How Do Plants Breathe? Understanding Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration
Plant respiration is the key process that enables plants to convert the sugars (produced via photosynthesis) into usable energy. While it might be tempting to think that only animals need respiration, plants, too, respire continuously. From respiration in plants class 7 up to advanced studies like respiration in plants class 11 or higher, students learn that this phenomenon is crucial to maintain every plant function—right from transporting nutrients to repairing tissues.
In simple terms, plant respiration utilises oxygen to break down glucose and release carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This fundamental step is essential for growth, reproduction, and overall survival. Whether you are studying respiration in plants class 10 or exploring higher-level biology, understanding respiration helps appreciate the delicate balance between photosynthesis and energy release.

Plant Respiration Takes Place Continuously
A common question is whether respiration in plants takes place in day or night. The straightforward answer is: it happens both during the day and at night. However, it is most noticeable after sunset because photosynthesis slows or stops without sunlight, making the release of carbon dioxide more apparent. Hence, plant respiration at night is often emphasised because plants then mainly emit CO₂ (rather than taking it in for photosynthesis).
The Plant Respiration Equation
To understand plant respiration more clearly, look at the classic plant respiration equation that summarises aerobic respiration:
Glucose ($C_6H_{12}O_6$) + Oxygen ($O_2$) → Carbon Dioxide ($CO_2$) + Water ($H_2O$) + Energy (ATP)
This formula remains consistent from respiration in plants class 7 to respiration in plants class 11 and beyond. Plants utilise this energy to drive a host of vital functions, including nutrient uptake, cell division, and overall metabolism.
Also, read Transpiration in Plants
Major Pathways: Types of Respiration in Plants
When discussing types of respiration in plants, we typically focus on two main categories:
Aerobic Respiration
Occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Food (glucose) is fully oxidised into carbon dioxide and water.
Yields a large amount of energy (ATP).
Primarily takes place in the mitochondria.
Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs in the absence (or limited supply) of oxygen.
Glucose is partially broken down, producing substances like ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and CO₂ in some organisms (e.g., yeast).
Yields less energy compared to aerobic respiration.
Primarily occurs in the cytoplasm.
Most higher plants rely on aerobic respiration. However, in oxygen-deprived conditions (such as waterlogged soils), roots may experience brief periods of anaerobic respiration.
How Plants Respire through Different Parts
Respiration in Leaves
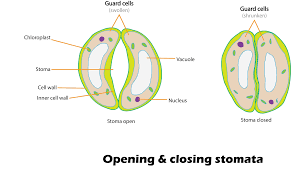
Leaves use stomata—tiny openings on the leaf surface—to exchange gases.
Oxygen diffuses in through the stomata, reaches the cells, and helps break down glucose.
Carbon dioxide produced is then released back out through the stomata.
This process goes on continuously, but you can observe plant respiration at night more distinctly since photosynthesis is not overshadowing it.
Respiration in Stems
Stems of herbaceous (non-woody) plants also have stomata.
Woody stems, on the other hand, have special pores called lenticels.
Lenticels allow gas exchange, ensuring the stem cells receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
Respiration in Roots
Roots absorb oxygen present in the air spaces within the soil.
The oxygen then diffuses into root hairs, which are extensions of root epidermal cells.
Carbon dioxide produced is released back into the soil.
This is why waterlogged soils can be harmful: excessive water reduces air pockets, limiting oxygen supply.
Also, read Transport in Plants
Do Plants Respire During the Day or Only at Night?
Students often wonder if respiration in plants takes place in day or night. The truth is that respiration happens throughout the day. However, the net effect of carbon dioxide release is more evident at night because photosynthesis (which consumes CO₂) stops in the absence of sunlight.
In daylight, any CO₂ generated by plant respiration often gets reused in photosynthesis. That is why you might have heard the caution against sleeping under a tree at night. During nighttime, there is no photosynthesis to absorb CO₂, so the local concentration around a tree can become relatively higher compared to daytime levels (though it is usually not dangerous in open spaces).
Differences Between Photosynthesis and Respiration
Below is a quick comparison to clarify why respiration in plants class 10 and respiration in plants class 11 often emphasise how these processes are complementary:
Additional Points on Plant Respiration
Respiration in Aquatic Plants: Aquatic plants often have specialised tissues (aerenchyma) that facilitate gas exchange even in submerged conditions.
CAM Plants (e.g., Cacti): These desert plants open their stomata mostly at night to minimise water loss. They store CO₂ at night and use it for photosynthesis during the day.
Respiration and Growth: The rate of respiration can increase during active growth phases or when plants are flowering or fruiting.
By exploring these unique scenarios, we can deepen our understanding beyond the basics covered in respiration in plants class 7 and respiration in plants class 10 syllabi.
Fun Task: Simple Experiment to Observe Plant Respiration
What You’ll Need
A glass jar
A small healthy potted plant with leaves
Plastic wrap or a transparent plastic bag
A rubber band
Steps
Take the small potted plant and cover the pot (soil and roots) with plastic wrap, making sure it is tightly sealed around the pot’s edges so air cannot escape from the soil.
Place the plant and pot inside the glass jar. Seal the jar with the lid or plastic bag secured by the rubber band.
Keep the jar in a moderately lit area (not in direct sunlight, which can overheat the plant).
Observe for a few hours or overnight.
