How ATP Powers Cellular Functions in Living Organisms
ATP, or Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP full form), is often described as the energy currency of the cell. In Class 9 biology, students frequently ask, "what is the energy currency of the cell class 9?" and "why is ATP called the energy currency of the cell class 9?" Understanding ATP is key to grasping how cells store and utilise energy to power life’s processes.
What is ATP?
ATP is a nucleotide that plays an essential role in almost every cellular activity. It is created within mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, by capturing chemical energy from digested food. This energy is then stored in ATP's three phosphate groups, making it a vital molecule that explains why ATP is called energy currency of the cell.
For instance, ATP is not just an abstract concept—its role can be seen in every muscle contraction, nerve impulse, and cell division. In fact, many students search for terms like atp as energy currency of cell pdf and energy currency of the cell notes to understand this fundamental concept.
Structure of the ATP Molecule
The structure of ATP is relatively simple yet incredibly efficient:
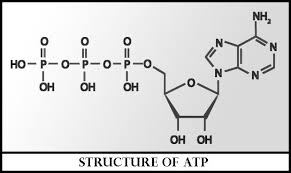
Adenine: A nitrogenous base.
Ribose: A five-carbon sugar that forms the backbone.
Three Phosphate Groups: Attached in a chain to the ribose sugar. The bonds between these phosphates are known as high-energy bonds. You might wonder, where are these high energy bonds found in atp? They are specifically located between the alpha, beta, and gamma phosphate groups.
These high-energy bonds store vast amounts of energy. When the outer phosphate bond is broken during hydrolysis (a process that involves the addition of a water molecule), a significant amount of energy is released. This process answers the query, how does ATP release energy, making ATP an ideal molecule for energy transfer within cells?
How does ATP Release Energy?
ATP releases energy through a process called hydrolysis. When the bond between the gamma and beta phosphate groups is broken, ATP is converted into ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) plus an inorganic phosphate. This reaction is highly exergonic, meaning it releases energy that the cell harnesses for various functions. This mechanism is so central that many ask, why ATP is called energy currency of the cell because brainly—it literally powers processes like muscle contractions, nerve transmission, and active transport across cell membranes.
Functions and Importance of ATP in Metabolism
ATP is indispensable for metabolism—the sum of all chemical reactions in the body. Some of its key roles include:
Energy Transfer: ATP supplies energy for both exergonic (energy-releasing) and endergonic (energy-consuming) reactions.
Biosynthesis: It powers the synthesis of essential macromolecules required for growth and repair.
Cell Signalling: Acts as a neurotransmitter in the tissue present in the brain and functions in cell signalling pathways.
Mechanical Work: Fuels processes such as muscle contraction and cellular locomotion.
These diverse roles show why ATP is the energy currency of the cell example in real life. Detailed diagrams and notes are available in resources like energy currency of the cell ppt and energy currency of the cell pdf which provide a comprehensive view of ATP’s structure and function.
Also, read: Metabolism and Metabolic Pathways
Key Points to Remember
While many resources cover the basics, here are some unique points to enhance your understanding:
ATP Recycling: After energy is released, ATP can be regenerated from ADP through cellular respiration—a cycle that ensures a continuous energy supply.
Adaptability Across Organisms: ATP’s role is conserved across all life forms, from the simplest bacteria to complex human tissues, including the tissue present in the brain.
Environmental Impact: The efficiency of ATP production in mitochondria has implications in studying metabolic diseases and potential treatments for energy metabolism disorders.
Real-World Applications of ATP
Understanding ATP isn’t just academic—it has real-world applications:
Medical Science: Therapies targeting mitochondrial dysfunction can help treat metabolic and degenerative diseases.
Sports Science: Knowledge about ATP informs training regimes and recovery strategies in athletes.
Biotechnology: ATP-based assays are used to measure cell viability and contamination in various industries.
These applications underscore why many educators and students search for what is the energy currency of the cell class 9 and why is atp called the energy currency of the cell class 9 when exploring cellular energy.
Fun Facts about ATP
Universal Energy Molecule: ATP is found in every living cell, making it a universal energy carrier.
Rapid Turnover: The average human body recycles its entire mass of ATP several times per day.
High Energy Efficiency: The energy released from breaking ATP’s high energy bonds is almost perfectly transferred to other cellular processes.


FAQs on ATP: The Cell’s Energy Currency Made Easy
1. What is meant by the 'energy currency' of the cell, and which molecule is it?
The 'energy currency' of the cell refers to a molecule that stores and transports chemical energy within cells for metabolic processes. The primary energy currency in all living organisms is Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
2. Why is ATP specifically called the 'energy currency' of the cell?
ATP is called the energy currency because, like money, it can be 'spent' to power cellular reactions. Energy from food (like glucose) is converted into ATP, which provides small, usable amounts of energy for immediate work, making it the cell's main spendable energy source.
3. How does an ATP molecule release the energy needed for cell activities?
ATP releases energy through a process called hydrolysis. When a cell needs energy, the bond holding the third phosphate group is broken with the help of water. This releases a significant amount of energy and converts ATP into ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate).
4. What is the main difference between ATP and ADP?
The main difference lies in the number of phosphate groups and their energy state. ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) has three phosphate groups and is a high-energy molecule. ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) has only two phosphate groups and is a lower-energy molecule, formed after ATP has released its energy.
5. Which part of the cell is mainly responsible for producing ATP?
The vast majority of ATP is produced in the mitochondria through a process called cellular respiration. This is why mitochondria are often called the 'powerhouses' of the cell.
6. How is the function of ATP similar to a rechargeable battery for the cell?
This is a great analogy. ATP is like a fully charged battery, ready to provide power. When it releases energy, it becomes ADP, which is like a used or dead battery. The cell then 'recharges' ADP back into ATP using energy from the breakdown of food.
7. What are some key functions in our body that are powered by ATP?
ATP powers nearly every activity in our cells. Some key examples include:
- Muscle contraction for movement.
- Nerve impulse transmission for thinking and reacting.
- Active transport, which moves substances across cell membranes against a concentration gradient.
- Synthesis of molecules like proteins and DNA.
8. If glucose is a source of energy, why does the cell need to make ATP instead of using glucose directly?
Using glucose directly would be like using a large power plant to charge a single phone—it's inefficient and releases too much energy at once. The cell breaks down glucose in a controlled way to create many small, manageable packets of energy in the form of ATP, which can be used precisely where and when needed without waste.
9. What happens to the ADP molecule after ATP has released its energy?
After ATP becomes ADP, it doesn't get discarded. It is quickly recycled back to the mitochondria. There, energy from cellular respiration is used to attach a new phosphate group to the ADP, converting it back into a high-energy ATP molecule, ready to be used again.
10. What makes the phosphate bonds in ATP 'high-energy'?
The three phosphate groups in ATP are all negatively charged, so they strongly repel each other. Forcing these negatively charged groups to bond together requires a lot of energy, which then gets stored in those chemical bonds. This stored potential energy, especially in the bond between the second and third phosphates, is what makes them 'high-energy' bonds.










