What Are the Natural and Man-Made Sources of Water?
Water is the foundation of life, but not all water is the same. Understanding the sources of water helps us grasp how humans, animals, and plants access this vital resource. This topic explains the main natural and man-made sources of water, their types, importance, and how we can protect them to ensure a sustainable future for all.
What are the Sources of Water?
Sources of water are locations or origins from where we obtain water for drinking, cooking, agriculture, and industrial needs. Even though about two-thirds of Earth’s surface is covered by water, only a small portion is fresh and suitable for daily use. Most available freshwater is found in specific sources, each vital for different purposes.
Natural and Man-Made Sources of Water
There are two main groups of sources of water: natural and man-made (artificial). Natural sources include rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, underground water, and rain. Man-made sources involve reservoirs, dams, canals, wells, and tube-wells created to store or extract water. Both types play a major role in supporting human societies and natural ecosystems.
Types of Water Sources
The primary types of sources of water are:
- Surface Water: Water present on Earth's surface in bodies like rivers, lakes, ponds, and reservoirs. It depends on rainfall and is commonly used in farming and urban supply.
- Groundwater: Water stored beneath the ground in porous rocks and aquifers. It is accessed using wells and is crucial for drinking and irrigation, especially in regions with less rain.
- Rainwater: Water that falls as precipitation. Often harvested and stored for later use, especially in places prone to drought.
Some regions also use artificial water sources such as dams and canals to ensure a steady water supply. For more about water’s role in the environment, see Environmental Issues.
Examples: 10 Sources of Water
Here are ten sources of water you might observe around you:
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Ponds
- Streams
- Wells
- Bore-wells (Tube-wells)
- Rainwater
- Dams
- Reservoirs
- Canals
These different sources of water are visualised in many school charts and worksheets, especially for kids learning about natural resources.
Sources of Water Diagram
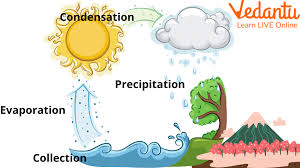
This diagram shows how water continually cycles through nature, moving between clouds, rain, rivers, lakes, underground, and back into the atmosphere. This process, called the water cycle, ensures that our natural sources of water get replenished.
Natural Sources of Water
Natural sources of water occur without human intervention. They include:
- Rivers: Flowing bodies of water that originate from mountains or springs.
- Lakes: Large standing freshwater bodies.
- Ponds and Streams: Smaller water bodies important for local ecosystems.
- Wells: Access groundwater stored in aquifers.
- Rain: The purest form, crucial in rainwater harvesting.
Most of the world’s drinking water is sourced from these natural points, but only a tiny fraction of Earth's water is clean freshwater. If you want to learn more about how water supports plant and animal life, visit Terrestrial Ecosystem.
Man-Made Sources of Water
Humans have developed artificial sources of water to provide a reliable supply. Common examples include:
- Dams: Large structures that collect and store river water.
- Reservoirs: Artificial lakes for storage and supply.
- Canals: Channels for diverting water for agriculture.
- Tube-wells: Deep wells that tap underground water.
These projects are essential in urban planning and agriculture, especially in regions like Mumbai, where water sources must meet high demand.
Sources of Drinking Water vs. Sources of Water Pollution
Not all sources of water provide safe drinking water. Pollution can come from:
- Industrial waste
- Agricultural runoff
- Sewage discharge
- Dumping of plastics and chemicals
The main sources of water pollution pose a risk to health and disrupt aquatic life. Protecting sources of drinking water is a top priority for communities worldwide. You can explore Water Pollution and Its Control for more details.
Importance and Uses of Water Sources
The different sources of water are essential for:
- Drinking & Cooking: Clean water is necessary for health and survival.
- Agriculture: Irrigation ensures food crops grow even during dry spells.
- Industry: Used in factories, cooling, and electricity generation.
- Supporting Biodiversity: Rivers and lakes provide habitats for countless species.
In medicine, water is vital for hygiene and preparing medicines (Tablet Medicine). It is also critical for health care and sanitation.
Why Should We Conserve Water?
Although water seems abundant, freshwater is limited. Overuse and pollution deplete main sources of water. Conservation ensures:
- Future generations have access to clean water.
- Crops and food supply remain stable.
- Ecosystems continue to function.
- Reduction in diseases caused by contaminated sources of water pollution.
