How Arteries and Veins Function in the Human Body
Understanding the difference between arteries and veins is crucial when studying the human circulatory system. These blood vessels play essential roles in circulating blood throughout the body but differ widely in structure and function. In this guide, we will explore the arteries and veins in-depth, highlight the structural difference between arteries and veins, explain the function of artery and vein, and provide an easy-to-follow arteries and veins diagram to enhance your understanding.
What are Arteries and Veins?
Arteries are specialised blood vessels that transport blood away from the heart. Typically, they carry oxygen-rich blood to the various parts of the body—except for the pulmonary arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Conversely, veins return blood to the heart, usually carrying deoxygenated blood (with the pulmonary veins being the notable exception as they transport oxygenated blood from the lungs). Recognising this basic difference between arteries and veins is fundamental for understanding how our circulatory system functions.
Structural Difference Between Arteries and Veins
When comparing the structural difference between arteries and vein, consider these key points:
Wall Composition: Arteries have thick, muscular walls made up of three distinct layers (intima, media, and adventitia) that enable them to handle the high pressure generated by the heart. Veins, however, have thinner walls with less muscle, suitable for the lower pressure in these vessels.
Lumen Size: The lumen of an artery is narrow, ensuring efficient blood flow under pressure, whereas veins have a wider lumen to accommodate a larger volume of blood as it returns to the heart.
Presence of Valves: Veins contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood, a feature not found in arteries.
Colour and Position: Arteries are often shown in red and are typically located deeper within the body, while veins appear bluish and are more superficial, often closer to the skin.
Function of Artery and Vein
The function of artery and vein is central to their roles in the circulatory system. Arteries transport blood away from the heart under high pressure, ensuring oxygenated blood reaches all tissues. In contrast, veins collect blood from the body tissues and return it to the heart under lower pressure. This difference is vital for the efficient exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products in the capillaries.
Detailed Comparison: Arteries and Veins Diagram
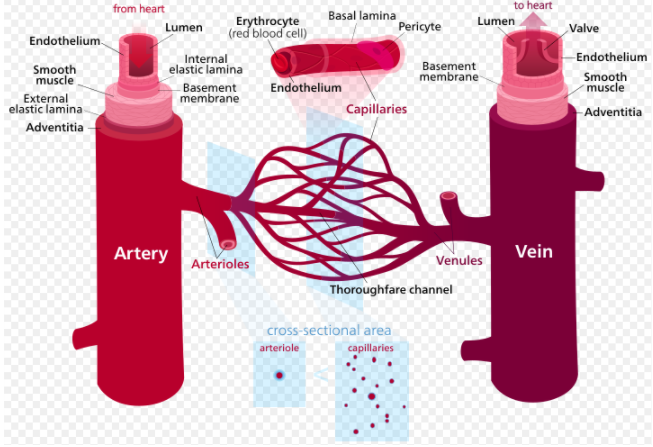
The branching of arteries from the heart into arterioles and subsequently capillaries.
How veins merge from capillaries back into larger vessels to return blood to the heart.
The relative differences in wall thickness, lumen size, and the presence of valves in veins.
Types of Arteries and Veins
Different types of arteries and veins play specialised roles in the circulatory system:
Arteries:
Elastic Arteries: Large vessels such as the aorta that expand and recoil with each heartbeat.
Muscular Arteries: Medium-sized arteries that distribute blood to various regions.
Arterioles: Small branches leading to capillaries where vital exchange of gases and nutrients occurs.
Veins:
Deep Veins: Located within muscles and crucial for returning blood from the limbs.
Superficial Veins: Found near the skin’s surface and visible in many parts of the body.
Pulmonary Veins: Transport oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Systemic Veins: Return deoxygenated blood from body tissues to the heart.
Fun Facts about Arteries and Veins
Surprising Strength: Despite being less visible, arteries are remarkably resilient. They must withstand blood pressures that can exceed 120/80 mmHg.
One-Way Valves: The valves in veins act like one-way gates, preventing blood from flowing backward and ensuring it moves steadily towards the heart, especially in the limbs.
Pulmonary Paradox:The pulmonary circulation uniquely reverses the usual roles: pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Real-World Applications
Understanding the difference between arteries and veins is not merely academic—it has significant real-life implications:
Medical Diagnostics: Knowledge of the structural and functional differences is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as atherosclerosis in arteries and varicose veins in the venous system.
Surgical Precision: Surgeons rely on detailed arteries and veins diagrams to plan operations and avoid complications during vascular surgeries.
Health and Fitness: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and maintains the health of blood vessels, promoting better blood circulation and overall well-being.
Innovative Treatments: Advances in biomedical engineering, such as the development of artificial blood vessels, are directly informed by our understanding of the function of artery and vein and their structural differences.
Modern imaging techniques like Doppler ultrasound and CT angiography have significantly enhanced our understanding of both arteries and veins. These technologies allow real-time visualisation of blood flow, detection of blockages, and aid in designing personalised treatments. Moreover, researchers are exploring bioengineered vessels that mimic the structural difference between arteries and vein to improve outcomes in vascular surgery.


FAQs on Difference Between Arteries and Veins: Complete Guide
1. What is the main functional difference between arteries and veins?
The primary functional difference is the direction of blood flow relative to the heart. Arteries are blood vessels designed to carry blood away from the heart and distribute it to the body's tissues. In contrast, veins are responsible for collecting blood from the tissues and carrying it back towards the heart.
2. How does the wall structure of arteries compare to that of veins?
Artery walls are significantly thicker, more muscular, and more elastic than vein walls. This robust structure is essential to withstand the high pressure of blood being pumped directly from the heart. Veins, which handle lower-pressure blood, have thinner, less muscular walls.
3. Why do veins have valves while arteries do not?
Veins are equipped with one-way valves to prevent the backflow of blood. This is especially important in the limbs, where blood must flow against gravity to return to the heart under low pressure. Arteries do not require valves because the powerful, high-pressure force from the heart's pumping action ensures that blood flows consistently in one direction.
4. Are there any exceptions to the rule about oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in these vessels?
Yes, the pulmonary circulation system is the major exception to this general rule.
- The pulmonary artery is unique as it carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- The pulmonary veins are unique because they carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart.
5. How does blood pressure differ in arteries and veins, and what is the significance?
Blood pressure is much higher in arteries than in veins. Arteries receive blood directly from the heart's powerful contractions, resulting in high pressure and a palpable pulse. As blood flows through the circulatory system, this pressure gradually decreases. By the time it reaches the veins for its return journey, the pressure is very low, which is why veins have valves to assist blood flow.
6. What do the colours red and blue represent in diagrams of arteries and veins?
This is a widely used scientific convention for illustration. Red is used to represent oxygenated blood, which is typically carried by arteries from the heart to the body. Blue is used to represent deoxygenated blood, which is usually carried by veins from the body back to the heart. It is important to remember that deoxygenated blood is actually dark red, not blue.
7. What are capillaries and how do they relate to arteries and veins?
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body and they form a vast network that connects the smallest arteries (arterioles) to the smallest veins (venules). Their primary importance is as the site of exchange:
- Oxygen and nutrients pass from the capillaries into the body's cells.
- Carbon dioxide and other waste products pass from the cells into the capillaries.
8. How is the knowledge of differences between arteries and veins applied in common medical procedures?
This understanding is fundamental in medicine. For example, blood samples are drawn from veins because they are closer to the skin's surface and have low blood pressure, making the procedure safer. Conversely, blood pressure is measured in an artery (like the brachial artery in the arm) to get an accurate reading of the force of blood circulation directly from the heart.










