What Is PCR and Why Is It Essential in Modern Biology?
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. This PCR full form represents a revolutionary PCR technique developed in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis. PCR is a method in molecular biology that enables scientists to create millions of copies of a specific DNA segment quickly and efficiently. By understanding the PCR definition and principles of PCR, students can appreciate how this process is used to amplify tiny amounts of DNA.
Also Read: Genes
The PCR Principle
The PCR principle is based on the natural process of DNA replication. It utilises enzymes to replicate DNA segments in a controlled manner. In this PCR technique, a short segment of DNA is amplified through cycles of temperature changes. These cycles include:
Denaturation: Heating the DNA to separate its two strands.
Annealing: Cooling the DNA so that primers bind to their complementary sequences.
Elongation: Raising the temperature again so that the DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strands.
This cycle is repeated multiple times (typically 20–40 cycles) to achieve the exponential amplification of the DNA segment. A well-designed PCR diagram can visually illustrate these three steps, helping to reinforce the PCR principle in a clear, step-by-step manner.
PCR Components
Understanding the PCR components is crucial. The main PCR components include:
DNA Template: The original DNA sample containing the target sequence.
DNA Polymerase: Often Taq polymerase, which is thermostable and essential for DNA synthesis.
Oligonucleotide Primers: Short sequences of DNA that initiate the replication process by binding to the template.
Deoxyribonucleotide Triphosphates (dNTPs): The building blocks of DNA that provide energy for the polymerisation reaction.
Buffer System: Contains magnesium and potassium ions to maintain optimal conditions for the PCR reaction, ensuring fidelity and stability.
By familiarising yourself with these PCR components, you will better understand how the PCR technique works as a whole.
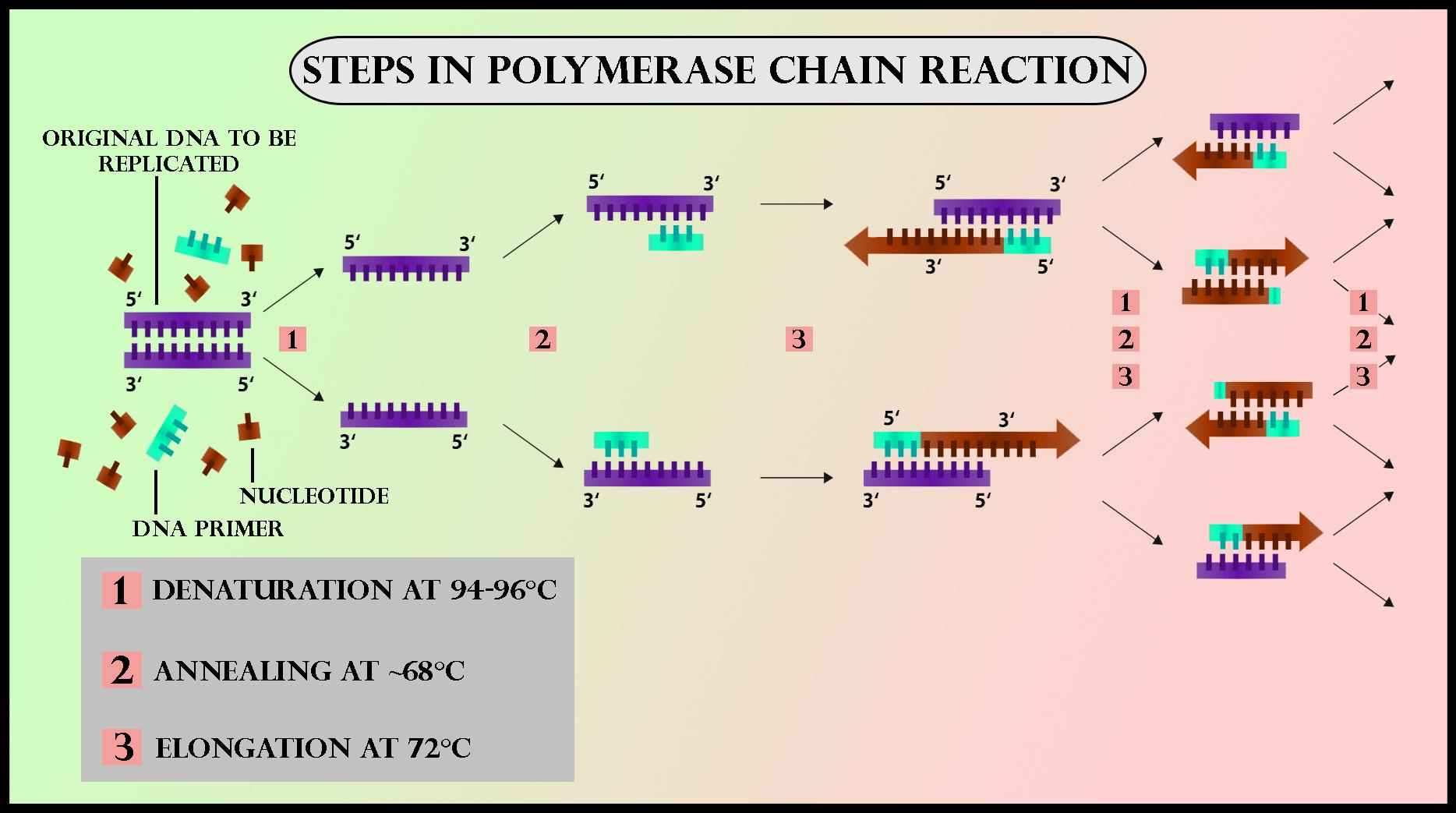
Detailed PCR Steps
Denaturation: The reaction mixture is heated to about 94℃ for 0.5 to 2 minutes. This step breaks the hydrogen bonds between the DNA strands, converting double-stranded DNA into single strands.
Annealing: The temperature is then lowered to 54–60℃ for around 20–40 seconds. During annealing, primers attach to the complementary sequences on the single-stranded DNA. The specificity of this step is critical for the PCR definition and ensures that only the target region is amplified.
