Sprouts and Microgreens: Definitions, Nutrition, and Uses
Sprouts have a much more limited developing pattern of 2-7 days, though microgreens are normally gathered 7-21 days after germination when the plant's most memorable genuine leaves have arisen. Microgreens are more like child greens in that their stems and leaves are viewed as consumable. Microgreens require more ventilation and sunlight, which reduces the chances of bacterial growth. There is no need to add additional nutrients or plants to the soil for growth. Plants use the energy stored in seeds to germinate and prepare them for consumption.
What are Sprouts?
A sprout is a seed that germinates and grows into a young plant. They are grown Hydroponically (Using Only Water). Sprouts are nutritious and low in calories. People often germinate in water, grow quickly, and can be harvested in 2-6 days. Sprouts have been a staple food for decades, and have been a raw food staple that has been praised for their nutritional value.
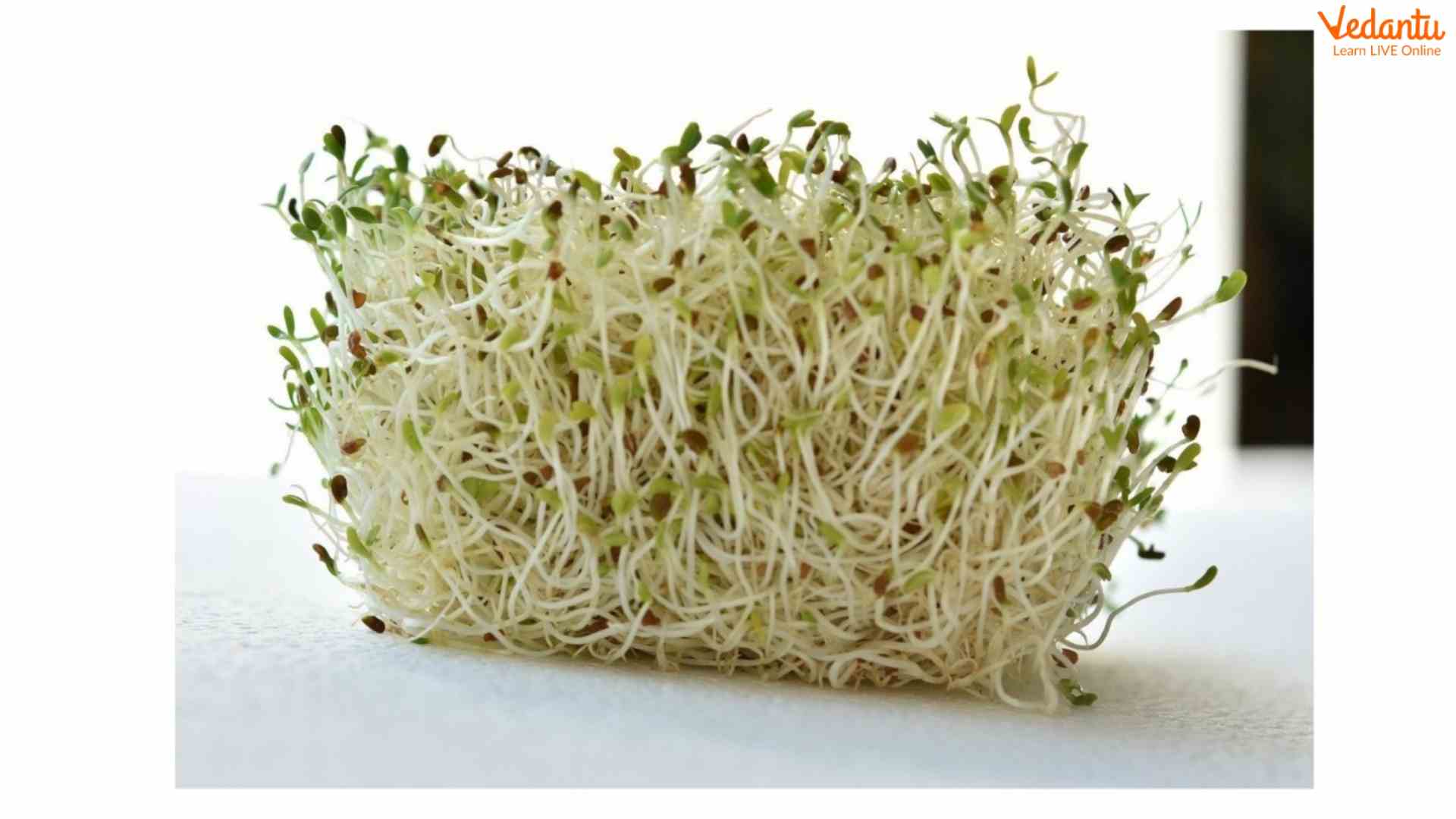

Sprouts
What is Microgreen?