Expected Result: You may notice water droplets forming on the jar’s inner surface. This moisture partly comes from the plant’s respiration (release of water vapour) and transpiration. This simple activity helps illustrate that plants release moisture and gases during respiration, even in a sealed environment.
Interactive Quiz on Respiration in Plants
Which plant parts use stomata for respiration?
A. Leaves and stems of herbaceous plants
B. Roots only
C. Flowers only
D. None of the above
What is the primary site of aerobic respiration within plant cells?
A. Cytoplasm
B. Mitochondria
C. Nucleus
D. Vacuole
Which of these is the correct plant respiration equation for aerobic respiration?
A. CO₂ + H₂O → Glucose + O₂
B. Glucose + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
C. CO₂ + O₂ → Glucose + ATP
D. Glucose + CO₂ → O₂ + H₂O
Which of the following is a reason why waterlogged soil harms roots?
A. It contains more oxygen than usual.
B. It blocks sunlight needed by roots.
C. It reduces air pockets, limiting oxygen supply.
D. It makes stomata close permanently.
Which structure aids gas exchange in woody stems?
A. Stomata
B. Lenticels
C. Root hairs
D. Mesophyll cells
Check Your Answers Below!
Answer Key
A
B
B
C
B
Expert Tips to Strengthen Your Understanding
Conduct simple experiments to observe CO₂ production or water vapour release, as hands-on activities enhance comprehension.
Compare daytime and nighttime conditions to see how plant respiration at night differs in net gas exchange.
Explore real-life scenarios, like overwatered potted plants, to study how root cells struggle in low-oxygen conditions.’
Conclusion
By understanding plant respiration, students not only appreciate how plants use oxygen to release energy but also see how it balances photosynthesis. This knowledge is foundational for topics like plant physiology, ecology, and environmental science—whether you are exploring types of respiration in plants or examining the exact plant respiration equation.


FAQs on Plant Respiration: Processes, Equations & Key Facts
1. What is the overall chemical equation for aerobic respiration in plants?
The balanced chemical equation for aerobic respiration, where glucose is broken down to release energy, is: C₆H₁₂O₆ (Glucose) + 6O₂ (Oxygen) → 6CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide) + 6H₂O (Water) + Energy (ATP). This fundamental process occurs in the mitochondria of all living plant cells.
2. Do all living parts of a plant respire?
Yes, every living cell in a plant—whether in the leaves, stems, or roots—needs energy to function and stay alive. Therefore, all these parts actively respire 24 hours a day. While leaves are the primary sites for photosynthesis, they also respire, especially at night.
3. What is the primary importance of respiration for a plant?
Respiration is vital because it converts the chemical energy stored in glucose (produced during photosynthesis) into a usable form of energy called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). This energy powers all essential life processes, including:
- Growth and development of new tissues.
- Active transport of minerals and water.
- Synthesis of proteins, hormones, and other vital molecules.
- Cellular repair and maintenance.
4. How is respiration in plants different from photosynthesis?
These two processes are essentially opposites but are linked. Key differences include:
- Process: Respiration is a catabolic process that breaks down glucose, while photosynthesis is an anabolic process that builds glucose.
- Energy: Respiration releases energy (exergonic), whereas photosynthesis requires light energy (endergonic).
- Gases: Respiration consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide and releases oxygen.
- Occurrence: Respiration occurs in all living cells continuously (day and night). Photosynthesis only occurs in cells with chlorophyll and in the presence of light.
5. Do plants release carbon dioxide or oxygen at night, and why?
At night, plants release carbon dioxide. This is because photosynthesis, which uses CO₂ and produces O₂, stops in the absence of light. However, respiration, which uses O₂ and produces CO₂, continues. Therefore, there is a net release of carbon dioxide from the plant during the night.
6. How does photosynthesis affect the net gas exchange in a plant during the day?
During the day, both respiration and photosynthesis occur simultaneously. However, the rate of photosynthesis is typically much higher than the rate of respiration. As a result, the plant consumes more carbon dioxide for photosynthesis than it releases through respiration. Similarly, it produces far more oxygen than it consumes. This leads to a net release of oxygen and a net uptake of carbon dioxide during daylight hours.
7. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in plants?
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and completely breaks down glucose to release a large amount of energy (approx. 36-38 ATP). Anaerobic respiration (or fermentation) occurs in the absence of oxygen. It only partially breaks down glucose, producing substances like ethanol and carbon dioxide, and releases significantly less energy (only 2 ATP). Plants may resort to anaerobic respiration temporarily in conditions like waterlogged soil.
8. How do different parts of a plant, like stems and roots, carry out respiration?
Plants lack a specialised respiratory system, so gas exchange happens through different structures:
- Leaves: Gas exchange primarily occurs through small pores called stomata.
- Stems: Woody stems have specialised pores called lenticels in the bark that allow oxygen to reach the inner tissues.
- Roots: Root cells take in oxygen from the air spaces present in the soil through their large surface area, particularly via the root hairs.
9. Why is it a misconception that sleeping under a tree at night is dangerous?
While it is true that plants release carbon dioxide at night, the amount is very small and insignificant in an open, well-ventilated area. The concentration of CO₂ will not rise to dangerous levels. The belief that it is harmful is a common myth; the natural ventilation outdoors ensures that the gas disperses quickly, posing no threat to human health.










