How Do Neurons and Glial Cells Keep the Nervous System Working?
Nervous tissue is an essential part of our bodies, helping us respond to the world around us. It plays a key role in sending and receiving messages throughout the body, keeping us safe and active.
In animals, there are four main types of tissues:
Connective tissue
Epithelial tissue
Muscular tissue
Nervous tissue
Here, we will focus on nervous tissue in detail, which is especially important for nervous tissue class 9 studies. Let us learn about its structure, location, characteristics, nervous tissue function, and nervous tissue types.
Explanation of Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue makes up the major parts of the Central Nervous System (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which comprises branching nerves that connect various organs and tissues to the CNS.
It primarily consists of neurons (nerve cells) and glial cells.
Neurons transmit signals (electrochemical impulses) throughout the body.
Glial cells support and nourish neurons, remove debris, and provide insulation.
This tissue is specialised for quick signal transmission. When a neuron is stimulated, it sends out an electrical impulse that travels rapidly, ensuring swift communication within the body.
Structure of Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is composed of distinct cells known as neurons and several types of glial cells. A typical neuron has three main parts:
Cell Body (Soma)
Responsible for the basic metabolic processes of the cell.
Dendrites
Short, branching extensions that receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors.
Carry incoming information toward the cell body.
Axon
A long, slender projection that carries impulses away from the cell body.
Ends in axon terminals, which form specialised junctions (synapses) with target cells (other neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells).
Information Flow in a Neuron
Signals travel in a single direction:
Dendrites → Cell Body → Axon → Synapse → Target Cell
Glial cells (e.g., astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia) perform various supporting functions such as:
Providing nutrients to neurons
Maintaining the chemical environment
Forming insulating layers (myelin sheath) around axons
Cleaning up debris
Location of Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is found in:
The brain and spinal cord, which form the CNS.
The nerves that branch out into every region of the body, forming the PNS.
These nerves extend to the muscles, glands, and sensory organs, allowing us to sense and respond to the environment.
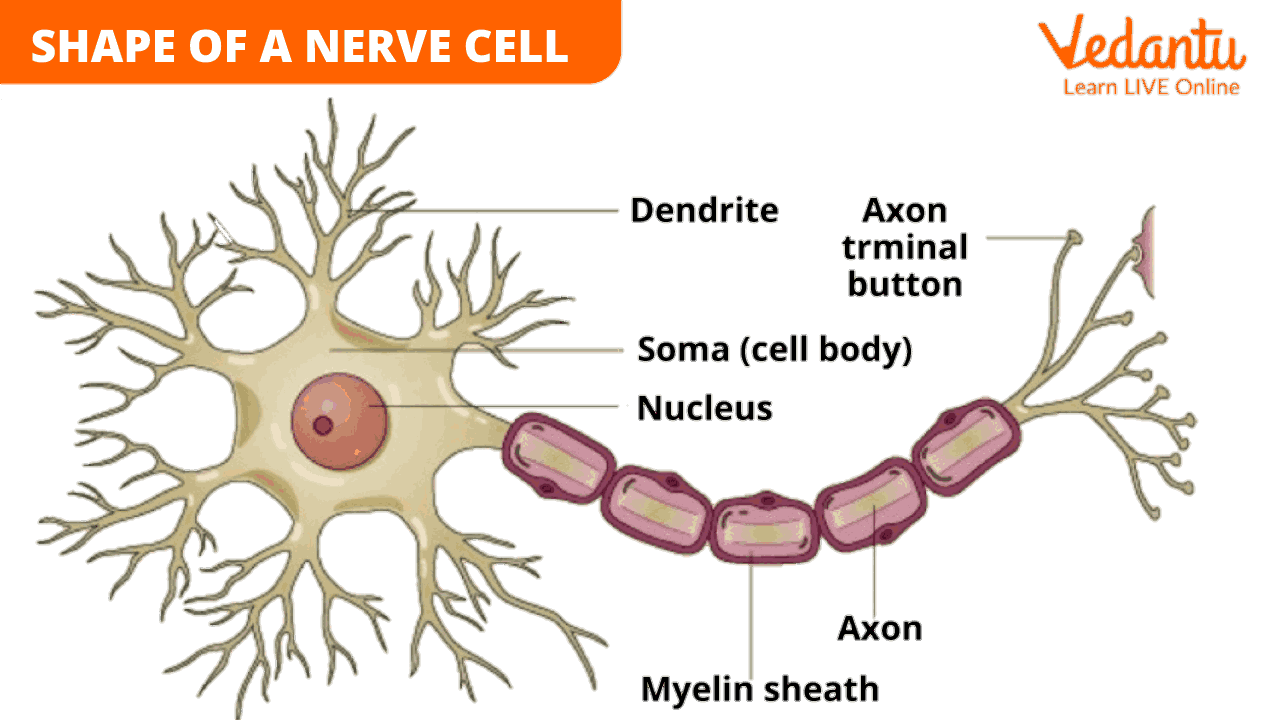
Nervous Tissue Diagram
A simplified representation of a neuron typically includes:
A central cell body with a nucleus
Several branching dendrites
A single elongated axon that may be covered with a myelin sheath
Axon terminals at the end for communication
Characteristics of Nervous Tissue
Composed of two main cell types: neurons and glial cells