As the name suggests, microgreens are young plants. They are more nutritious than adults. This little vegetable was popularised through cooking shows and gourmet restaurants, but now you can see it growing on grocery store shelves or people's windowsills. There are many different types of microgreens, and the most commonly grown microgreens are beets, radishes, and broccoli. They add flavour and colour adding an interesting twist to dishes. Almost any vegetable or herb can be grown as a microgreen.
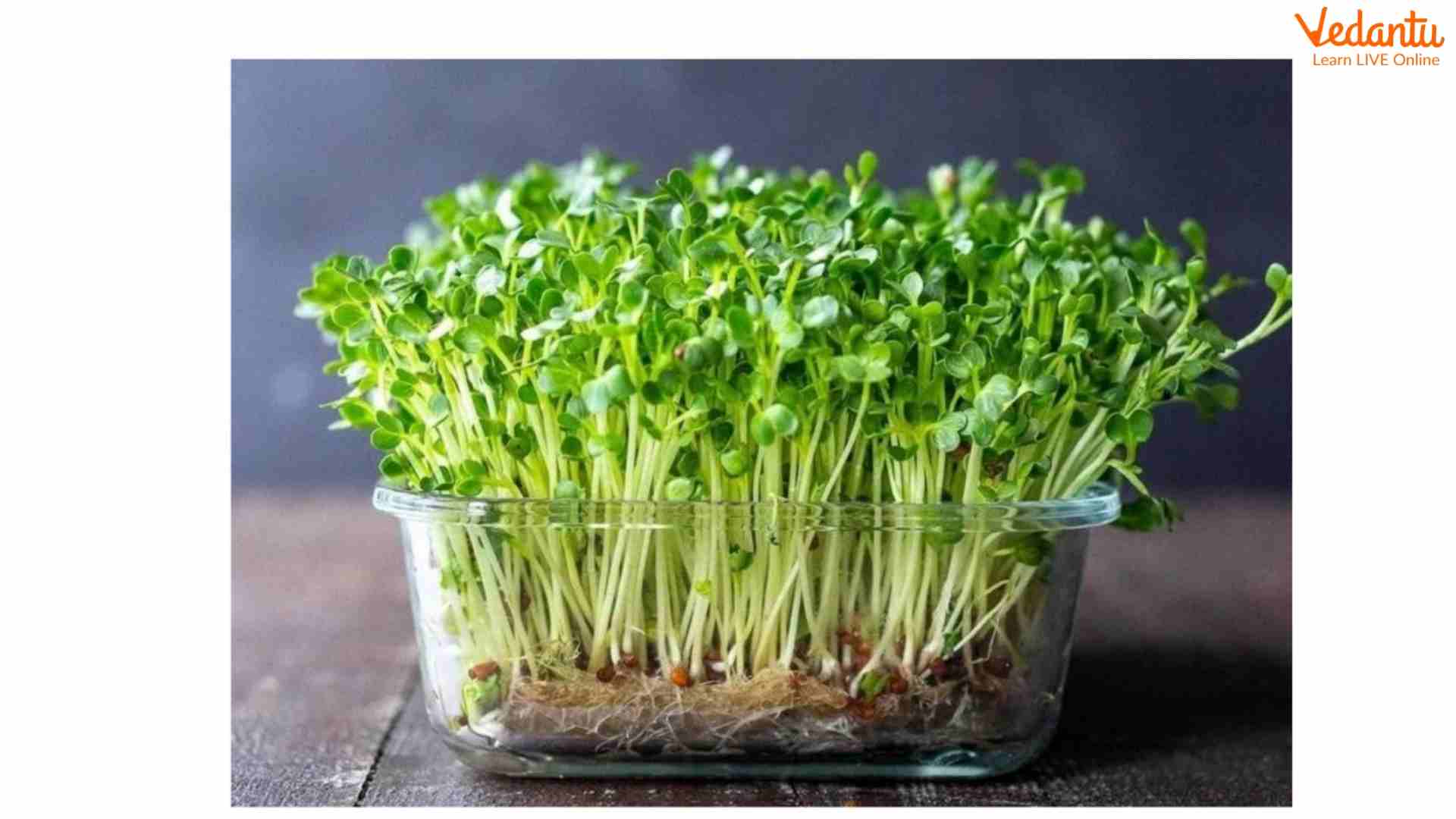

Microgreen
Sprouts Preparation
Let us now see the method to prepare sprouts from moong or chickpeas (chana).
