Why Understanding Life Cycles Matters in Biology
What would happen if people were born as fully developed adults? We are fortunate that we start out as newborns and gradually progress through stages to become adults. These stages of life are called a life cycle. The developmental stages that take place throughout the course of an organism's existence are referred to as its life cycle. When a living thing dies, its life cycle is over. In this article, we will discuss information on life cycle, the different stages of the life cycle, and observe the life cycle diagram of certain living organisms.
What is a Life Cycle?
Plants and animals in their life cycles often go through three fundamental stages: they begin as fertilised eggs or seeds, then mature into immature juveniles, and eventually they become adults. An organism will reproduce while it is in the adult stage, creating the following generation.
Depending on the species, a life cycle may include more than three fundamental phases. The human life cycle, for instance, consists of five primary stages. Depending on the species, the names of each stage can also change slightly. For instance, a nymph is a term used to describe a young dragonfly.
An organism may spend varying amounts of time at each stage. One species of cicada, for example, can remain an immature nymph for 17 years. The cicada only has a short lifespan after reaching adulthood—about 24 hours—before passing away. Some species live longer as adults. Elephants, for example, mature after 15 years and live over 30 years as adults.
Do you know that certain trees are thousands of years old? The length of time it takes an organism to complete its life cycle is known as its life span. Some species of bees, for instance, have limited life spans of four to five weeks.
Life Cycle of Organisms
In many simple organisms, such as bacteria and other protists, the life cycle is completed in a single generation: an organism begins by splitting into two new individuals, which completes the cycle. The life cycle starts with the fission of an existing individual. Higher animals also have a single generation in their life cycle, which includes the fusing of male and female sex cells (gametes), maturation into sexual maturity, and production of gametes, which kickstarts the cycle once more (assuming that fertilisation takes place).
Bacterial life cycles are referred to as haplontic. This term refers to the fact that it covers a single generation of haploid-cell organisms (i.e., containing one set of chromosomes). Higher animals have a diplontic one-generational life cycle, meaning that only creatures with diploid body cells are involved (i.e., contain two sets of chromosomes). Haploid sex cells are produced by organisms with diplontic cycles, and each of these gametes needs to join with another gamete in order to obtain the double set of chromosomes required to develop into an entire organism. Due to the presence of both a diploid generation (the sporophyte) and a haploid generation, the life cycle of plants is known as diplohaplontic (the gametophyte).
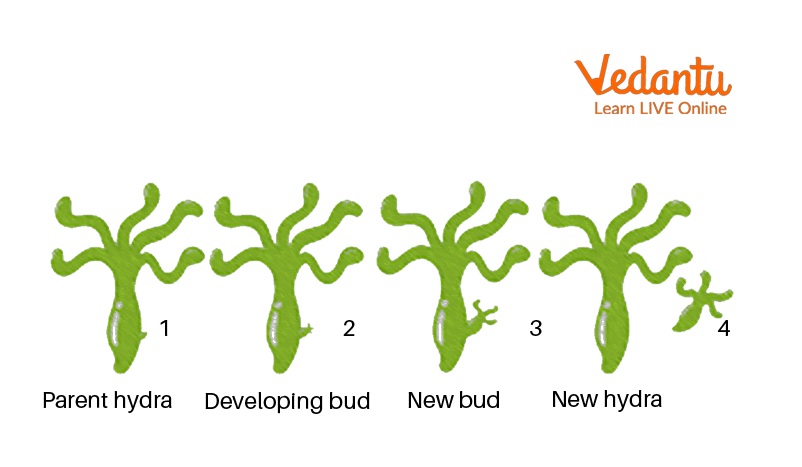
The Life Cycle of Hydra
Life Cycle of Plants
A sort of life cycle known as alternation of generations is one in which a number of plant generations distinguish between haploid and diploid organisms. Alternation of generations is a prevalent factor in plants, algae, and fungi. This is comparable to sexual reproduction in animals, where each generation contains both haploid and diploid cells. The haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte, as well as asexual and sexual reproduction, alternate in plants. The life cycle of plants is referred to as an alternation of generations for this reason. The capacity of plants for both sexual and asexual reproduction helps in their capacity for environmental adaptation.
A seed, a seedling, and a mature plant are the three key stages of a flowering plant's simple life cycle. A germinated seed grows into a young seedling. The seedling will eventually grow into an adult, capable of reproducing itself, at which point it will produce flowers and seeds. The following generation will emerge if these seeds are fertilised. Flowering plants might take anything from a year and decades to complete their life cycle.