Elongation: The temperature has increased to 72–80℃. Here, the DNA polymerase enzyme adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the primers, synthesising new DNA strands in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Under optimum conditions, the DNA polymerase can extend roughly 1000 base pairs per minute.
By repeating these PCR steps multiple times, the target DNA is amplified exponentially, making it easier to study even very small samples.
Types of PCR
There are several types of PCR designed for different applications. Some of the major types of PCR include:
Real-Time PCR: Also known as quantitative PCR, it allows real-time monitoring of the amplification process using fluorescent reporters. The fluorescence signal is directly proportional to the number of PCR-amplified DNA molecules.
Nested PCR: This method improves sensitivity and specificity by reducing non-specific binding. It uses two sets of primers in two successive PCR runs.
Multiplex PCR: Multiple targets are amplified simultaneously in a single reaction, making this technique ideal for applications where several DNA sequences need to be studied at once.
Quantitative PCR: Similar to real-time PCR, it provides a quantitative analysis of the DNA present in the sample.
Arbitrary Primed PCR: This is a DNA fingerprinting method that uses primers with arbitrary sequences to generate unique PCR patterns.
Each of these types of PCR can be selected based on the requirements of the experiment, and understanding the different types of PCR helps in choosing the appropriate method for specific applications.
Applications of PCR
The PCR technique has widespread applications in various fields. Here are some notable applications of PCR:
Medicine:
Diagnosis of genetic disorders by testing for specific mutations.
Monitoring gene expression in gene therapy.
Detecting disease-causing genes in family members.
Forensic Science:
Genetic fingerprinting to identify individuals from small DNA samples.
Solving crimes by matching DNA profiles.
Paternity testing.
Research & Genetics:
Comparing genomes of different organisms.
Phylogenetic analysis of DNA from diverse sources, including ancient fossils.
Analysis of gene expression and gene mapping.
Unique Insights on PCR
Beyond these standard applications, there are additional unique aspects of the PCR technique that set it apart:
Troubleshooting and Quality Control:Optimising PCR conditions is crucial. Factors such as primer design, magnesium ion concentration, and cycle number can affect the efficiency of the PCR technique. Researchers often use a PCR diagram to troubleshoot and adjust these parameters.
