Structure and Classification of Arthropods (Insects, Crustaceans, and More)
Phylum Arthropoda is the largest group in the animal kingdom, including insects, spiders, crabs, and more. Recognized for their jointed limbs and exoskeleton, they are found in almost every habitat on Earth. Their diversity and adaptability make arthropods essential for ecosystems, agriculture, and scientific studies, making them a vital topic in biology.
Phylum Arthropoda: Definition and Overview
**Phylum Arthropoda** refers to a vast group of invertebrate animals distinguished by their segmented bodies, jointed appendages, and hard exoskeleton made of chitin. The word "Arthropoda" originates from Greek, meaning "jointed foot." Over 85% of known animal species belong to this phylum, making it the most successful group on Earth. Arthropods thrive in land, air, and water, displaying remarkable adaptability.
Phylum Arthropoda Characteristics
Arthropods are diverse but share some unifying features. Their physical and biological traits enable them to prosper in various environments. Understanding these characteristics is fundamental for biology students and is frequently tested in exams and MCQs.
- Exoskeleton: A hard outer shell made primarily of chitin, providing support and protection.
- Segmented Body: Divided into head, thorax, and abdomen; sometimes segments are fused.
- Jointed Appendages: Structures for walking, feeding, sensing, or defense.
- Bilateral Symmetry: Both sides of the body are mirror images.
- Open Circulatory System: Blood flows freely within body cavities.
- Ventral Nerve Cord: Nervous system with a brain and nerve cord along the front (ventral) side.
- Presence of Compound Eyes: Especially in insects, allowing detailed vision.
- Respiratory Systems: Gills in aquatic forms, tracheae or book lungs in terrestrial forms.
- Molting (Ecdysis): Shedding and renewing the exoskeleton for growth.
For a detailed view on animal adaptations and segmented body plans in other phyla, explore animal adaptations on Vedantu.
Phylum Arthropoda Diagram
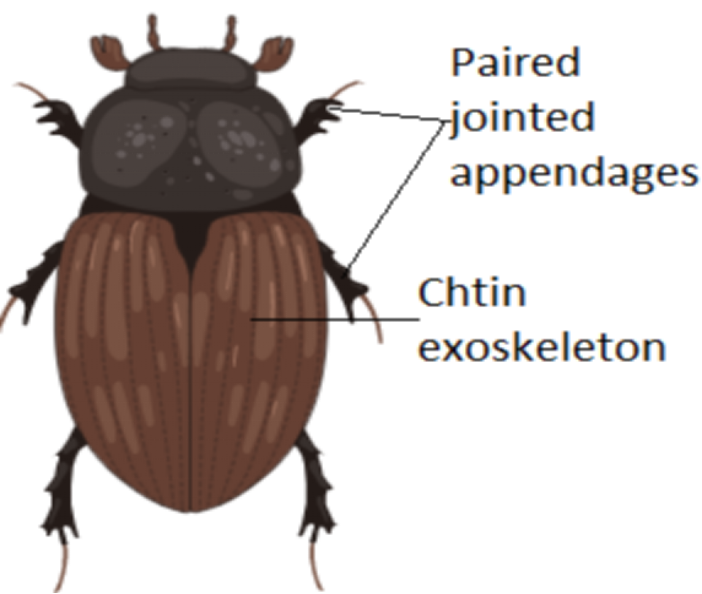
This diagram shows a classic beetle, showcasing the segmented body (head, thorax, abdomen), jointed legs, and hard exoskeleton—distinctive features of phylum Arthropoda.