Practices like rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation help preserve these precious resources. For techniques on saving water, see Rain Water Harvesting Methods.
How Does the Water Cycle Replenish Water Sources?
- Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and rivers.
- It forms clouds in the sky through condensation.
- Clouds release water as rain or snow.
- Rain fills surface water bodies and seeps into the ground.
- This groundwater is later used by plants, animals, and people.
This cycle makes water a renewable resource and keeps aquifers and rivers supplied even during dry seasons. More on this can be found in Water Cycle Diagram.
How Can We Preserve Sources of Water?
Protecting sources of water for kids and communities involves simple steps:
- Harvest and store rainwater.
- Use drip irrigation in farming to reduce waste.
- Fix leaking taps and pipes at home.
- Reuse water from certain cleaning processes for gardening.
- Raise awareness about water’s value and sources of water pollution in your area.
Teaching these conservation habits early using sources of water worksheets for kindergarten and class 1 students is a great start. Learn more at How Can We Conserve Water?.
Page Summary
Understanding the main sources of water, both natural and artificial, is central to managing our planet’s most precious resource. Protecting these sources from pollution and overuse is crucial for health, agriculture, and ecosystems. Vedantu helps students build strong foundations on such environmental topics, preparing them for real-world challenges and solutions.


FAQs on Sources of Water: Meaning, Types, and Significance
1. What are the main sources of water?
The main sources of water are natural bodies that provide usable water for homes, agriculture, and industries. Common sources include:
- Rainwater
- Surface Water (rivers, lakes, ponds)
- Groundwater (wells, tube wells, aquifers)
- Glaciers and ice caps
- Seas and Oceans (for desalination)
2. What is groundwater and how is it important?
Groundwater is water stored beneath the Earth's surface in soil and rock layers called aquifers.
Its importance includes:
- Main source for drinking and irrigation in many regions
- Less likely to be polluted compared to surface water
- Available even during dry seasons
3. How do we get water from surface sources?
Surface water is obtained directly from rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams.
Methods to collect surface water include:
- Building dams and reservoirs
- Constructing canals for irrigation
- Direct pumping for household use
4. What are the advantages of rainwater harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting means collecting and storing rainwater for later use.
Its advantages include:
- Reduces dependence on ground and surface water
- Recharges groundwater levels
- Helps prevent flooding and soil erosion
- Supplies water during shortages
5. What are the differences between surface water and groundwater?
Surface water and groundwater differ in their locations and uses.
Main differences:
- Surface water is found in rivers, lakes, and ponds; groundwater is beneath the earth in aquifers.
- Surface water is more exposed to pollution; groundwater is usually cleaner.
- Surface water is easily accessible, while groundwater requires digging wells or boreholes.
6. Why is water from rivers not always fit for drinking?
River water often contains impurities like dirt, harmful bacteria, and chemicals, making it unsafe to drink directly.
Rivers can get polluted by:
- Industrial and household waste
- Sewage discharge
- Flood runoff carrying pesticides and fertilizers
7. What are the uses of water in our daily life?
Water is essential for multiple daily activities.
Major uses include:
- Drinking and cooking
- Bathing and cleaning
- Irrigation in agriculture
- Industry and manufacturing
- Generating hydroelectric power
8. How do glaciers and ice caps act as sources of water?
Glaciers and ice caps store fresh water as ice in mountains and polar regions.
They act as sources of water by:
- Melting during warmer seasons to feed rivers and streams
- Supplying water for irrigation and drinking downstream
- Maintaining river flow during dry periods
9. Why is it important to conserve water sources?
Water conservation protects our limited freshwater sources for future generations.
Conserving water is important because:
- Prevents water scarcity and droughts
- Sustains agriculture and food security
- Maintains ecological balance
- Reduces cost and energy for supply and treatment
10. What is potable water?
Potable water is water that is safe and clean enough for drinking.
It must:
- Be free from harmful germs and chemicals
- Appear clear, tasteless, and odorless
- Meet health and hygiene standards set by authorities
11. How do human activities affect sources of water?
Human activities can pollute or deplete water sources.
Major impacts include:
- Dumping industrial waste and sewage into rivers and lakes
- Overuse of groundwater leading to water table decline
- Pesticides and chemicals from agriculture mixing with water
- Deforestation increasing soil erosion and siltation of water bodies