Responsible for receiving and transmitting signals (electrochemical impulses)
Neurons can live for a very long time but generally cannot divide or replace themselves once fully mature
Includes special junctions called synapses where chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) carry signals
Highly specialised, ensuring rapid communication and response to internal and external stimuli
Nervous Tissue Function
What is the nervous tissue function? It is crucial for:
Signal Transmission
Neurons generate, conduct, and transfer nerve impulses using chemical neurotransmitters.
Coordination and Control
The brain and spinal cord integrate information, making decisions and directing responses.
Response to Stimuli
Sensory inputs trigger signals that travel to the CNS, which then organises appropriate motor outputs.
Memory and Cognition
Neurons in certain regions can store information (although their regeneration is very limited).
Support and Protection
Glial cells provide nutrition, protection, and structural support to neurons.
Nervous Tissue Types
There are generally two major nervous tissue types:
Neurons (Nerve Cells)
Specialised in generating and transmitting impulses.
Neuroglia (Glial Cells)
Support neurons by providing insulation, nutrients, and protection.
When you study nervous tissue class 9 textbooks may further classify neurons based on their structure or function:
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons – Carry impulses from sense organs to the CNS.
Motor (Efferent) Neurons – Carry impulses from the CNS to muscles or glands.
Interneurons – Connect sensory and motor neurons within the CNS.
Although we often refer to these as “types,” some sources may highlight 4 types of nervous tissue by grouping neurons and glial cells in different ways. For simplicity, remember that neurons and glial cells are the foundational cellular components of all nervous tissue.
Different Types of Nerves
Nerves are bundles of axons enclosed within protective layers. Based on their functions, nerves can be broadly classified into:
Motor Nerves
Carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands.
Enable actions like walking, talking, and moving away from danger.
Damage can lead to weakness or loss of muscle function.
Sensory Nerves
Conduct impulses from sensory receptors (skin, muscles, internal organs) to the CNS.
Help detect pain, temperature, pressure, and more.
Damage may cause numbness, tingling, or hypersensitivity.
Autonomic Nerves
Regulate involuntary actions such as heart rate, digestion, and glandular secretions.
Subdivided into:
Sympathetic Nervous System – Prepares the body for fight-or-flight responses (e.g., increases heart rate).
Parasympathetic Nervous System – Conserves energy and aids digestion, excretion, etc.
Cranial Nerves
Twelve pairs emerging directly from the brain.
Involved in functions like smell, vision, facial movements, tongue movements, and salivation.
Listed from front to back: Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, Spinal Accessory, and Hypoglossal.