Purpose: Prepare sprouts from seeds such as bruises and vats.
Required Ingredients:
A small cup of green gram or tea, water, and light muslin.
Procedure:
Place a few seeds (moong or chana) in a container of water. Set aside for a day.
The next day, drain the water completely and place the seeds in a container.
Wrap the container in a cloth and leave for a day or two.
Water the seeds when they dry out.
Observation:
White structures could have grown from seeds, called sprouts.
List of Sprouts
Moong Bean Sprouts
As mentioned earlier, moong bean sprouts are the most common. They offer allow-calorie content: a cup of green sprouts provides 31 calories. It also contains carbohydrates, protein, folic acid, vitamin C, and iron. Although moong beans are highly nutritious, they become more beneficial once sprouted. It is also rich in antioxidants. Several studies have shown that eating these sprouts can help fight free radicals and enhance anti-cancer properties. It can be eaten raw or fried with vegetables to make the perfect breakfast plate.
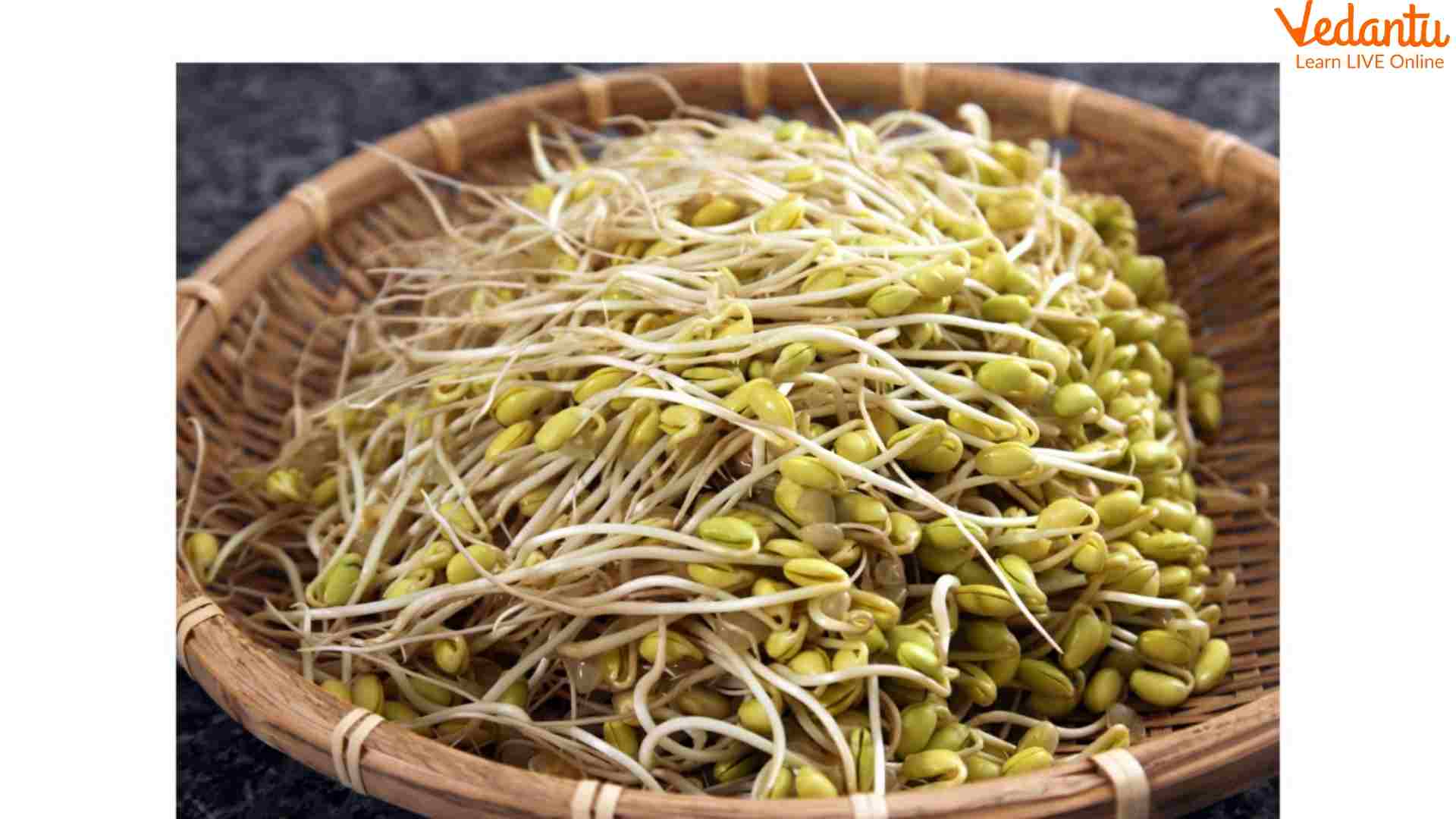

Mung Bean Sprouts
Kidney Beans
Our favourite sprouts, or razma, are another type of bean that can be grown. There are many sizes and colour options, but most of them can be germinated. Nuts are low in calories and rich in protein. They