How Inhalation and Exhalation Occur in the Human Body
Breathing is one of the most fundamental activities our bodies perform every second. It operates automatically to ensure a continuous supply of oxygen while expelling carbon dioxide. Although it might seem simple, the mechanism of breathing is a highly coordinated process that involves our respiratory organs, skeletal muscles, and the nervous system. This article will not only discuss the mechanism of breathing. but will also explain the mechanism of breathing in humans step by step, highlighting every crucial detail that helps us maintain life.
What is Breathing?
Breathing, often referred to as external respiration, is the physical exchange of gases—oxygen and carbon dioxide—between an organism and its environment. When we inhale, oxygen from the atmosphere is taken into the lungs. When we exhale, we release carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, back into the environment.
Breathing involves the inhalation and exhalation process, which is primarily controlled by the diaphragm (a dome-shaped muscular sheet at the base of the thoracic cavity) and the intercostal muscles (muscles situated between the ribs). Together, these muscles alter the volume and pressure inside the thorax, enabling air to move in and out of our lungs.
Also Read: Difference Between Breathing and Respiration
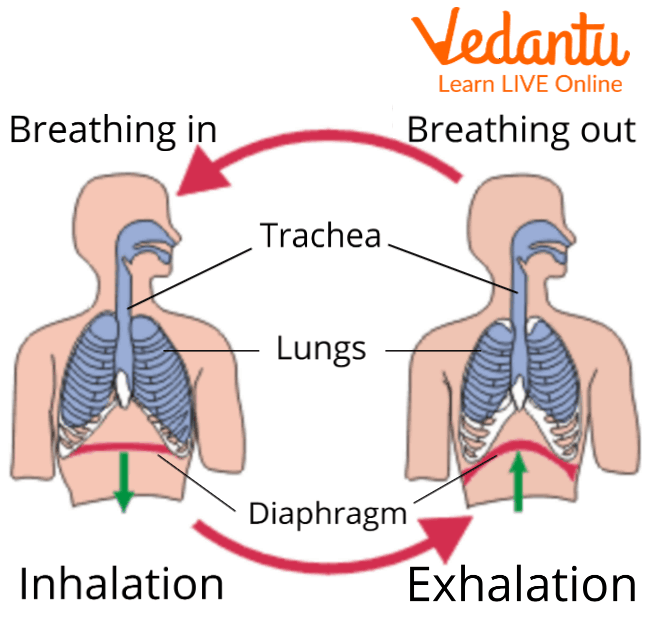
Steps of the Breathing Mechanism
What are the steps of the breathing mechanism? Let us break down the two main phases involved:
1. Inhalation (Inspiration)
Muscular Contraction: During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, moving downwards. Simultaneously, the external intercostal muscles contract, pulling the rib cage up and out.
Volume and Pressure Changes: As the chest cavity expands, the volume inside the thorax increases. This drop in pressure within the lungs relative to the external air pressure causes air to rush in.
Air Entry: Oxygen-rich air then enters through the nose or mouth, passes the pharynx, trachea, and bronchi, eventually reaching the alveoli—tiny air sacs where gas exchange begins.
2. Exhalation (Expiration)
Muscular Relaxation: In exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and moves upwards into a dome shape. The external intercostal muscles also relax while the internal intercostal muscles may contract slightly to aid forceful expiration.
Volume and Pressure Changes: With the decrease in thoracic volume, the pressure inside the lungs becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure.
Air Exit: Carbon dioxide-rich air is pushed out of the lungs, through the airways and finally released into the atmosphere.
These two steps—inhalation and exhalation process—constitute the mechanism of breathing. To understand this even better, let us explore a simplified mechanism of breathing flow chart below.
Mechanism of Breathing Flow Chart
Start
|
Diaphragm + External Intercostal
Muscles Contract (Inspiration)
|
Thoracic Cavity Volume Increases
|
Pressure in Lungs Decreases
|
Air Rushes In
|
Gas Exchange
|
Diaphragm + Intercostal Muscles Relax
(Expiration Begins)
|
Thoracic Cavity Volume Decreases
|
Pressure in Lungs Increases
|
Air is Expelled
|
End
This mechanism of breathing flow chart visually represents how changes in pressure and volume result in the inward and outward movement of air.
Mechanism of Respiration
Although breathing is vital, it is only one component of respiration. The mechanism of respiration covers both breathing (external respiration) and the actual use of oxygen in the cells (internal or cellular respiration). Here, we will focus on the external and internal transport of gases that underpin our survival.
Oxygen Transport
Oxygen from the alveoli diffuses into the blood, binding primarily to haemoglobin (forming oxyhaemoglobin).
This oxygenated blood travels through the pulmonary veins to the heart, which then pumps it to tissues all over the body.
Internal Respiration
Inside the tissues, oxyhaemoglobin releases oxygen for cellular metabolic activities.
Cells use oxygen to break down glucose and generate energy (ATP). As a by-product, carbon dioxide is produced.
Carbon Dioxide Transport
Carbon dioxide is transported from the tissues back to the lungs in three ways:
Dissolved in blood plasma as carbonic acid.
Converted to bicarbonate ions.
Bound to haemoglobin to form carbaminohaemoglobin.
Eventually, carbon dioxide is released into the alveoli and exhaled.
When you explain the mechanism of breathing in humans, it is essential to include these gas transport steps, because breathing alone does not complete the whole picture of how cells receive oxygen and expel carbon dioxide.
