Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Human Resources Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts summarised in the Class 8 Geography Chapter 5 Revision Notes on Human Resources?
The key concepts in Human Resources Class 8 Notes include population distribution, population density, population growth, factors influencing human resources (such as birth rate, death rate, migration), and the role of human resources in national development. Understanding these helps students connect how people impact the economy, resource management, and societal progress.
2. How can revision notes help students quickly prepare for Geography Chapter 5 Human Resources?
Revision notes provide a quick summary of important points, definitions, diagrams like the population pyramid, and examples essential for exam preparation. They help students revise efficiently by focusing on crucial topics, clarify complex concepts, and give a structure for last-minute review, increasing confidence before exams.
3. What summary should students create for quick revision of Human Resources in Class 8 Geography?
For quick revision, students should summarise:
- Definition and importance of human resources
- Major factors affecting population distribution and density
- Population growth patterns and causes
- Population composition and the use of population pyramids
- Impact of human resources on economic and social development
4. Why is understanding the interconnection between population growth and resource management important while revising Human Resources Notes?
Grasping the link between population growth and resource management is vital because rapid population growth can increase pressure on resources and infrastructure, while well-managed growth supports sustainable development. Effective revision of these interconnections helps students answer application-based questions in exams.
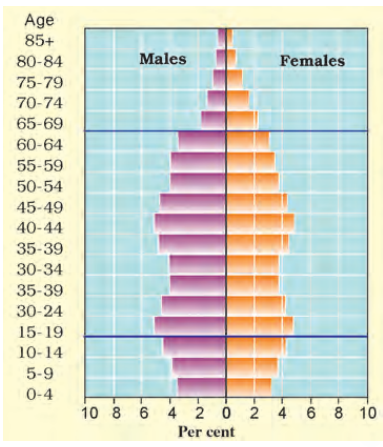
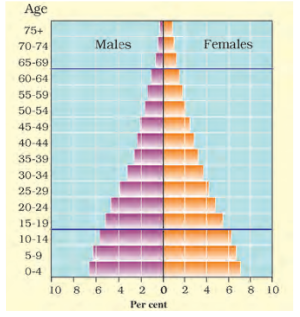
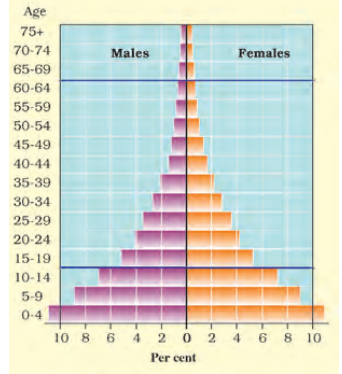
5. What is a population pyramid and how does it help in quick revision for Class 8 Geography Chapter 5?
A population pyramid is a graphical representation showing the age and sex structure of a country’s population. It helps in quick revision as it visually summarises demographic trends, such as birth rates, death rates, and age groups, allowing students to instantly recall and compare population compositions.
6. How can students efficiently revise key terms and definitions from Human Resources Class 8 Notes?
Students should list out and repeatedly review key terms like population density, migration, demography, natural growth rate, and birth rate. Creating flashcards, mind maps, or a glossary section in their revision notes enhances memory retention of definitions.
7. In what revision order should students study the Class 8 Geography Chapter 5 Notes for maximum understanding?
The most effective revision order is:
- Start with key concepts and definitions
- Move to factors affecting population
- Study population distribution and density
- Revise population growth and its causes
- Cover application-based topics like effects of migration and challenges of overpopulation
- End with population pyramid and summary points
8. What common misconceptions should students avoid when revising Human Resources Notes for Class 8 Geography?
Students should avoid confusing population density with population distribution, believing higher population always means economic success, or assuming migration only increases population. Clarifying these during revision helps prevent errors in exam answers.
9. How do quick revision notes highlight the challenges associated with overpopulation and underpopulation?
Quick revision notes summarise that overpopulation leads to strain on resources and services, while underpopulation can cause labour shortages and economic stagnation. Awareness of these challenges ensures students can answer high-order thinking questions effectively.
10. What are some effective strategies for remembering factors influencing population distribution, as per Human Resources revision notes?
Effective strategies include:
- Grouping factors into geographical (topography, water, climate, soil, minerals) and socio-economic/cultural categories
- Using mnemonics or mind maps
- Relating factors to real-world examples discussed in the notes, like the Ganga plains or the city of Pune
11. Why is it helpful to use concept maps for revising the Human Resources chapter?
Concept maps visually link main ideas such as human resources, factors affecting population, and outcomes like economic development, making it easier to see connections and recall information during exams.