are also very healthy because they are low in fat and carbohydrates. In addition, it also contains iron, folic acid, and vitamin C. Once sprouted, nuts are rich in melatonin, which is important in regulating the sleep cycle. Melatonin also has antioxidant properties that fight free radicals and prevent cell damage.
Melatonin can be naturally produced in the body, but levels are lower in adults because its production declines over time. Thus, consuming melatonin from other foods, such as bean sprouts, may help prevent sleep disturbances and other age-related health problems. By consuming it, you can also protect yourself from other chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease. The sprouts are a little hard.
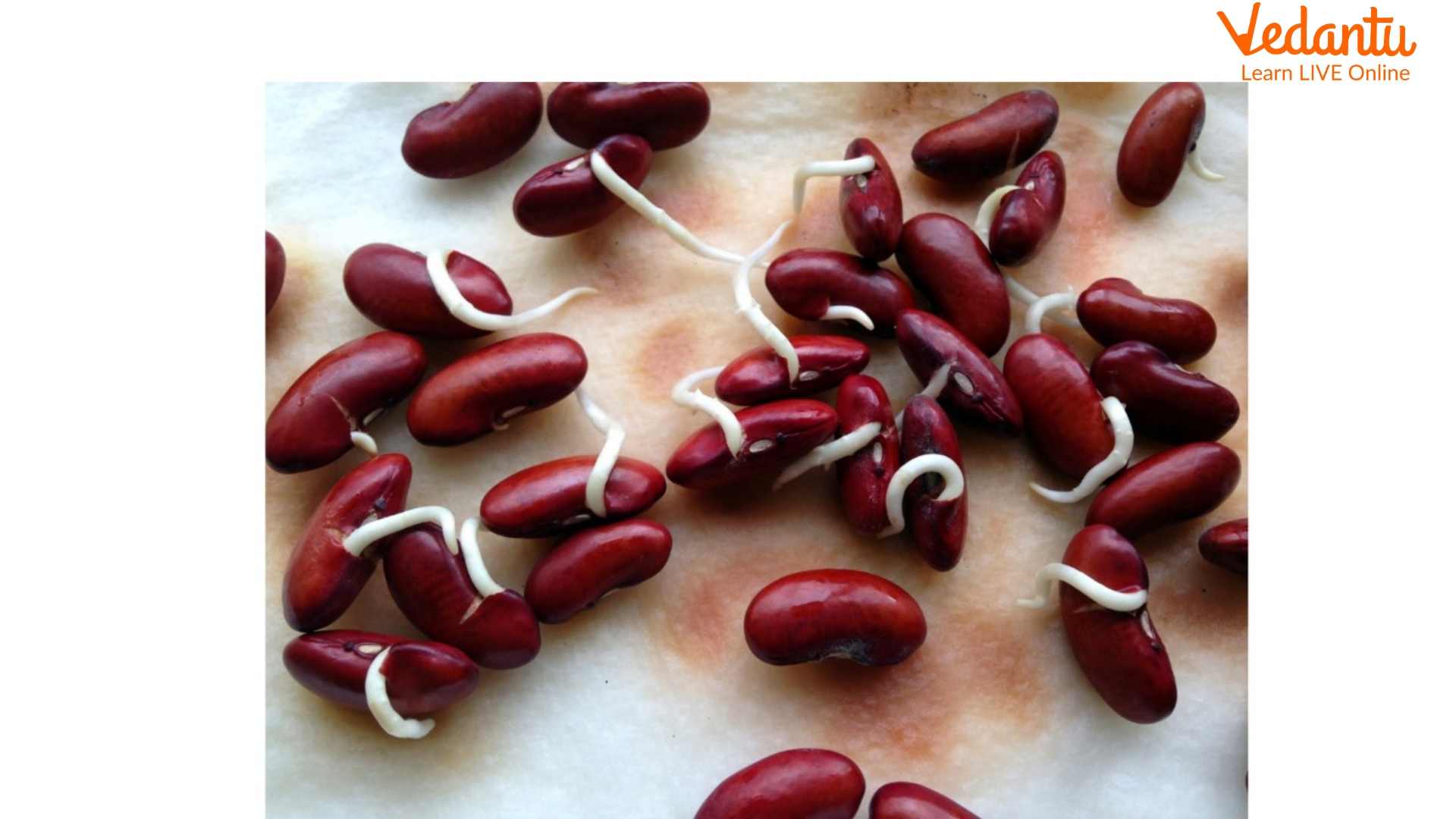

Rajma Sprouts
Peas Sprouts
Because peas are inherently sweet, sprouts are also sweet. Peas come in two varieties: green and yellow. Both germinate and are very nutritious. Their only drawback is their high-calorie content (a cup of peas provides 149 calories). But they are also rich in protein and carbohydrates and low in fat. The great thing about sprouted peas is that they contain twice as much vitamin B9 or folic acid as raw peas.
