How Organisms Interact With Each Other and Their Environment
Ecology is the branch of biology that examines how organisms interact with each other and their physical surroundings. It encompasses the study of individual organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and the biosphere. By analysing these interactions, ecologists aim to understand the distribution and abundance of life on Earth.
Biotic and Abiotic Factors
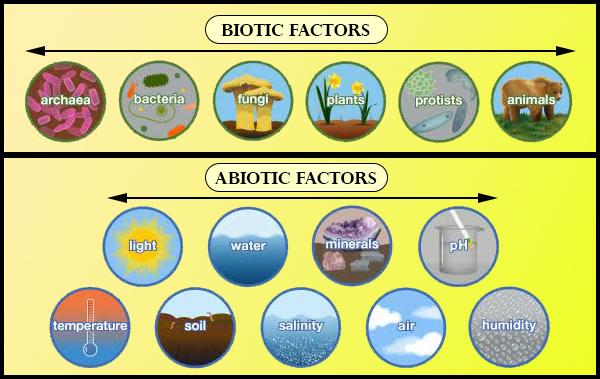
In ecology, the environment is composed of both living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components.
Biotic Factors: These include all living organisms within an ecosystem, such as plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and protists. They interact in various ways, including predation, competition, symbiosis, and mutualism.
Also Read: Biotic Components
Abiotic Factors: These are the non-living physical and chemical elements of an environment. Examples include sunlight, temperature, water, air, minerals, and soil. Abiotic factors significantly influence the survival and reproduction of organisms.
Also Read: Abiotic Component
Types of Ecology
Ecology is a broad field with several sub-disciplines, each focusing on different aspects of organisms and their environments.
1. Organismal Ecology: This branch studies individual organisms' behaviours, physiology, and morphology in response to environmental challenges. It examines how organisms adapt to their abiotic and biotic environments.
2. Population Ecology: Focusing on groups of individuals of the same species, population ecology investigates factors affecting population size, density, distribution, and growth over time. It also explores interactions such as competition and predation.
3. Community Ecology: This area examines how different species interact within a community and the consequences of these interactions. It studies patterns such as species diversity, community structure, and the dynamics of predator-prey relationships.
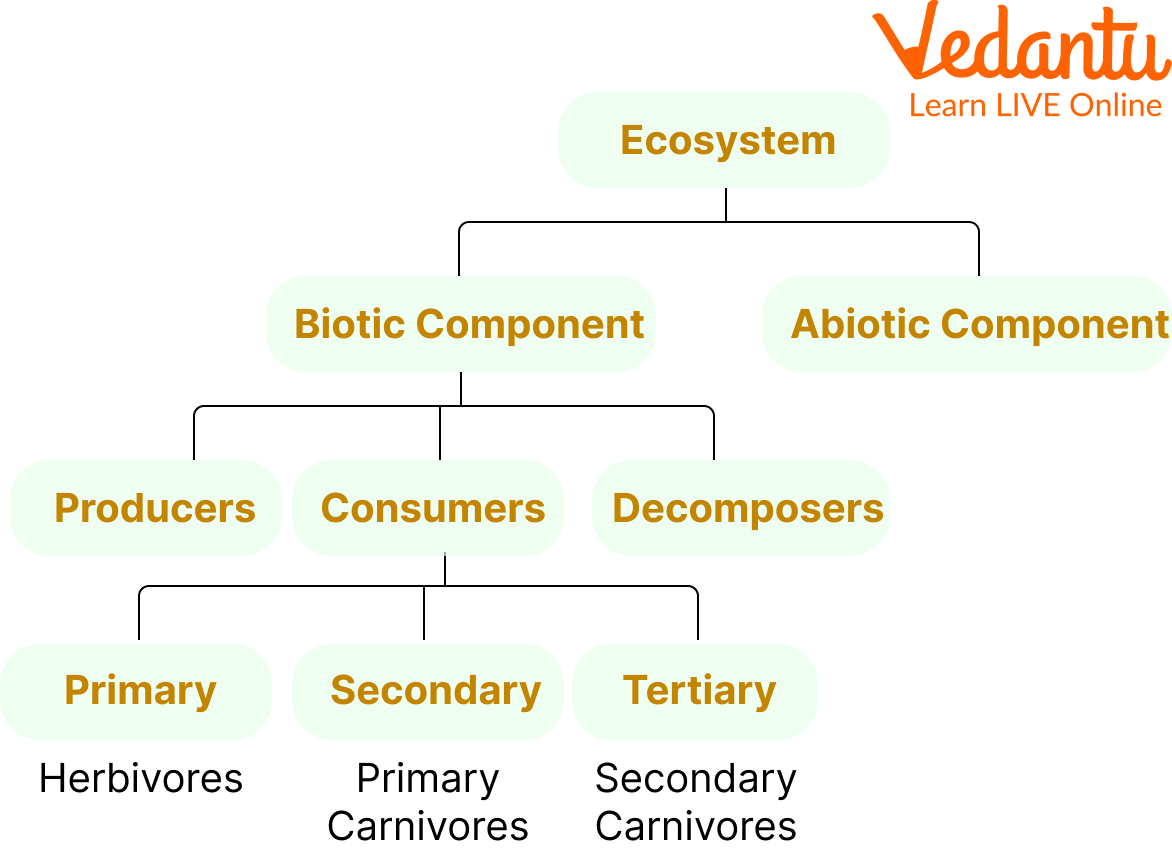
4. Ecosystem Ecology: Ecosystem ecology looks at energy flow and nutrient cycling among the various biotic and abiotic components. It aims to understand how ecosystems function and maintain their productivity.
