fractions, types of fractions (proper, improper, mixed), parts of a fraction (numerator and denominator), equivalent fractions, comparison, and operations (addition, subtraction, simplification) according to the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus. These notes help in quick revision before exams.
2. How are fractions represented on a number line according to the revision notes?
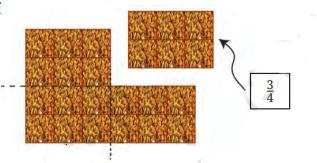
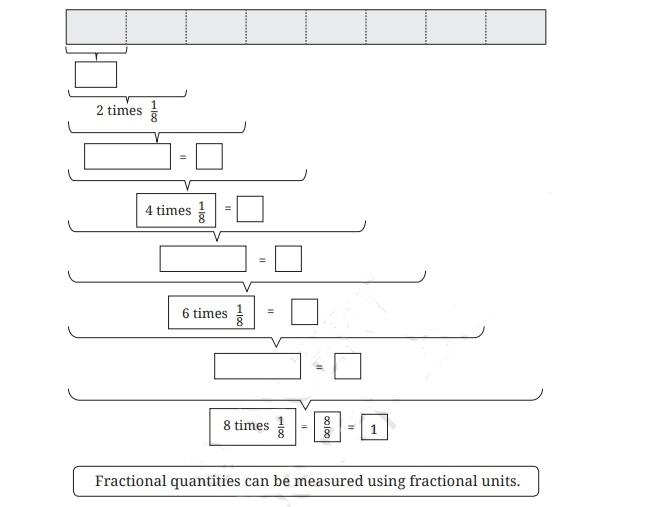
In the revision notes for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7, fractions are shown on a number line by dividing the section between two whole numbers into equal parts. Each part represents a fraction of the whole, helping students to visualise fractions as real values between integers.
3. What are the steps to simplify a fraction as per Class 6 revision notes?
To simplify a fraction:
- Find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator.
- Divide both the numerator and denominator by the GCD.
- The resulting fraction is in its lowest form as required in the revision notes.
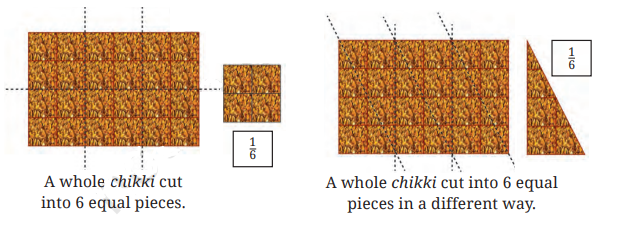
4. What are equivalent fractions, and how are they identified during revision?
Equivalent fractions are fractions that have different numerators and denominators but represent the same value. They can be identified by multiplying or dividing both the numerator and denominator by the same non-zero number. The revision notes recommend practising this concept for mastering comparisons and calculations.
5. Why is understanding fractions important according to the revision notes?
Understanding fractions provides a foundation for future subjects like decimals, percentages, and ratios. It also enhances logical reasoning and problem-solving skills, and is practical in daily life—for example, dividing items or measuring quantities. The revision notes stress its importance for both academics and real-life applications.
6. How should a student structure their revision of Chapter 7 Fractions for maximum retention?
To maximise retention:
- Start by revising key terms such as numerator, denominator, and types of fractions.
- Practise visualising fractions using number lines and real-life objects.
- Focus on operations and simplification for fluency in calculations.
- Regularly attempt sample questions and quizzes from the revision notes.
7. How do you compare fractions with different denominators as summarised in the Class 6 Maths revision notes?
To compare fractions with different denominators:
- Find a common denominator (usually the least common multiple).
- Convert both fractions so their denominators match.
- Compare the numerators directly to determine which fraction is greater.
8. What mistakes should students avoid when revising fractions for Class 6?
Common mistakes to avoid include:
- Confusing the roles of numerator and denominator.
- Comparing fractions without first making the denominators the same.
- Not simplifying answers to the lowest terms, as required by NCERT.
- Misapplying operations to mixed and improper fractions.
9. In what ways can the revision notes for Fractions help in quick exam preparation?
The revision notes act as a concise summary of all important concepts and formulas needed for Chapter 7. They provide stepwise explanations, tips for comparison and operations, and include solved examples for practice. This helps students revise quickly and efficiently before assessments.
10. How can understanding the concept of equivalent and mixed fractions aid in solving word problems?
Knowledge of equivalent and mixed fractions allows students to convert complex fractions into simpler, more workable forms, and to interpret real-world quantities correctly. This skill is essential in word problems involving division, measurement, or distribution and is a key focus in the revision notes to build problem-solving abilities.