Additional Concepts to Improve Learning
Mnemonic for Cranial Nerves
Here is a simple mnemonic to remember the 12 cranial nerves:
On Old Olympus Towering Top A Friendly Viking Grew Vines And Hops
O: Olfactory
O: Optic
O: Oculomotor
T: Trochlear
T: Trigeminal
A: Abducens
F: Facial
V: Vestibulocochlear
G: Glossopharyngeal
V: Vagus
A: Spinal Accessory (often just Accessory)
H: Hypoglossal
Quick Quiz (with Answers)
1. Question: Which cells in nervous tissue support neurons by providing nourishment and insulation?
A: Glial cells
2. Question: Which part of a neuron receives signals from other neurons?
A: Dendrites
3. Question: Name the long projection of a neuron that transmits impulses away from the cell body.
A: Axon
4. Question: How many pairs of cranial nerves are there in humans?
A: Twelve
5. Question: Which type of nerves control involuntary functions like digestion?
A: Autonomic nerves
Feel free to test yourself and reinforce your understanding of nervous tissue.
Related Topics


FAQs on Nervous Tissue: Structure, Types, and Functions
1. What is nervous tissue and where is it located in the human body?
Nervous tissue is a highly specialised tissue responsible for receiving stimuli and transmitting signals throughout the body. It forms the communication network of the nervous system. It is primarily located in the brain and spinal cord, which form the Central Nervous System (CNS), and in the nerves that branch out to all parts of the body, forming the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
2. What are the two main types of cells that make up nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue is composed of two principal types of cells:
- Neurons (Nerve Cells): These are the primary functional units that generate and transmit electrical signals called nerve impulses.
- Glial Cells (Neuroglia): These are non-neuronal cells that provide structural support, nourishment, and insulation for the neurons, and maintain overall nervous system health.
3. What are the three main parts of a neuron and their functions, as per the Class 9 syllabus?
A typical neuron, as studied in Class 9, consists of three main parts:
- Cell Body (Soma): Contains the nucleus and cytoplasm, and controls the cell's metabolic activities.
- Dendrites: These are short, branching extensions that receive electrochemical signals from other neurons and carry them toward the cell body.
- Axon: This is a single, long projection that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
4. What are the three basic functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system performs three fundamental, overlapping functions:
- Sensory Input: Gathers information from sensory receptors that monitor changes inside and outside the body.
- Integration: Processes and interprets the sensory input and decides what action should be taken.
- Motor Output: Sends signals to effector organs (muscles or glands) to cause a response.
5. How does a nerve impulse travel in a single direction along a neuron?
A nerve impulse travels unidirectionally through a neuron due to its specialised structure. The signal is first received by the dendrites, which then passes it to the cell body for processing. From there, the impulse is transmitted down the entire length of the axon to its endpoint, the axon terminals. This specific pathway, from dendrite to axon, ensures that information flows in one consistent direction.
6. What is a synapse and why is it so important for communication between nerve cells?
A synapse is a microscopic gap or junction between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. It is critically important because it allows signals to be passed from one cell to the next. When a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters across the synapse. These chemicals are then detected by the next neuron, allowing the impulse to continue its journey, enabling complex communication and control throughout the body.
7. How does nervous tissue fundamentally differ from muscular tissue in its function?
The primary difference lies in their core function. Nervous tissue is specialised for communication; it transmits rapid electrochemical signals over long distances to coordinate and control body functions. In contrast, muscular tissue is specialised for contraction; its cells are designed to shorten in length, which generates force and produces movement. While nervous tissue directs actions, muscular tissue executes them.
8. If neurons are so important, why can't most of them regenerate after being severely damaged?
Most neurons in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) lose their ability to divide and regenerate because they are highly specialised cells. Once mature, they lack structures like centrioles, which are essential for cell division (mitosis). Their complex connections and functions make replication difficult. While glial cells can provide some minor repair, the neuron itself cannot be easily replaced, which is why injuries to the brain and spinal cord are often permanent.










