Essential Lung Cancer Terminology and Exam Preparation Tips
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the lungs, it is called lung cancer. Lung cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph nodes or other organs in the body, such as the brain. Cancer from other organs also may spread to the lungs. When cancer cells spread from one organ to another, they are called metastases.
Lung cancers usually are grouped into two main types called small cell and non-small cell (including adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma). These types of lung cancer grow differently and are treated differently. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer. For more information, visit the National Cancer Institute’s Lung Cancer.
Lungs in Body
The lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs situated on one or the other side of the chest (midsection). The windpipe (windpipe) conducts breathed air into the lungs through its cylindrical branches, called bronchi. The bronchi likewise partition into increasingly fewer s (bronchioles), eventually getting bitsy.
The bronchioles in the long run end in bunches of bitsy air sacs called alveoli. Carbon dioxide, a byproduct of digestion, is an entry from the blood to the alveoli, where it very well may be breathed out. Between the alveoli is a dainty layer of cells called the interstitium, which contains veins and cells that assist with supporting the alveoli.
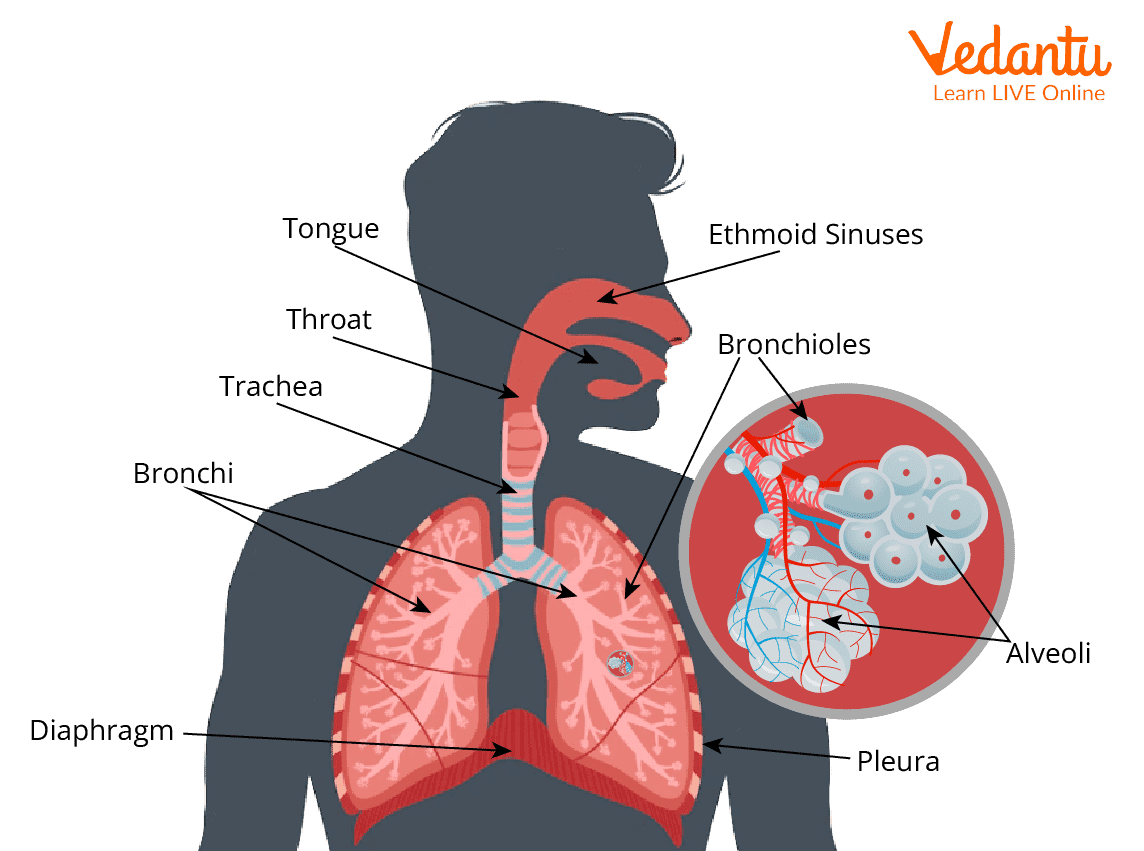
Labelling of Respiratory Parts in Human Body
Lung Cancer Symptoms
Lung cancer generally does not beget signs and symptoms in its foremost stages. Signs and symptoms of lung cancer generally do when the complaint is advanced.
