How Do Nerve Cells Work? An Easy Guide for Students
In biology, the classical doctrine of the nervous system determines that it is a fairly complex part of an animal that coordinates its moves and sensory data via transmitting indicators to and from one-of-a-kind elements of its frame. The nervous system detects environmental modifications that impact the frame and then works in tandem with the endocrine system to reply to such occasions.
Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms approximately 550 to six hundred million years in the past. However, this classical doctrine has been challenged for a long time by using discoveries about the life and use of electrical alerts in plants. On the basis of these findings, a few scientists have proposed that a plant apprehensive system exists and that a systematic area referred to as plant neurobiology should be created.
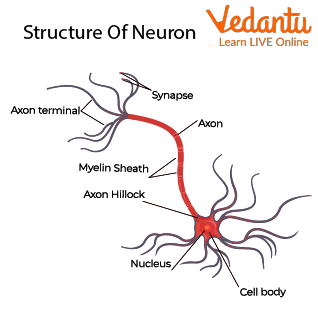
Structure Of Nueron
Structure of Nerve Cell
The shape, size, and structure of nerve cells depend on their position and function in the body. Usually, the size of nerve cells varies depending on how long the electrical impulses are to be transmitted.
The nerve cell is a specialized individual cell that forms our nervous system. All the human body neurons have three parts, a cell body, an axon, and dendrites. The nerve cell parts consist of the following:
(Image will be Uploaded soon)
Cell Body:
The cell body in a nerve cell is its core. It is also called soma. The cell body consists of the nerve cell’s nucleus along with other specialized cell organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other components. The cell body is an essential part of a neuron and carries genetic information. It also helps maintain the cell’s overall structure and provides energy to carry out the cell’s activities.
Axon:
An axon is a part of the nerve cell, which is a long tube-like structure that joins the cell body at a specific position. The axon is primarily involved in carrying the electrical signals from the cell body to the neuron ending and transmitting it to other surrounding neurons.
Dendrites:
They are the root-like projections on a cell body that facilitate the transmission and receiving of messages to and back from other neurons. Dendrites process and send the electrical impulses received from the axon endings to the cell body.
Myelin Sheath:
It is the outermost layer of a nerve cell. Its primary function is to cover and protect the nerve fibers in the neurons.
Synapse:
It is known as the ending part of the nerve or nerve junction. Its primary function is to permit the entry of electrical impulses from one neuron to another.
Types of Nerve Cell or Neurons
Now that we have studied the nerve cell parts and length of nerve cells, let’s look at the different types of neurons. Depending on their functions, neurons can be broadly classified into three types:
Sensory Neurons:
Sensory neurons are generally found in the sense organs of the human body, such as the eyes, nose, skin, tongue, and ears. These nerve cells are triggered by the chemical and physical inputs of our environment, such as sound, heat, and light. The sensory neurons facilitate the movement of sensory impulses from the sensory organs to the central nervous system. There are approximately 10 million sensory neurons in the human body.
Motor Neurons:
Motor neurons are the ones that facilitate the transmission of motor impulses from the central nervous system to the different parts of the body. These types of neurons play a major role in the voluntary and involuntary movements of the body. The motor neurons are primarily found in various glands and muscles of the human body.
Interneurons:
Interneurons are those neurons that act as a mediator between sensory neurons, motor neurons, and the central nervous system. They help in the smooth transmission of signals. They help in conducting smooth communication between the neurons and the central nervous system. The interneurons are present in all parts of the body and are exclusively found in the central nervous system.
Functions of Nerve Cells
The primary function of every nerve cell present in the human body is to transmit messages. But the nerve cells are also involved in the following activities:
It helps the body to respond to the surrounding stimuli.
It helps the body in the smooth conduct of metabolic activities.
It helps in both the voluntary and involuntary movement of the body parts.
It helps establish communication between the central nervous system and the body parts by enabling the smooth transmission of messages.
What is the Nervous System?
The human nervous system is a complex network of neurons that are arranged in the central and peripheral nervous systems. It is made up of two parts:
The central Nervous System comprises neurons and neural pathways, along with spinal cord, and brain. It plays a role in controlling involuntary muscle movements and body functions such as breathing, heart rate, digestion, thermoregulation, sweating and urination. It also has control over voluntary muscle movements.
The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves like cranial and spinal, either singly or in groups, which relay sensory information from the periphery of the body to the central nervous system.
If you have ever wondered, How many nerves are in the Human Body, You should know that the total number of nerves in the human body is much greater than the number of nerves in most animals.
Human Nerves
The nerves and cells referred to as neurons, send messages during your frame. All nerves are vital for correct everyday functioning.
The Smallest and the Biggest nerve in human body
The length of nerves in Human Body varies. The shortest nerve is a tiny, one-millimetre-long channel in the base of your thumb called the median nerve. The longest nerve is the sciatic nerve, which travels from the lower back down through the thigh and foot. Regardless, nerves play an important role in your body’s ability to control movement and maintain equilibrium. Nerve cells allow communication between areas of your brain; they also help regulate temperature and respiration by warming blood as it passes through them, and they release neurotransmitters that send other signals around our bodies like hormones or adrenaline.