It is a powerful vitamin because a deficiency can cause birth defects such as neural tube defects and heart defects. Mothers should take this vitamin to prevent birth defects in the foetus. Instead of taking supplements, you can grow peas because of their high folic acid content.

Peas Sprouts
Bengal Gram Sprouts
Bengali gram sprout Another very common sprout is the Bengali gram sprout or Kalachana. Unlike kidney beans and kidney beans, they are rich in carbohydrates and vitamin B6. The best thing about this sprout is that it helps with weight loss, diabetes, and more without affecting cholesterol levels. From them, you can cook delicious cabbage. With other bean sprouts and chopped onions, tomatoes, and squeezed lemon juice, you will have a delicious sprout salad.

Bengal Gram Sprouts
Sprouts Examples
Below is a list of the most common types of sprouts available on the market.
Bean sprouts and kidney beans: sprouts such as lentils, red beans, chickpeas, kidney beans, mung beans, black beans, kidney beans, mung beans, and snow sprouts. Sprouted grains: brown rice, buckwheat, spinach, Kamut, quinoa, buckwheat sprouts, etc.
Microgreen Examples
Various types of microgreens in the Brassicaceae family: cauliflower, broccoli, white cabbage, watercress, turnip and arugula. Asteraceae family: lettuce, endive, chicory and radicchio. Poppy family: fennel, carrot, fennel and celery. Amaryllis family: garlic, shallots, leeks.