A new cough that does not go down
Coughing up blood, indeed a small quantum
Breathing problem
Chest pain
Hoarseness
Losing weight without trying
Bone pain
Headache
Stage 1 Lung Cancer Symptoms - Some people with stage 1 lung cancer will witness symptoms, but they vary from person to person.
The common trusted source symptoms of lung cancer include the following:
Breathing problems cancer-related daily tasks.
Patient cough that has not vanished after 2 – 3 weeks.
Coughing up blood or blood-stained mucus.
Other symptoms of lung cancer include the following:
Appetite loss
Weight loss
General fatigue
Shoulder, chest, or back pain
Croaky voice
Continual lung problems, similar to bronchitis or pneumonia
Lung Cancer Causes
Smoking causes the majority of lung cancers — both in smokers and in people exposed to derivative smoke. But lung cancer also occurs in people who nowise smoked and in those who nowise had dragged exposure to secondary smoke. In these cases, there will be no sign of lung cancer.
How Smoking Causes Lung Cancer
Doctors believe smoking causes lung cancer by harming the cells that line the lungs. When you inhale cigarette smoke, which is full of cancer-causing cancer small (carcinogens), changes in the lung tissue begin nearly directly. At first, your body may be suitable to repair this damage. But with each repeated exposure, normal cells that line your lungs are sharply damaged. Over time, the damage causes cells to act abnormally and ultimately cancer may develop.
Types of Lung Cancer
Doctors divide lung cancer into two major types predicated on the appearance of lung cancer cells under the microscope. Your doctor makes treatment opinions predicated on which major type of lung cancer you have.
Types of lung cancer include the following:
Small cell lung cancer occurs nearly simply in heavy smokers and is less commotion-small cell lung cancer.
Non-small cell lung cancer - Non-small cell lung cancer is an umbrella term for several types of lung cancers. Non-small cell lung cancers include scaled cell cancer, adenocarcinoma, and large cell melanoma.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Cancer stages inform us how far cancer has spread and help guide treatment. The chance of successful or healing treatment is much more advanced when lung cancer is diagnosed and treated beforehand. Because lung cancer affects the symptoms in the earlier stages, opinion frequently comes after it has spread.
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Stages
Stage 1 - Cancer is found in the lung, but it has not spread outside the lung.
Stage 2 - Cancer is found in the lung and close lymph knots.
Stage 3 - Cancer is in the lung and lymph bumps in the middle of the chest.
Stage 3A - Cancer is found in lymph knots, but only on the same side of the chest where the cercancert started growing.
Stage 3B - Cancer has spread to lymph knots on the contrary side of the chest or to lymph bumps above the collarbone.
Stage 4 - Cancer has spread to both lungs, into the area around the lungs, or to distant organs.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Stages
There are two stages of SCLC, limited and expansive. In the limited stage, cancer is found in only one lung or near lymph bumps on the same side of the chest.
The expansive stage means cancer has spread
Throughout one lung
On the contrary lung
To lymph nodes on the contrary side
To fluid around the lung
To bone marrow
To distant organs
About 2 out of 3 people rushed to Source with SCLC are earlier in the expansive stage when their cancer is diagnosed.
Interesting Facts
Lung Cancer in the lungs is the main disease enemy of all kinds of people in America. Almost 400,000 individuals in the US are living with lung cancer in the lungs. 81% of those living with lung cancer in the lungs are over the age of 60. The infection troubles the older the most harshly.
Important Questions
1. Give some preventive measures for lung cancer.
Do Not Smoke - However, do not start, If you've nowise smoked. Talk to your children about not smoking so that they can understand how to avoid this major threat factor for lung cancer. Begin conversations about the risks of smoking with your children beforehand so that they know how to respond to peer pressure.
Stop Smoking-Stop Smoking Now - Quitting reduces your danger of lung cancer, indeed if you've smoked for eras. Talk to your doctor about remedies and stop-smoking aids that can help you quit. Options include nicotine relief products, medicines and support groups.
2. What are the complications that a person faces suffering from lung cancer?
Below are some complications for lung cancer:
Pain - Advanced lung cancer that spreads to the lining of a lung or another area of the body, similar to a bone, can affect pain. Tell your doctor if you suffer pain, as numerous treatments are available to control pain.
Fluid in the Chest (Pleural Effusion) - Lung cancer can affect fluid to accumulate in the space that surrounds the affected lung in the chest hollow (pleural space).
Fluid Accumulating in the Chest can Affect Shortness of Breath - Treatments are available to drain the fluid from your chest and reduce the threat that pleural effusion will do again.