Classification and Subphyla of Arthropoda
Phylum Arthropoda is classified into several important subphyla. Each group is unique and includes familiar and ecologically significant animals. Classification is crucial for academic answers, MCQs, and competitive exams.
| Subphylum | Main Groups | Distinctive Features |
|---|---|---|
| Chelicerata | Spiders, mites, scorpions, horseshoe crabs | No antennae; chelicerae for feeding; mainly terrestrial |
| Myriapoda | Centipedes, millipedes | Many body segments, each with legs; one pair (centipede) or two pairs (millipede) per segment |
| Hexapoda | Insects | Three body regions; three pairs of legs; often have wings |
| Crustacea | Crabs, lobsters, shrimp, barnacles | Mainly aquatic; two pairs of antennae; gills for respiration |
This table highlights key differences and examples among subphyla. For further study on the classification of the animal kingdom, Vedantu offers detailed charts and explanations.
Phylum Arthropoda Examples
Examples from Phylum Arthropoda are everywhere around us. They include tiny insects in our gardens to seafood in our meals. Here are some typical representatives from each subphylum.
- Chelicerata: Spiders, scorpions, ticks, horseshoe crabs
- Myriapoda: Centipedes, millipedes
- Hexapoda: Ants, butterflies, grasshoppers, cockroaches
- Crustacea: Crabs, lobsters, shrimp, prawns, barnacles
Insects are especially important in the food chain and pollination. Many fascinating life cycles, like caterpillar to butterfly transformation, belong to this phylum.
Body Structure and Adaptations
The body structure of arthropods includes distinct head, thorax, and abdomen, with specialized appendages. Their exoskeleton acts like armor, providing both protection and surface for muscle attachment. Adaptations like wings in insects or claws in crabs show evolutionary brilliance. For more, study the adaptations in land and aquatic animals in the terrestrial ecosystem section.
- Exoskeleton: Made of chitin; sometimes hardened with minerals.
- Appendages: Specialized for tasks like movement, feeding, or sensing.
- Segmentation: Allows flexibility and complex movement.
- Respiratory Adaptations: Tracheae in insects, gills in crustaceans, book lungs in spiders.
- Metamorphosis: Most insects undergo complete changes from larva to adult.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Arthropods display diverse reproductive patterns. Most are dioecious (separate sexes), and many have complex life cycles with metamorphosis. Their reproductive capabilities contribute to their global success and impact on agriculture, medicine, and the environment.
- Mating occurs between male and female.
- Females lay eggs or larvae are directly hatched (varies among groups).
- Insects like butterflies show a larval (caterpillar), pupal, and adult (butterfly) stage.
- Other groups, like crabs, carry eggs until they hatch as miniature adults or larvae.
Metamorphosis (change from larva to adult) is a key adaptation, allowing resource sharing between stages and higher survival rates. Learn about the structure and function of muscles to understand movement in arthropods.
Significance and Applications of Phylum Arthropoda
Arthropods are crucial in ecosystems, agriculture, food webs, and human economy. Their role as pollinators, decomposers, and food sources cannot be overstated. Certain crustaceans are delicacies, while insects like bees help produce fruits and crops.
- Environmental Impact: Essential for nutrient recycling and soil health.
- Agricultural Uses: Pollination, pest control, and soil aeration.
- Medical Relevance: Some arthropods act as disease vectors, important in human health studies (see endocrinology and related topics).
- Economic Value: Honey, silk, shellfish are products from arthropods.
- Scientific Research: Model organisms for genetics, development, and physiology.
Phylum Arthropoda MCQs and Class 12 Focus
For class 12 and competitive exams, important questions, MCQs, and diagrams from Phylum Arthropoda are common. Focus on features, classification, life cycles, and examples. Practicing MCQs and drawing diagrams will boost your scores. For practice, refer to Vedantu’s section on biological classification MCQs.
Phylum Arthropoda Explanation in Everyday Life
Arthropods are everywhere—from the honey bees pollinating crops to mosquitoes affecting human health. They shape food science, medicine, and the environment. Understanding their biology helps in agriculture, disease control, and biodiversity conservation. You can learn more about the nutritional value of such organisms in our nutrition section.
Page Summary
Phylum Arthropoda is essential for understanding animal diversity, ecology, and practical biology. Their unique body plan, adaptability, and real-world relevance make them important in classrooms and scientific research. Exploring these animals offers insights into evolution, environmental balance, and human welfare. For more topics, browse detailed Vedantu explanations and diagrams.


