How Do Bacteriophages Infect and Kill Bacteria?
A bacteriophage is a virus that specifically infects bacteria. It targets bacterial cells, replicates inside them, and then releases new viral particles. This process plays a crucial role in controlling bacterial populations in various environments and has attracted considerable interest from researchers in fields such as microbiology and biotechnology.
Bacteriophage Definition
When asked, “What is bacteriophage and its function?” we can define bacteriophages as unique viruses that invade and reproduce within bacterial cells. These viruses can be highly specific to particular bacteria, making them potentially valuable tools in combating bacterial infections.
Bacteriophage Structure
A typical bacteriophage structure includes:
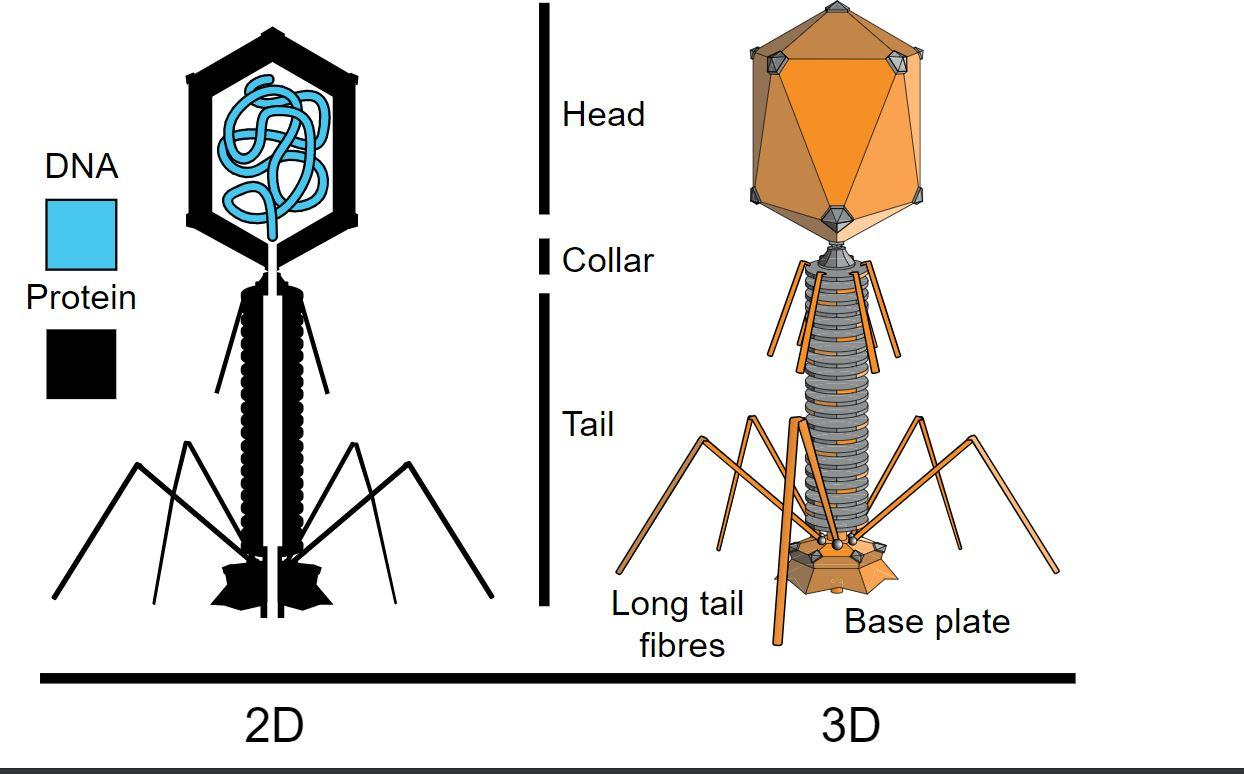
Head (Capsid): Contains genetic material (DNA or RNA) tightly packed inside a protein shell.
Collar: A short segment connecting the head to the tail.
Tail: A helical tube surrounded by a contractile sheath. Often ends with a basal plate and tail fibres.
Such features are best understood by referring to a bacteriophage diagram, which typically shows the head, collar, tail, and tail fibres needed for attachment to the bacterial cell surface.
Bacteriophage Life Cycle
A bacteriophage life cycle generally follows two main pathways:
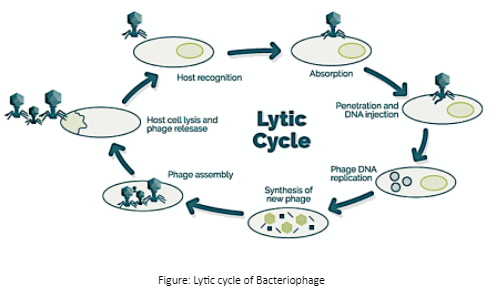
1. Lytic Cycle
Attachment (Adsorption): The phage uses its tail fibres to bind to specific receptors on the bacterial surface.
Penetration: The tail contracts, injecting the viral DNA or RNA into the bacterium.
Replication and Synthesis: Viral genetic material hijacks the bacterium’s machinery to produce new phage components.
Assembly: Newly formed viral heads, tails, and other parts come together to create complete bacteriophages.
Release: The bacterial cell lyses (bursts), releasing numerous new phages to infect other bacteria.
2. Lysogenic Cycle
Integration: Instead of immediately replicating, the phage DNA becomes part of the bacterial chromosome, forming a “prophage.”
Dormancy: The infected bacterium continues to live and reproduce normally, passing on the prophage DNA to daughter cells.
