




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Basic Chemistry Laboratory Techniques Experiment
In general, laboratory equipment is made from glass, as it is resistant to chemicals. Two types of glasses are used, borosilicate and soda-lime. The soda-lime glass is resistant to heat up to 300-400oC, and borosilicate is resistant to heat up to 700 to 800oC. The expansion coefficient of soda lime glass is high, so used to make instruments like glass test tubes, pipettes, capillaries, etc. While the expansion coefficient of borosilicate glass is low, so used glass instruments that do not break on sudden heat change.
Chemistry is composed of two parts, theory and practical. Laboratory techniques help us understand the theory in real life.
Laboratory techniques perform experiments, and these techniques help us understand the concepts.
Personal protective equipment in the chemistry lab like safety goggles, a lab coat and latex gloves project us while performing experiments.
Knowledge of laboratory techniques helps us perform experiments without harming ourselves.
Using borosilicate glass instead of ordinary glass is necessary to know before experimenting.
Table of Content
Aim
Cutting Glass Tube or Glass Rod
Working of Bunsen Burner
Measuring the volume of Liquid
Heating A solution in a Test Tube
Result
Aim
To perform basic chemistry laboratory techniques;
Cutting glass Tube or Glass rod
Working of a Bunsen burner
Measuring the Volume of Liquid
Heating a solution in a Test tube
Cutting Glass Tubes or Glass Rods
Apparatus Required
Soda-Glass Tube/Rod
Triangular File

A Portion of a Flexible Glass Rod of Diameter 2 cm
Theory
A glass rod or tube is a laboratory instrument used to mix chemicals and stirring purposes. They are made of solid glass and available in various lengths. Glass tube is hollow and used to make various instruments.
Procedure
The first step is to take a portion of a flexible glass rod of diameter 2 cm and put the glass tube or rod on the table as shown in the glass rod diagram, and hold it with your hand.
Then, keep the lower end of the triangular file with a sharp edge perpendicularly to the rod.
Now pull the file towards you to make a deep scratch on the glass rod shown in the triangular file diagram.
Then, hold the rod such that the thumb of both hands remains close to scratch.
Now, break the rod from your hand with a cloth so it may not harm your hand.
If it is not broken, then make a deep scratch on the earlier mark and break it again in the same way.
We get a tube of glass open at both ends.
Now trim one edge of the rod with a wire gauge.
Seal the other edge by heating it on a Bunsen burner by rotating it back and forth till it gets rounded.
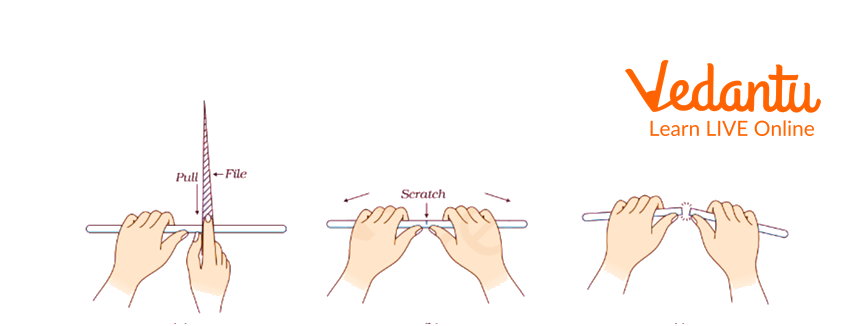
Cutting Glass Tube Using a Triangular File
Result
The glass tube/ rod is cut successfully to the desired length.
Working of Bunsen Burner
Apparatus Required
Bunsen Burner
Theory
A Bunsen burner is a heating device used in laboratories to heat chemicals and perform reactions. It was introduced by German scientist Robert Bunsen in 1855.
The Bunsen burner is made of cast iron so that it remains straight. A gas-inlet tube connected with it horizontally into the side of the iron base.
That is connected by a rubber tube. The nipple of the burner is made up of a brass rod with a pinhole running by it.
The lower end of the nipple is attached to the base, and the upper end carries the burner.
There are two opposite air holes near the lower end of the burner for air regulation.
A metallic air-adjusting disc is also attached at the lower end of the burner tube, corresponding to air holes.
Procedure
The rubber tube of the burner is attached to a gas tap. When the tap is open, the burner lightens.
Once the gas passes through the nipple it falls in pressure, as a result, the air sucked in from the holes and the burner lightens.
The mixture of air and combustible gases burns the top of the burner.
The flame of the burner is of two types-luminous and non-luminous.
Non-luminous gas is the hottest and is used for heating purposes.
The luminous zone is the brightest part of the flame and is used for reducing processes like the charcoal cavity test, and the borax test.