FAQs on What Is Phylum Arthropoda?
1. What is Phylum Arthropoda?
Phylum Arthropoda is the largest phylum in the animal kingdom, consisting of invertebrate animals with jointed legs and an exoskeleton.
Key features of Arthropoda include:
- Segmented body divided into head, thorax, and abdomen
- Jointed appendages (legs, antennae)
- Chitinous exoskeleton for protection
- Bilateral symmetry
- Open circulatory system
2. What are the main characteristics of Arthropoda?
Arthropods are defined by their exoskeleton and jointed legs.
Main characteristics include:
- Exoskeleton made of chitin
- Segmented body
- Paired, jointed appendages
- Open circulatory system
- Bilateral symmetry
- Well-developed sense organs
3. What are the different classes of Arthropoda?
Phylum Arthropoda is divided into several major classes based on body structure and habitat.
Main classes include:
- Insecta (insects)
- Arachnida (spiders, scorpions)
- Crustacea (crabs, lobsters, prawns)
- Myriapoda (centipedes, millipedes)
- Trilobita (extinct group)
4. What is the significance of Arthropoda in the ecosystem?
Arthropods play vital roles in all ecosystems as decomposers, pollinators, and food sources.
Ecological significance includes:
- Pollination of plants (by bees, butterflies)
- Decomposition of organic matter (by beetles, crustaceans)
- Food for other animals (fish, birds, mammals)
- Controlling pest populations (by predatory arthropods)
5. Why are Arthropods called 'jointed-legged animals'?
Arthropods are often called 'jointed-legged animals' because their limbs are composed of segments connected by joints, allowing flexible movement.
This adaptation helps in:
- Efficient walking, swimming, and flying
- Specialized tasks like grasping and feeding
6. How do Arthropods grow with a hard exoskeleton?
Arthropods grow by periodically shedding their exoskeleton in a process called moulting or ecdysis.
Key points:
- Old exoskeleton splits and is left behind
- Animal expands body and secretes a new, larger exoskeleton
- Growth occurs mostly right after moulting
7. Name some examples of Arthropoda and their economic importance.
Examples of Arthropods include insects, crabs, spiders, centipedes, and prawns. They have great economic value.
Economic importance:
- Honey bees produce honey and aid in pollination
- Silkworms produce silk
- Shrimps and crabs are important seafood
- Lac insects produce shellac
- Some insects act as pest controllers
8. Which features distinguish Arthropoda from other animal phyla?
Arthropoda differ from other animal phyla mainly by their jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton.
Distinguishing features:
- Pair of jointed legs
- Body divided into distinct regions
- Exoskeleton periodically moulted
- Open circulatory system
9. What is the open circulatory system in Arthropoda?
Arthropods possess an open circulatory system, where blood flows through body cavities rather than closed blood vessels.
Highlights:
- Blood (hemolymph) directly bathes organs
- No closed network of capillaries
- Blood is pumped by a tubular heart
10. How are respiratory organs in Arthropoda adapted to different environments?
Arthropods use various respiratory organs suited to their habitats.
Respiratory adaptations include:
- Tracheal tubes in insects for air breathing
- Book lungs in spiders and scorpions
- Gills in aquatic crustaceans
11. How are Arthropoda classified based on body segmentation?
Arthropods can be classified by the number and arrangement of their body segments.
Types of body segmentation:
- Head, thorax, abdomen in insects
- Cephalothorax and abdomen in crustaceans and arachnids
- Uniformly segmented body in myriapods
12. What are some adaptations in Arthropods for survival?
Arthropods show several adaptations that enhance their survival.
Major adaptations:
- Exoskeleton prevents desiccation and offers protection
- Compound eyes provide wide vision
- Specialized mouthparts for various diets
- Camouflage to avoid predators