Difference Between Sprouts and Microgreens
Microgreen Nutrition Chart
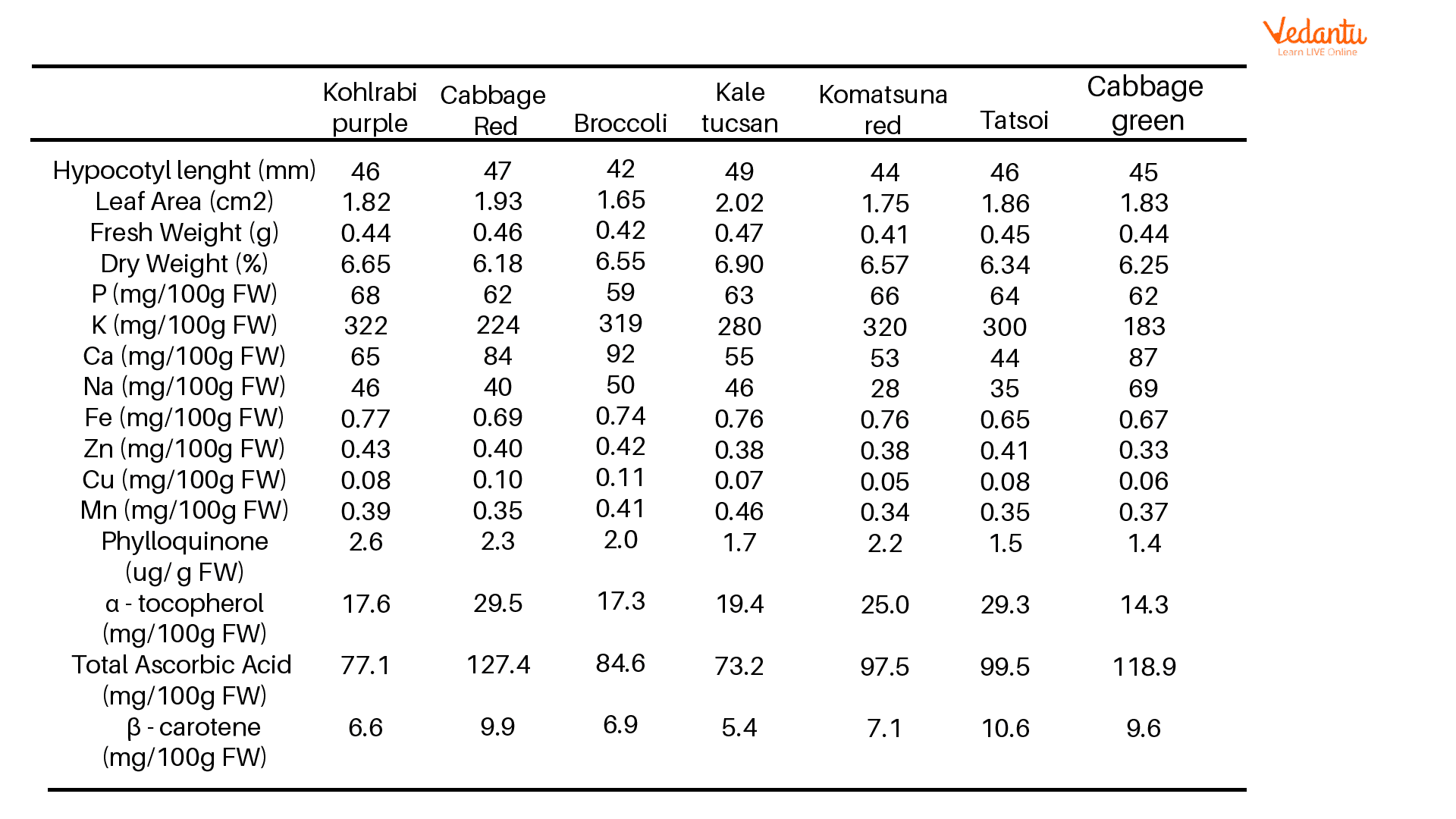
Microgreen Nutrition Chart
Interesting Facts
Sprouts are usually germinated and wholly grown in water and are harvested earlier on in the growing process than microgreens. Unlike a baby micro green, they are mild in flavour and used in dishes mostly for their texture. There is also an added risk of food poisoning due to the growing conditions of these seeds.
There are over 25 different types of microgreens. Microgreens can be harvested from many vegetables you may already know, such as arugula, broccoli, celery, and radishes. Microgreens contain 40 times more nutrients than their fully-grown counterparts. Most microgreens are a great source of vitamins A, C, E, and K.
Important Questions
1. What are the benefits of microgreens?
Ans: Below are some benefits of microgreens:
Microgreens can lower blood pressure. Foods that are high in fiber and vitamin K can be helpful in maintaining healthy blood pressure, and microgreens are high in both of these important elements as well as other vitamins and minerals.
Microgreens might help fight cancer. Research is ongoing into this subject, but some early evidence suggests that sulforaphane — a compound found at especially high levels in broccoli sprouts — may help fight cancer.