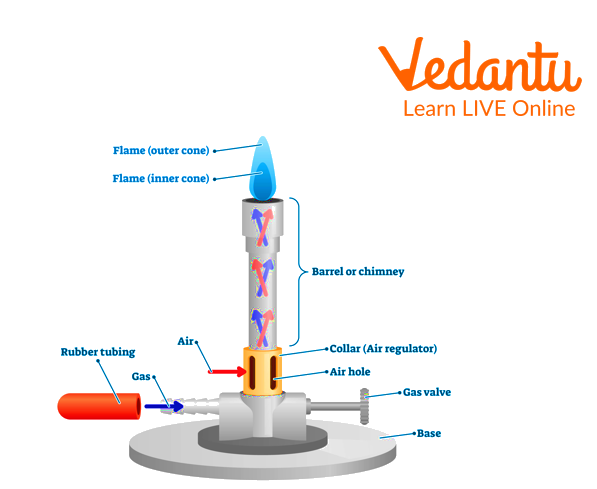
Bunsen Burner Diagram
Measuring the Volume of Liquid
Apparatus Required
Graduated Cylinder/burette/pipette
Pipettes
Flask
Liquid for measuring
Theory
In the laboratory, burettes, pipettes and graduated cylinders are used for measuring the volume of cylinders. They measure liquid at a certain temperature. The burette and pipette measure a limited volume of liquid at a specific temperature.
Aqueous solution wet the glass surface and form a concave meniscus in the cylinder or burette.
The central part of the meniscus is flat. When we measure the volume the apparatus coincides with a flat portion of the liquid and give the volume of the liquid. It is necessary to note the volume of liquid at the same level as the liquid to avoid errors.
Some coloured liquids like KMnO4 form a convex meniscus. It coincides with the upper surface of the meniscus.
So, burettes and pipettes give an accurate measure of liquids.
Procedure
First, clean the cylinder used for measuring the liquid.
Then fill the cylinder with the liquid that is to be measured.
Fill the cylinder slightly more to compensate for the film formed by that liquid.
Then take the reading of the clear liquid from above from the meniscus and in coloured liquid from below to avoid errors.
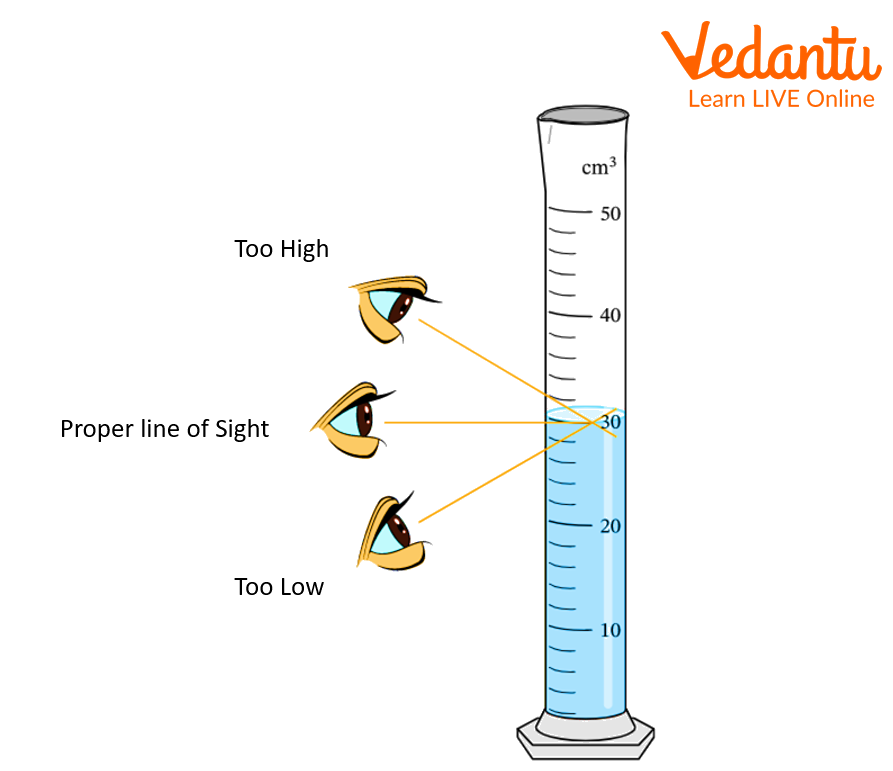
Measuring the Volume of a Liquid

Wash Bottle Diagram

A Jet of Water Coming Out of a Tube
Result
The liquid taken is measured successfully.
Heating a Solution in a Test Tube/Beaker
Apparatus Required
Test Tube/Beaker
Bunsen Burner
Test tube holder
Liquid
Theory
The liquids are heated in a test tube with the help of a test tube holder. The test tube or beaker of made up of borosilicate glass. So that it stays intact during heating. Some anti-bumping chips are added in liquids to avoid bumping of liquid while heating it. The test tubes or beakers do not keep directly on the heat. Beakers are placed on wire gauze, and test tubes are placed just below the surface of the liquid, not at the bottom of the heat.