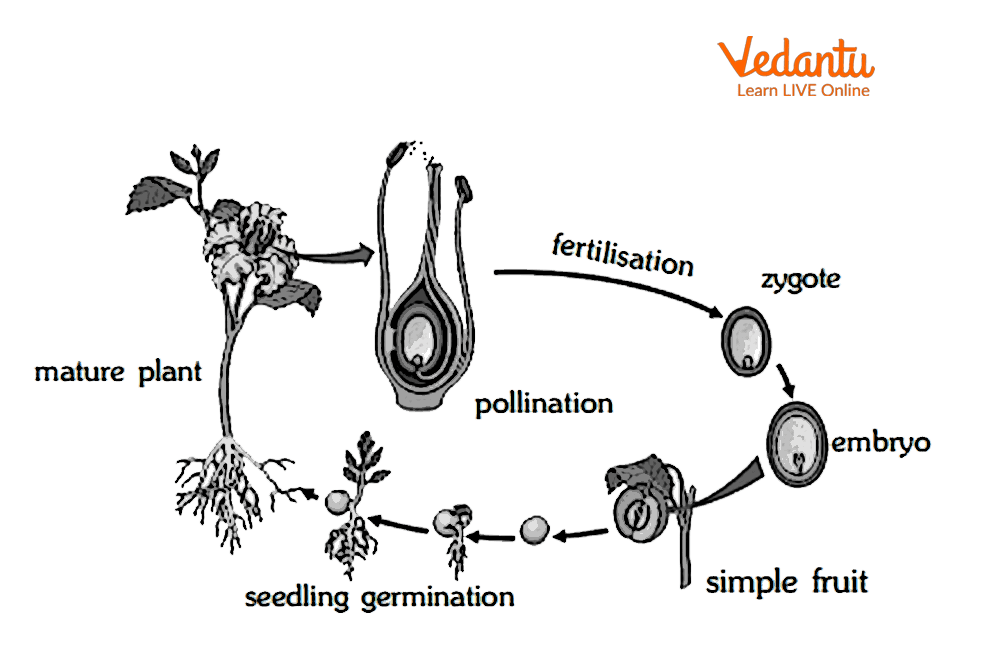
The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant
Life Cycle of Animals
The various phases of an animal's lifespan are included in its life cycle. Depending on the species of animal, life cycles might differ. For insects, it may only last a few weeks or less. All animal cycles start with a process of growth and development, which is followed by reproduction, despite the differences. The reproductive stage of the life cycle signifies its conclusion, as many animals frequently pass away after reproducing just once.
There are five main stages to the complex human life cycle. A fertilised egg is where the life cycle begins. An infant is then born after spending about forty weeks in the womb. From the time of birth until about age one, we call it infancy. A human enters the childhood stage of their life cycle after a year. Up to puberty, childhood exists. Humans enter adolescence at around the age of twelve when puberty begins. Although the duration of this stage may vary, humans normally attain adulthood when they are between the ages of eighteen and twenty. Humans frequently reproduce as adults, creating the following generation. A human's life cycle takes about seven billion years to complete in total.
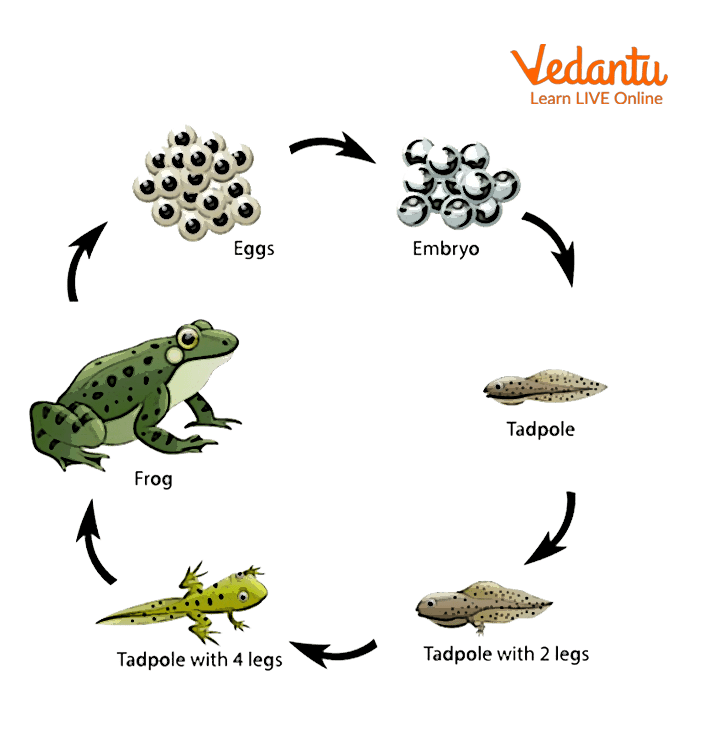
The Life Cycle Diagram of a Frog
Interesting Facts
Environmental factors including water, temperature, and light have an impact on how organisms evolve.
