How Structure and Function Set Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Apart
Cells are the basic building blocks of life, from the simplest bacteria to complex plants and animals. At the microscopic level, life can be divided into two major types: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. These two types differ in structure, size, and function, and understanding these differences is crucial for studying biology.
But did you know that the first cells on Earth, the prokaryotic cells, appeared around 3.5 billion years ago? It is from these tiny organisms that all other life evolved!
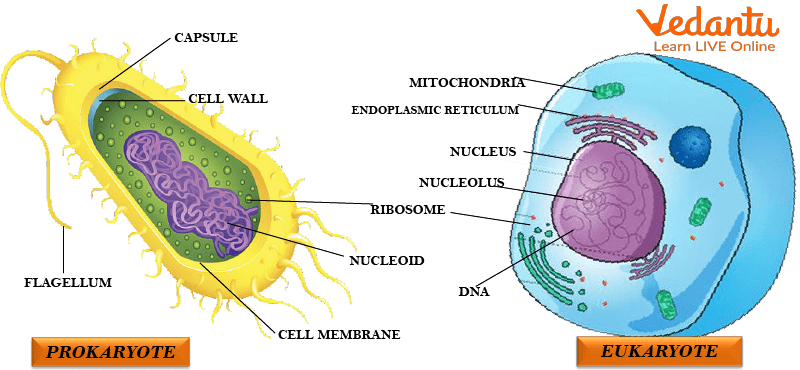
What are Prokaryotic Cells?
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and smallest type of cells, usually measuring between 0.2 μm – 2.0 μm in diameter. These cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is located in a region called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic cells are typically unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and archaea.
Key characteristics of prokaryotic cells include:
No membrane-bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria, Golgi bodies).
A protective cell wall made of complex chemicals.
Smaller ribosomes compared to eukaryotic cells.
DNA is in a circular form.
Reproduction occurs through binary fission.
What are Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells, measuring between 10 μm – 100 μm in diameter. These cells contain a defined nucleus, which houses the cell's DNA. Eukaryotic cells are found in both unicellular organisms (like yeast) and multicellular organisms (like plants and animals).
Key characteristics of eukaryotic cells include:
A well-defined nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Presence of membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, chloroplasts, and the endoplasmic reticulum.
Linear DNA is stored within the nucleus.
Larger ribosomes compared to prokaryotic cells.
Reproduction through mitosis (in multicellular organisms) and sometimes meiosis (for sexual reproduction).
Key Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Table
Real-World Applications of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is not only fundamental to biology but also to various real-world applications. For example, genetic engineering uses bacteria (prokaryotic cells) to produce insulin. Stem cell research involves eukaryotic cells and holds the potential for groundbreaking medical treatments. In agriculture, understanding plant cells' structure helps in improving crop resistance and yield.
Interactive Quiz: Test Your Knowledge on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells!
1. Which of the following is a characteristic of prokaryotic cells?
a) Membrane-bound nucleus
b) Circular DNA
c) Larger ribosomes
d) Complex organelles
2. Which type of cell is responsible for producing energy through mitochondria?
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
c) Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
d) None of the above
Check Your Answers Below!
b) Circular DNA
b) Eukaryotic cell


FAQs on Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells: Key Differences Explained
1. What are the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The primary differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lie in their structure and complexity. Here are the key distinctions:
- Nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a true, membrane-bound nucleus that encloses their genetic material. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus; their DNA is located in a region called the nucleoid.
- Organelles: Eukaryotic cells contain various membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which are absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Size: Prokaryotic cells are typically much smaller (0.1–5.0 µm) and simpler than eukaryotic cells (10–100 µm).
- DNA Structure: Prokaryotic DNA is usually a single, circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotic DNA is organised into multiple, linear chromosomes.
2. What is the single most defining characteristic that distinguishes a eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic one?
The single most defining characteristic is the presence of a true, membrane-bound nucleus in eukaryotic cells. This structure houses the cell's genetic material (DNA), separating it from the cytoplasm. This compartmentalisation allows for more complex genetic regulation and is a fundamental feature that prokaryotic cells completely lack.
3. What are some common examples of organisms with prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Organisms can be classified based on their cell type:
- Prokaryotic Organisms: These are always unicellular and include domains like Bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Streptococcus) and Archaea.
- Eukaryotic Organisms: These can be unicellular or multicellular. Examples include all animals, plants, fungi (like yeast and mushrooms), and protists (like amoeba and paramecium).
4. Despite their differences, what key structures do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share?
Yes, despite their complexity differences, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share four fundamental components essential for life:
- Plasma Membrane: A lipid bilayer that acts as a selective barrier for the cell.
- Cytoplasm: The jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the internal components.
- DNA: The genetic material that carries the instructions for cell function and heredity.
- Ribosomes: The sites of protein synthesis, although they differ slightly in size (70S in prokaryotes, 80S in eukaryotes).
5. How does the structure and location of DNA differ in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
The organisation of genetic material is a key point of difference. In prokaryotic cells, the DNA is typically a single, circular chromosome that is located in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. It is not enclosed by a membrane. In contrast, eukaryotic cells have multiple, linear chromosomes that are contained within a membrane-bound nucleus and are tightly coiled around proteins called histones.
6. Do both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a cell wall?
Not all of them, and their composition differs. Most prokaryotes (like bacteria) have a rigid cell wall made of peptidoglycan, which provides structural support. In eukaryotes, cell walls are only present in some organisms. Plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose, and fungi have one made of chitin. Animal cells, however, do not have a cell wall.
7. How do the methods of cell division differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through a simple process called binary fission, where the cell's DNA replicates and the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells undergo more complex processes. They use mitosis for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, and meiosis to produce gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction.
8. Why are viruses not classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Viruses are considered acellular, meaning they are not cells at all. They are not classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic because they lack the basic components of a living cell, such as a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes. Viruses are essentially genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat and can only replicate by infecting a living host cell and hijacking its machinery.
9. What is the functional importance of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells?
The presence of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes allows for compartmentalisation of cellular functions. This is a major advantage as it allows different metabolic processes to occur simultaneously in specific locations without interfering with each other. For example, cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria while photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts (in plants). This separation increases the efficiency and complexity of cellular activities, which is not possible in the simpler, non-compartmentalised cytoplasm of prokaryotes.