Key Features
Lung Cancer in the lungs is the most conspicuous reason for cancer-related mortality around the world.
Around 60% of those determined to have lung cancer in the lung span of one year after determination and the five-year endurance for all patients with lung cancer in the lungs is just 16%, a rate that has been tumours fundamentally in the beyond 10 years.


FAQs on Lung Cancer Explained: Meaning, Symptoms & Key Terms
1. What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is a disease characterised by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the tissues of one or both lungs. These cells form tumours that can interfere with the lung's primary function of supplying oxygen to the body. If left untreated, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis.
2. What are the main types of lung cancer explained in Biology?
Lung cancer is primarily classified into two main types based on the appearance of the cancer cells under a microscope. These types grow and spread differently.
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): This is the most common type, accounting for about 80-85% of all lung cancers. It includes subtypes like adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): This type is less common but tends to grow and spread faster than NSCLC. It is almost exclusively found in heavy smokers.
3. What are the primary causes and risk factors for lung cancer?
The most significant cause of lung cancer is smoking tobacco, which is linked to the vast majority of cases. However, several other risk factors exist, including:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Exposure to radon gas, a naturally occurring radioactive gas.
- Occupational exposure to carcinogens like asbestos, arsenic, and diesel exhaust.
- A family history of lung cancer.
- Previous radiation therapy to the chest.
4. What are the common symptoms of lung cancer that one should be aware of?
The symptoms of lung cancer may not be apparent in the early stages. However, as the disease progresses, common signs include a persistent cough that worsens over time, coughing up blood (hemoptysis), chest pain that is often worse with deep breathing, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, and shortness of breath.
5. How is lung cancer diagnosed according to standard medical procedures?
Diagnosing lung cancer involves several steps. A doctor typically starts with a physical exam and a review of medical history. If lung cancer is suspected, imaging tests like a chest X-ray or a CT (Computed Tomography) scan are ordered to look for abnormal masses. For a definitive diagnosis, a biopsy is performed, where a small tissue sample is removed from the suspicious area and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
6. Can a person who has never smoked get lung cancer?
Yes, it is possible for non-smokers to develop lung cancer. While smoking is the leading cause, approximately 10-20% of lung cancer cases occur in people who have never smoked. The primary cause in non-smokers is exposure to radon gas. Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollution, workplace carcinogens, and certain genetic mutations that can make cells more susceptible to becoming cancerous.
7. How do doctors differentiate lung cancer from pneumonia, given their similar symptoms?
The initial symptoms of lung cancer and pneumonia can overlap, including coughing and chest pain. However, doctors differentiate them through further investigation. Pneumonia is an infection and usually responds to antibiotics, with symptoms improving within a short period. If symptoms persist despite treatment, or if an imaging test like a CT scan shows a solid mass (tumour) rather than just inflammation or fluid typical of an infection, doctors will suspect lung cancer and proceed with a biopsy for confirmation.
8. How exactly does smoking cause lung cancer at a cellular level?
Tobacco smoke contains over 70 known carcinogens (cancer-causing chemicals). When inhaled, these chemicals damage the DNA of the cells lining the lungs. Our bodies have mechanisms to repair this DNA damage, but the constant exposure from smoking overwhelms these repair systems. Over time, the accumulated damage can lead to mutations in critical genes that control cell growth, such as tumour suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes. This leads to uncontrolled cell division, which is the hallmark of cancer.
9. Why can lung cancer sometimes return even after successful treatment?
The return of lung cancer, known as recurrence, can happen for a few key reasons. Sometimes, a small number of cancer cells, too tiny to be detected by scans, can survive the initial treatment (like chemotherapy or radiation). These microscopic residual cells can eventually grow into new tumours. Recurrence can be:
- Local: The cancer returns in the same spot in the lung.
- Regional: It appears in nearby lymph nodes.
- Distant: It metastasises to other parts of the body, like the brain, bones, or liver.
10. What is the fundamental difference between using chemotherapy and radiation therapy to treat lung cancer?
Both chemotherapy and radiation therapy are common treatments, but they work in fundamentally different ways. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment, meaning the drugs travel throughout the entire body via the bloodstream to kill cancer cells wherever they are. This makes it effective against cancer that has spread. In contrast, radiation therapy is a local treatment. It uses high-energy rays, like X-rays, to target and destroy cancer cells in a very specific, defined area, minimising damage to surrounding healthy tissue.