5. Landscape Ecology: This field studies the spatial patterns and ecological processes across large geographic areas. It focuses on how landscape structure affects the abundance and distribution of organisms.
6. Global Ecology: Also known as biosphere ecology, it examines ecological phenomena at the planetary scale. This includes studying global biogeochemical cycles and the effects of climate change on biodiversity.
7. Molecular Ecology: Integrating molecular biology with ecological studies, this branch explores genetic relationships within and between populations. It aids in understanding evolutionary patterns and processes.
Importance of Ecology
Ecology plays a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of the natural world and addressing environmental challenges.
1. Conservation of Biodiversity: By understanding species interactions and their habitats, ecologists can develop strategies to protect endangered species and preserve biodiversity.
2. Natural Resource Management: Ecological knowledge guides the sustainable management of resources like forests, fisheries, and water systems, ensuring their availability for future generations.
3. Pollution Control: Ecologists study how pollutants affect ecosystems and devise methods to mitigate their impact, leading to healthier environments.
4. Climate Change Mitigation: Understanding ecological processes helps predict the impacts of climate change and develop strategies to combat its effects on ecosystems.
5. Ecosystem Services: Ecology highlights the benefits ecosystems provide, such as pollination, water purification, and soil fertility, which are essential for human survival.
Examples of Ecology in Action
1. Human Ecology: This examines the relationships between humans and their environments, focusing on how cultural and social factors influence ecological interactions.
2. Niche Construction: Organisms often modify their environments to enhance their survival. For example, beavers build dams, creating wetlands that benefit various species.
3. Urban Ecology: Studying ecological processes in urban settings helps in designing cities that support both human well-being and biodiversity.
4. Restoration Ecology: This involves restoring degraded ecosystems to their natural state, such as reforestation projects or wetland rehabilitation.


FAQs on Ecology Explained: Key Concepts, Types, Importance & Examples
1. What is the basic definition of ecology as a branch of biology?
Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical (abiotic) environment. It seeks to understand the distribution, abundance, and relationships of living things and how these relationships influence the structure and function of ecosystems.
2. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem?
The key difference lies in whether the factor is living or non-living. Biotic factors are all the living or once-living components, such as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. Abiotic factors are the non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment, including sunlight, temperature, water, and soil composition.
3. What are the major levels of organisation studied in ecology?
Ecology is studied at several hierarchical levels, each building on the last. The primary levels are:
- Organism: An individual living being.
- Population: A group of individuals of the same species living in the same area.
- Community: All the different populations of different species interacting in a particular area.
- Ecosystem: A community of organisms interacting with their physical environment (abiotic factors).
- Biosphere: The part of Earth where life exists, including all ecosystems.
4. What are the main types or branches of ecology?
Ecology is a broad field with several specialised branches. The main types include:
- Organismal Ecology: Studies an individual organism's adaptations to its environment.
- Population Ecology: Focuses on factors affecting population size and composition.
- Community Ecology: Examines interactions between different species in a community.
- Ecosystem Ecology: Analyses energy flow and nutrient cycling among biotic and abiotic components.
- Landscape Ecology: Studies ecological processes across large geographic areas.
- Global Ecology: Examines ecological phenomena at a planetary scale, like climate change.
5. How is an organism's niche different from its habitat?
While related, a habitat and a niche are distinct concepts. A habitat is the physical environment where an organism lives—its 'address'. In contrast, a niche describes the functional role an organism plays within that ecosystem—its 'profession'. This includes its diet, behaviour, and interactions with other species and abiotic factors, defining how it survives and contributes to the ecosystem.
6. How do biotic and abiotic factors interact to shape an ecosystem?
Abiotic and biotic factors are deeply interconnected. Abiotic factors like sunlight, water availability, and temperature set the fundamental conditions for life. These conditions determine which plants (producers) can grow. The types of plants then influence which animals (consumers) can live there, creating a food web. In turn, biotic factors like beavers building dams or earthworms aerating the soil can modify the abiotic environment, demonstrating a constant, dynamic interaction.
7. Why is the study of ecology so important for human well-being and the planet?
The study of ecology is crucial because it helps us understand and manage our planet's resources sustainably. Its importance includes:
- Conserving Biodiversity: Protecting species and their habitats.
- Natural Resource Management: Guiding the sustainable use of forests, water, and fisheries.
- Pollution Control: Identifying the impact of pollutants and finding solutions.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Predicting and combating the effects of global warming.
- Maintaining Ecosystem Services: Ensuring the continuation of essential natural processes like pollination, water purification, and soil formation that support human life.
8. How does the study of ecology help explain the process of evolution?
Ecology and evolution are inextricably linked. Ecology sets the stage for evolution by defining the environmental pressures an organism faces. These pressures, such as competition for resources, predation, and climate, drive the process of natural selection. Organisms with traits better suited to their ecological niche are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass those traits on, leading to evolutionary adaptation over time.
9. What are some real-world examples of ecological principles in action?
Ecological principles are visible all around us. For example, restoration ecology is used to rehabilitate degraded areas like clear-cut forests or polluted wetlands. In agriculture, understanding predator-prey dynamics allows for biological pest control, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Furthermore, urban ecology helps design cities that support biodiversity and provide green spaces for human health.
10. What is the key difference between community ecology and ecosystem ecology?
The primary difference is the inclusion of non-living components. Community ecology focuses exclusively on the interactions between different species (biotic factors) within a defined area, such as predation, competition, and symbiosis. Ecosystem ecology expands on this by including the study of how energy flows and nutrients are cycled between the organisms (the community) and their physical environment (the abiotic factors).