Activation: Under specific triggers (like stress or damage to bacterial DNA), the prophage may exit the bacterial chromosome and switch to the lytic cycle, destroying the cell and releasing new phages.
Bacteriophage Function
The primary bacteriophage function is to infect and replicate within bacterial cells. Key points include:
Control of Bacterial Populations: Phages keep bacterial growth in check in natural ecosystems, including oceans and soil.
Potential Medical Applications: Researchers are exploring “phage therapy” to treat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
Biotechnological Uses: Bacteriophages can serve as tools for molecular genetics, gene delivery, and bacterial detection.
Are Bacteriophages Harmful to Humans?
Bacteriophages generally infect only bacteria, not human cells. This makes them unlikely to be harmful to humans. In fact, phages are found naturally in our environment, including within our bodies, where they help maintain a balance in the microbial flora.
Quick Quiz (With Answers)
1. Question: Which part of a bacteriophage contains its genetic material?
Answer: The head (capsid).
2. Question: Name the phase in which the phage integrates its DNA into the bacterial chromosome.
Answer: Lysogenic cycle.
3. Question: What advantage do bacteriophages have over some antibiotics?
Answer: They can target specific bacteria and are potentially effective against antibiotic-resistant strains.
Conclusion
By studying what is bacteriophage, examining its structure, and understanding both the lytic and lysogenic cycles, we gain a clearer picture of the role viruses play in bacterial control and biotechnology.


FAQs on Bacteriophage Explained: Definition, Structure & Functions
1. What is a bacteriophage and what is its primary function?
A bacteriophage, which literally means 'bacteria eater', is a type of virus that specifically infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. Its primary function is to take over a host bacterium's cellular machinery to create more copies of itself, which often results in the destruction (lysis) of the host cell.
2. What are the main parts of a typical bacteriophage structure?
A typical bacteriophage has a highly specialised structure that includes several key parts, each with a specific function:
Head or Capsid: A protein shell that encloses the viral genetic material, which can be DNA or RNA.
Tail: A hollow tube through which the genetic material is injected into the host bacterium. It consists of a contractile sheath and a central core.
Tail Fibres: Leg-like structures at the base of the tail that recognise and attach to specific receptor sites on the surface of the host bacterial cell.
3. What are the two main life cycles of a bacteriophage?
Bacteriophages primarily exhibit two types of life cycles:
The Lytic Cycle: In this cycle, the phage replicates rapidly within the host bacterium and concludes by causing the cell to burst (lyse), releasing numerous new phages to infect other cells.
The Lysogenic Cycle: In this cycle, the phage's genetic material integrates into the host bacterium's chromosome, becoming a 'prophage'. It remains dormant and is replicated along with the host's DNA, without immediately killing the cell. It can later enter the lytic cycle in response to certain triggers.
4. What is the key difference between the lytic and lysogenic cycles?
The key difference lies in the immediate outcome for the host cell. In the lytic cycle, the phage acts quickly, leading to the rapid production of new viruses and the host cell's destruction. In contrast, the lysogenic cycle involves the integration of the phage's DNA into the host genome, where it can remain dormant for many generations without causing harm, only activating to enter the lytic cycle later.
5. Are bacteriophages considered harmful to humans?
No, bacteriophages are not harmful to humans. They are highly specific and can only infect bacterial cells. They cannot recognise or infect eukaryotic cells, such as human, animal, or plant cells. This specificity is a key reason they are being researched as a potential therapeutic tool (phage therapy) to target harmful bacteria without affecting the patient's own cells.
6. Why is the specific structure of a bacteriophage, often described as 'robot-like', so important for its function?
The 'robot-like' appearance of a bacteriophage is a direct result of its evolution as a highly efficient biological machine for injecting genetic material. The structure is critical to its function: the head acts as a protective cargo container for its DNA, the tail fibres work as precise landing gear to identify and bind to the correct bacterium, and the contractile tail functions like a hypodermic syringe to forcibly inject the DNA past the tough bacterial cell wall.
7. What are some important applications of bacteriophages in biotechnology and medicine?
Bacteriophages are vital tools with several important applications:
Phage Therapy: They are used as an alternative or supplement to antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, especially those caused by antibiotic-resistant strains.
Genetic Engineering: They serve as 'vectors' to carry and introduce specific genes into bacteria for research or industrial purposes, such as producing insulin or other proteins.
Diagnostics: They can be used to detect the presence of specific bacteria in samples, a technique known as phage typing.
8. What happens if a bacteriophage tries to infect a bacterium that lacks the correct surface receptors?
If a bacterium does not have the specific surface receptors that a bacteriophage's tail fibres are designed to recognise, the phage cannot attach to the cell. Since attachment is the mandatory first step of infection, no further action occurs. The phage will be unable to inject its genetic material, and the infection will fail completely.
9. Do all bacteriophages contain DNA as their genetic material?
While the most commonly studied bacteriophages, like the T4 phage, contain double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), they are a diverse group. Different types of bacteriophages can have various forms of genetic material, including single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), single-stranded RNA (ssRNA), or even double-stranded RNA (dsRNA).
10. Who is credited with the discovery of bacteriophages?
The discovery of bacteriophages is credited to two scientists who worked independently. It was first observed by the English bacteriologist Frederick Twort in 1915 and then more formally described and named by the French-Canadian microbiologist Félix d'Hérelle in 1917. This discovery was foundational to the fields of virology and molecular biology.