Some microgreens can help lower cholesterol. A study found that red cabbage microgreens lower levels of LDL cholesterol, liver cholesterol, and inflammatory cytokines — all factors that can increase your risk for heart disease.
2. What are the benefits of eating sprouts?
Ans: Below are some benefits of sprouts:
Low-Calorie Treat - A bowl of sprouts, about 100 grams, contains just a little over 100 calories, packed with all the essential nutrients. It helps to keep the hunger pangs under control and helps to lose weight.
Filled with Fibre - Sprouts contain about 7.6 grams of fibre per serving. Fibre rich food is ideal for obese people as well as diabetics. Fibre is vital for the digestive system, keeps you satiated, delays gastric emptying time, prevents binge eating and is a godsend for people suffering from constipation.
Conclusion
Microgreens are delicious and can be easily incorporated into your diet in a variety of ways. As a rule, they are very nutritious and may even reduce the risk of certain diseases.
Sprouts tend to increase the nutritional value of sprouted grains, legumes, vegetables, nuts, or seeds. Sprouts also contain fewer antinutrients, making it easier for your body to absorb all of the nutrients they contain.


FAQs on Sprouts vs Microgreens: What Every Student Should Know
1. What is the fundamental difference between sprouts and microgreens?
The fundamental difference lies in their stage of development and the parts of the plant that are consumed. Sprouts are essentially germinated seeds, harvested just as the root (radicle) emerges. The entire thing—seed, root, and underdeveloped shoot—is eaten. Microgreens, on the other hand, are allowed to grow further until they develop their first set of true leaves (cotyledons). For microgreens, you only eat the stem and leaves, not the root or seed. This topic is a part of general Biology.
2. How does the growing process differ for sprouts versus microgreens?
The growing methods are distinct and lead to their key differences:
- Growing Medium: Sprouts are grown hydroponically, using only water and no soil. They are typically kept in jars or trays with high humidity. Microgreens are usually grown in a medium like soil or a soilless mat.
- Light Exposure: Sprouts require very little to no light, which is why they are often pale. Microgreens need several hours of light per day to perform photosynthesis, which gives them their green color and more complex flavour.
- Harvest Time: Sprouts are harvested very quickly, usually within 2-7 days. Microgreens have a longer growth cycle, typically harvested in 7-21 days, after their first true leaves have developed.
3. What are the main nutritional differences between sprouts and microgreens?
While both are nutritious, their profiles differ due to their growth stage. Sprouts draw nutrients directly from the seed, making them rich in fibre, enzymes, and protein. Microgreens, having been exposed to light and soil, start producing their own nutrients through photosynthesis. This often results in a higher concentration of vitamins (like C, E, and K) and carotenoids—sometimes up to 40 times more than their mature plant counterparts.
4. Can the same seeds be used to grow both sprouts and microgreens?
Yes, you can often use the same type of seed (e.g., radish, broccoli, mung bean) to grow either sprouts or microgreens. The outcome depends entirely on the method and duration of growth. For sprouts, you would germinate them in water for a few days. For microgreens, you would plant the same seeds in soil, provide light, and let them grow for a couple of weeks until leaves appear. However, seeds sold specifically for microgreens are often selected for leaf quality, while sprouting seeds are selected for germination rate.
5. Why do sprouts and microgreens have such different tastes and culinary uses?
The difference in taste comes from their developmental stage. Sprouts, having not performed photosynthesis, have a very mild, often nutty or earthy flavour and a high water content, giving them their characteristic crunch. They are typically added to dishes for texture. Microgreens, on the other hand, have developed chlorophyll and other compounds, giving them a more intense and complex flavour that often resembles a milder version of the mature plant (e.g., radish microgreens are peppery). This makes them excellent for use as a flavourful garnish or salad ingredient.
6. Are there any health risks associated with eating sprouts or microgreens?
The primary health risk is associated with sprouts. The warm, humid conditions needed for sprouting are also ideal for the growth of harmful bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella. If the seeds are contaminated, these bacteria can multiply rapidly. It is crucial to buy sprouts from reputable sources or rinse them thoroughly. Microgreens carry a much lower risk because they are grown in a more open environment with airflow and not in stagnant water, and the seed part is not consumed.