Advancements in PCR Technology: Recent developments include digital PCR, which allows the absolute quantification of DNA molecules. This innovation offers higher precision and sensitivity, making it invaluable for clinical diagnostics and research.
Environmental Applications: PCR is increasingly used in environmental biology to detect and quantify microbial populations, assess biodiversity, and monitor environmental pollutants by amplifying microbial DNA directly from environmental samples.
Related Links:


FAQs on PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Steps, Types, and Applications
1. What is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique in simple terms?
Polymerase Chain Reaction, or PCR, is a powerful laboratory method used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA. Think of it as a highly specific 'photocopier' for DNA, allowing scientists to amplify a very small amount of genetic material into a large enough quantity to be studied or analysed.
2. What are the three main steps involved in a single PCR cycle?
A typical PCR cycle consists of three core steps that are repeated many times:
- Denaturation: The reaction is heated to about 94-96°C to separate the double-stranded DNA template into two single strands.
- Annealing: The temperature is lowered to 50-65°C, allowing short DNA pieces called primers to bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded DNA template.
- Elongation: The temperature is raised to 72°C, the optimal temperature for the Taq polymerase enzyme to attach to the primers and synthesise a new complementary strand of DNA.
3. What are the essential components required to set up a PCR reaction?
To successfully perform PCR, several key components are mixed in a tube:
- DNA Template: The original DNA sample containing the target sequence to be amplified.
- Primers: Short, single-stranded DNA sequences that are complementary to the start and end of the target DNA region.
- Taq Polymerase: A special heat-stable enzyme that builds the new DNA strands.
- dNTPs (Deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates): The individual building blocks (A, T, C, G) that the polymerase uses to create the new DNA.
- Buffer Solution: Provides a stable chemical environment, including magnesium ions, which are essential for the polymerase to function.
4. What are some of the most common real-world applications of PCR?
PCR is a versatile technique with a vast range of applications across different fields. Some important examples include:
- Medical Diagnostics: Detecting the presence of viral or bacterial DNA/RNA, such as in tests for COVID-19 or HIV.
- Forensic Science: Amplifying tiny amounts of DNA from crime scenes (like hair or blood) for genetic fingerprinting and identifying suspects.
- Genetic Research: Studying gene expression, cloning genes, and analysing genetic mutations related to diseases like cancer.
- Paternity Testing: Comparing DNA sequences between a child and a potential father to establish biological relationships.
5. Why is Taq polymerase used in PCR instead of the DNA polymerase found in human cells?
The DNA polymerase in human cells would be destroyed by the high temperatures of the denaturation step (around 95°C). Taq polymerase is used because it is sourced from a bacterium, Thermus aquaticus, that lives in hot springs. This enzyme is naturally heat-stable and can withstand the repeated heating and cooling cycles of PCR without breaking down, making the entire process efficient and automatable.
6. How is the process of PCR different from natural DNA replication in our bodies?
While both processes copy DNA, they differ in key ways. Natural DNA replication copies the entire genome inside a living cell (in vivo) at a constant body temperature. In contrast, PCR happens in a test tube (in vitro), copies only a specific, targeted segment of DNA, and relies on repeated cycles of heating and cooling to separate and synthesise the strands.
7. Can PCR be used to analyse RNA, or does it only work on DNA?
Standard PCR can only amplify DNA. However, a variation called Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) is used for RNA. In RT-PCR, an enzyme called reverse transcriptase first converts the RNA template into a complementary DNA (cDNA) strand. This cDNA then serves as the template for a standard PCR amplification, allowing scientists to study RNA viruses or measure gene expression.
8. What is the difference between standard PCR and Real-Time PCR (qPCR)?
Standard PCR shows you the final amount of amplified DNA at the end of the reaction, usually visualized on a gel. Real-Time PCR (qPCR), on the other hand, is quantitative. It uses fluorescent dyes to measure the amount of amplified DNA in 'real-time' during each cycle. This allows scientists to determine the initial starting quantity of the DNA template, which is crucial for applications like measuring viral load or gene activity levels.