Summary
From the nervous system for kids, we know that the human body is home to a complex network of nervous systems that helps to regulate bodily processes. The human nervous system is made up of two components, central nerves and peripheral nerves, which perform different functions. A neuron transmits electrical impulses to every other neuron. It is made of a cell physique, cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm. There are three unique sorts of cells in the human body: nerve cells or neurons, epithelial cells and muscle cells. so, this brings us to the end of our article where we learnt everything about nerve cells including their types, and functions as well as various interesting facts about them. In case of further doubts feel free to ask in the comments.


FAQs on Nerve Cell: Definition, Structure & Key Functions
1. What is a nerve cell?
A nerve cell, more formally known as a neuron, is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It is a specialised cell responsible for receiving sensory input, processing information, and transmitting electrical and chemical signals to other nerve cells, muscles, or glands, thereby coordinating an organism's actions.
2. What are the three main parts of a nerve cell and their functions?
The three main parts of a typical nerve cell are the cell body (soma), dendrites, and axon. Their functions are:
- Cell Body (Soma): This is the core of the neuron, containing the nucleus and other organelles. It maintains the cell's structure and provides the energy needed to drive its activities.
- Dendrites: These are short, branch-like extensions that receive electrochemical signals from the axons of other neurons.
- Axon: This is a long, slender projection that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body and transmits them to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
3. What are the primary types of nerve cells based on their function?
Based on their function, nerve cells are broadly classified into three main types:
- Sensory Neurons: These neurons are responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment into internal electrical impulses. They carry signals from sense organs (like skin, eyes, and ears) to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Motor Neurons: These neurons carry signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands (effectors), controlling muscle movements and glandular secretions.
- Interneurons: Found exclusively within the CNS, interneurons act as connectors, forming circuits between sensory and motor neurons. They are involved in processing information and reflex actions.
4. How is a nerve impulse transmitted from one neuron to another?
A nerve impulse is transmitted between two neurons at a specialised junction called a synapse. The axon terminal of the first neuron (presynaptic) releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap. These neurotransmitters then travel across the gap and bind to receptors on the dendrites of the next neuron (postsynaptic), generating a new electrical signal in that cell.
5. What is the importance of the myelin sheath in a neuron?
The myelin sheath is a fatty, insulating layer that wraps around the axon of many nerve cells. Its primary importance is to increase the speed at which nerve impulses are transmitted. It does this by preventing the leakage of the electrical signal and allowing the impulse to jump between gaps in the sheath (called Nodes of Ranvier), a process known as saltatory conduction. This allows for much faster communication within the nervous system.
6. How are nerve cells specially adapted for their function of transmitting signals?
Nerve cells have several key adaptations for efficient signal transmission:
- They have a long axon to transmit signals over long distances within the body.
- The presence of a myelin sheath acts as an electrical insulator, speeding up signal conduction.
- They have numerous dendrites to create a large surface area for receiving signals from multiple other neurons.
- The axon terminals contain many mitochondria to provide the energy required for the synthesis and release of neurotransmitters.
7. What would happen if the myelin sheath on an axon was damaged or absent?
If the myelin sheath on an axon were damaged or absent, the transmission of nerve impulses would be significantly slowed down or even blocked. The electrical signal would dissipate and lose strength as it travelled along the axon, similar to an uninsulated electrical wire. This can lead to serious neurological conditions, such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS), where the body's immune system attacks the myelin sheath, causing symptoms like muscle weakness, poor coordination, and sensory problems.
8. How do sensory and motor neurons work together to cause a reflex action?
In a reflex action, like pulling your hand away from a hot object, sensory and motor neurons work in a circuit called a reflex arc. First, a sensory neuron detects the painful stimulus (heat) and sends a rapid signal to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, an interneuron immediately passes this signal to a motor neuron. The motor neuron then carries the impulse directly to the muscles in your arm, causing them to contract and pull your hand away. This happens without involving the brain for conscious thought, making the response extremely fast.
9. Why do nerve impulses travel in only one direction across a synapse?
Nerve impulses travel in a single direction because of the specific structure of the synapse. Neurotransmitters are only released from the axon terminal of the presynaptic (first) neuron and the receptors for these neurotransmitters are only located on the dendrites or cell body of the postsynaptic (second) neuron. This one-way arrangement of chemical release and reception ensures that information flows forward from one neuron to the next and not backward.
10. What is the main difference between a neuron and a neuroglial cell?
The main difference lies in their primary function. A neuron is the principal cell responsible for transmitting electrical signals and processing information in the nervous system. In contrast, a neuroglial cell (or glia) is a supporting cell. It does not transmit nerve impulses but provides physical and metabolic support, insulation (myelin), and protection to the neurons, ensuring they can function correctly.