Intrapleural Pressure and Lung Movement
Sometimes referred to as intrapleural breathing, this aspect deals with the pressure in the pleural cavity (the space between the lungs and the chest wall). This pressure is typically negative compared to atmospheric pressure, ensuring the lungs stay inflated.
Transpulmonary Pressure: The difference between intra-alveolar (inside the lungs) and intrapleural pressures. This gradient keeps the lungs expanded.
During Inhalation: The intrapleural pressure becomes more negative, increasing the transpulmonary pressure and allowing the lungs to expand.
During Exhalation: The pressure in the pleural cavity becomes less negative, causing the lungs to recoil and push air out.
Respiratory Gas Transport
After breathing brings oxygen into the lungs, the next phase is distributing these gases throughout the body. Oxygen and carbon dioxide travel via the bloodstream, aided by:
Haemoglobin in red blood cells, which binds oxygen.
Bicarbonate formation in plasma for carbon dioxide transport.
Protein Bonding (e.g., carbaminohaemoglobin) for additional CO₂ transport.
This distribution, combined with the mechanism of breathing diagram (which illustrates changes in lung volume and pressure), ensures every cell gains access to oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide efficiently.
Key Takeaways
Breathing is the physical process of air intake (inhalation) and air release (exhalation).
The mechanism of breathing relies on pressure differences created by the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
The mechanism of respiration expands on breathing by explaining how gases are exchanged at the alveoli and transported to and from body tissues.
Negative intrapleural pressure helps keep the lungs inflated, making inhalation easier.
Proper gas exchange ensures cells receive adequate oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide effectively.
Mnemonics for Easy Recall
A handy mnemonic to remember the phases of the inhalation and exhalation process is “DI-EG (Diaphragm – Intercostal, Expand – Gas in)” and “DI-CR (Diaphragm – Intercostal, Contract – Release gas)”:
DI-EG:
D – Diaphragm contracts
I – Intercostal muscles contract
E – Expansion of thoracic cavity
G – Gas (air) flows in
DI-CR:
D – Diaphragm relaxes
I – Intercostal muscles relax
C – Contraction of the thoracic cavity
R – Release of gas (air)
Quiz Time!
Which muscles are primarily involved in expanding the rib cage during inhalation?
A. Internal intercostal muscles
B. External intercostal muscles
C. Abdominal muscles
D. None of the above
What are the steps of the breathing mechanism?
(a) Inspiration followed by expiration
(b) Expiration followed by inspiration
(c) Only inspiration
(d) Only expiration
Which of these is NOT a way by which carbon dioxide is transported in the blood?
A. Bicarbonate ions
B. Carbaminohaemoglobin
C. Carbonic anhydrase
D. Dissolved in plasma
Answers to Quiz
B, 2. (a), 3. C


FAQs on Mechanism of Breathing: Step-by-Step Guide for Students
1. What are the two main phases in the mechanism of breathing?
The mechanism of breathing consists of two primary phases: inhalation (inspiration) and exhalation (expiration). Inhalation is an active process where air is drawn into the lungs, while exhalation is the largely passive process where air is expelled from the lungs.
2. What role do the diaphragm and intercostal muscles play during inhalation?
During inhalation, two key muscle groups contract:
- The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle at the base of the chest, contracts and flattens.
- The external intercostal muscles, located between the ribs, contract to pull the rib cage upwards and outwards.
3. How does the pressure inside our lungs change to allow for breathing?
Breathing operates on the principle of pressure gradients. During inhalation, the chest cavity expands, increasing lung volume and decreasing the air pressure inside the lungs to below atmospheric pressure, causing air to rush in. During exhalation, the chest cavity reduces in size, decreasing lung volume and increasing the pressure inside the lungs to above atmospheric pressure, which forces air out.
4. What is the main difference between breathing and respiration?
Although often used interchangeably, breathing and respiration are different. Breathing (or external respiration) is the physical act of moving air into and out of the lungs. Respiration is a much broader biochemical process that includes breathing, as well as the exchange of gases in the lungs (alveoli) and the use of oxygen by cells to produce energy (cellular respiration).
5. Why is a build-up of carbon dioxide a more powerful trigger for breathing than a lack of oxygen?
The body's respiratory centre is more sensitive to changes in blood carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels and pH than to oxygen levels. An increase in CO₂ forms carbonic acid in the blood, lowering its pH. Chemoreceptors detect this change instantly and signal the brain to increase the rate and depth of breathing to expel the excess CO₂. The trigger from low oxygen is a secondary, less sensitive mechanism.
6. How does the negative pressure in the pleural cavity assist in breathing?
The space between the lungs and the chest wall, known as the pleural cavity, maintains a pressure that is negative compared to the atmosphere. This intrapleural pressure acts like a suction, keeping the lungs adhered to the chest wall. When the chest expands during inhalation, this negative pressure ensures the lungs are pulled open along with it, allowing for efficient inflation.
7. After inhalation, how is oxygen transported to the body's tissues?
Once oxygen enters the lungs, it diffuses from the alveoli into the bloodstream. About 97% of this oxygen binds to haemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, forming oxyhaemoglobin. The circulatory system then transports this oxygenated blood from the heart to all the body's tissues, where the oxygen is released for cellular activities.
8. How do respiratory conditions like asthma affect the normal mechanism of breathing?
In conditions like asthma, the airways become inflamed and constricted, increasing resistance to airflow. While the fundamental mechanics of pressure changes from the diaphragm and intercostal muscles still operate, the narrowed passages make it much harder to move air. This leads to symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath, as more muscular effort is required to overcome the resistance.