The stages of development for birds are egg, chick, and adult.
Amphibians develop from an egg into a larva and then an adult.
From the seed to the seedling to the flowering plant, plants progress.
Insects develop from the egg to the larva, pupa, and adult stages.
Conclusion
The developmental stages that take place throughout the course of an organism's existence are referred to as its life cycle. A fertilised egg or seed, a young juvenile, and an adult are the three primary phases of a plant's or animal's life cycle, respectively. The exact name of each stage might vary significantly depending on the species, and some organisms may have more than three stages in their life cycle. This article aims to help students understand the life cycle of several organisms. It has provided all the information in detail.
List of Related Articles


FAQs on Life Cycle Explained: Definition, Stages & Examples
1. What is a life cycle in biology?
In biology, a life cycle refers to the series of developmental stages an organism goes through from its beginning as a new individual to the point where it can reproduce and create its own offspring. This cycle includes stages such as birth or germination, growth, reproduction, and eventually, death, ensuring the continuation of the species.
2. What are the fundamental stages common to most animal life cycles?
While specifics vary, most animal life cycles include four fundamental stages:
- Birth: The beginning of life, which can be through live birth (viviparous, like humans) or by hatching from an egg (oviparous, like birds).
- Growth: A period of development where the young organism grows in size and matures. This may involve gradual growth or dramatic changes like metamorphosis.
- Reproduction: The stage where a mature organism produces offspring, passing on its genetic material.
- Death: The end of an individual organism's life.
3. Could you explain the life cycle of a butterfly as an example of metamorphosis?
The life cycle of a butterfly is a classic example of complete metamorphosis, involving four distinct stages:
- Egg: Laid on a leaf, this is the first stage.
- Larva: The egg hatches into a larva, known as a caterpillar. Its main function is to eat and grow.
- Pupa: The caterpillar forms a protective casing around itself, called a chrysalis. Inside, it undergoes a radical transformation.
- Adult: The transformed insect emerges from the pupa as a butterfly. Its primary functions are to mate and lay eggs, starting the cycle anew.
4. How does the life cycle of a flowering plant typically work?
The life cycle of a typical flowering plant (angiosperm) begins with a seed. Under the right conditions, the seed undergoes germination and grows into a seedling. The seedling develops into a mature plant with roots, a stem, and leaves. It then enters the reproductive phase by producing flowers. Through pollination and subsequent fertilisation, the flower produces new seeds, often encased within a fruit. These seeds are then dispersed to start the life cycle over again.
5. What is the key difference between direct development and metamorphosis in animals?
The key difference lies in how the young organism resembles the adult. In direct development, the newborn or hatched animal looks like a miniature version of the adult and simply grows larger over time. Examples include humans, reptiles, and birds. In contrast, metamorphosis involves a young form, or larva, that looks completely different from the adult and must undergo a major physical transformation (e.g., a tadpole changing into a frog).
6. Why is the reproductive stage so essential for the continuation of a species' life cycle?
The reproductive stage is essential because it is the only mechanism through which a species can create new individuals. Without reproduction, a species would become extinct once all existing members complete their life cycles and die. It ensures the transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next, allowing the species not only to survive but also to adapt to changing environments over time.
7. How does the life cycle of a human compare to that of other animals?
The human life cycle is an example of direct development, without any larval or pupal stages. Key stages include infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age. A major distinguishing feature compared to most other animals is the exceptionally long period of childhood and adolescence. This extended growth phase is crucial for the development of complex cognitive skills, learning, and social behaviours that are characteristic of humans.
8. What is meant by 'alternation of generations', especially in the context of plant life cycles?
Alternation of generations is a type of life cycle, most prominent in plants and algae, where an organism alternates between two distinct multicellular forms. These are:
- The gametophyte generation, which is haploid (has one set of chromosomes) and produces gametes (sperm and eggs).
- The sporophyte generation, which is diploid (has two sets of chromosomes) and produces spores.
The cycle involves a gametophyte producing gametes that fuse to form a diploid sporophyte, which in turn produces haploid spores that grow into a new gametophyte.