Procedure
First, take a clean test tube.
Then fill the liquid you have to heat in a test tube.
Add a few anti-bumping chips to avoid bumping the liquid.
Now place the test tube on heat at an angle and heat it just below the surface of the liquid.
During heating, swirl the test tube occasionally for uniform heating.
Keep the mouth of the test tube away from your face to avoid an accident.
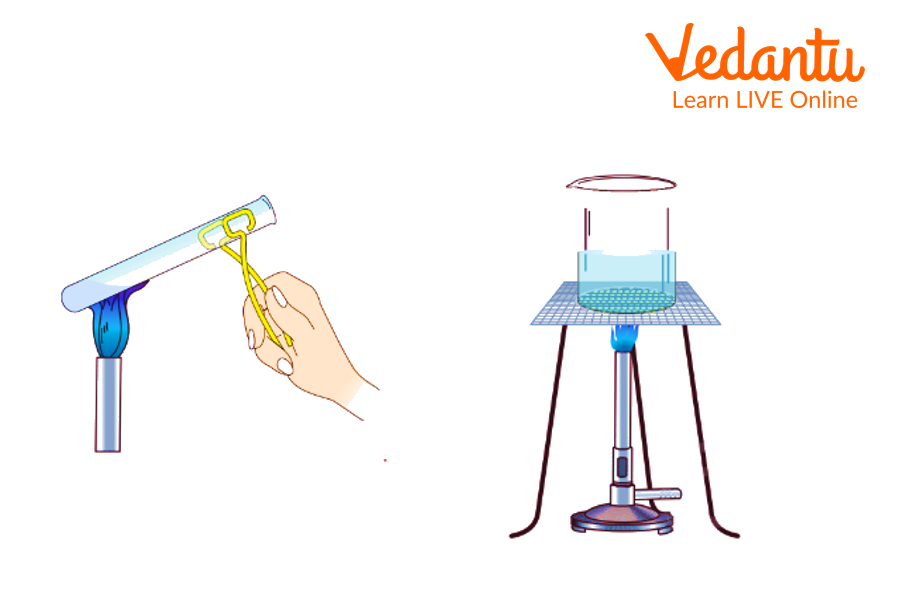
Heating the Solution in a Test Tube
Precautions
Try to make a deep scratch in one stroke with the file.
Keep the rod away from your face to protect it from injury.
Hold the rod with a cloth while breaking the rod to avoid injury.
Make sure the cylinder or burette you are using for measurement is clean and dry.
Keep the meniscus in mind while taking the reading of the volume filled in the cylinder.
Fill the cylinder slightly above to take the correct measure of liquid
Do not put the test tube directly on the heat, it can break the test tube.
Keep the test tube away from anyone’s face.
Watch glass must be cleaned properly before use.
Release the beam gently while weighing.
Lab Manual Questions
1. Why borosilicate glass is used for the preparation of lab instruments?
Ans. The borosilicate glass does not melt up to 700 to 800oC. Its coefficient of expansion is lower than other glasses, that’s why it is used for the preparation of laboratory instruments.
2. Which flame is used for heating purposes in the Chemistry laboratory?
Ans. Non-luminous flame is used for heating purposes in laboratories, as it combusts the hydrocarbons completely.
3. Why there are air holes in the Bunsen burner?
Ans. There are two air holes in the pipe of the Bunsen burner that helps the supply of air during burning.
4. Which type of flame is used to bend a glass tube?
Ans. The hottest broad flame of the Bunsen burner is used to bend a glass tube, to avoid flattening the glass.
Viva Questions
1. Can we use a knife over a triangular file for cutting glass rods?
Ans. We can not use a knife over a triangular file for cutting glass rods as it slips on glass and can harm you.
2. What do we have to do with the sharp edges of the glass rod after cutting it?
Ans. We should heat one end of the glass rod to seal it by rolling it over the heat flame, and one end of the rod should be trimmed with a wire gauge.
3. Name any two types of glass used in the chemistry laboratory.
Ans. Two glasses that use in the laboratory are soda lime glass and borosilicate glass.
4. What is the composition of soda lime glass?
Ans. The soda lime glass is made up of Na2SiO3.CaSiO3.4SiO3.
5. What is another name for borosilicate glass?
Ans. Borosilicate glass is also known as Pyrex glass or corning glass.
6. How to bend a glass tube perfectly?
Ans. First, place the glass tube on the red-hot zone of the Bunsen burner, and heat it. Keep rotating the tube for uniform heat. Start bending it slowly when it becomes red-hot and soft.
7. A metallic disc is being heated. Its area A (in m2 at any time t (in second) is given by A=5t2+4t+8. Calculate the rate of increase in area at t=3 s.
Ans. The rate of increase in area at t =3s is 34m2
8. Why do we clean the burette with the same solution that we are going to fill in it?
Ans. We clean the burette with the same solution to avoid contamination and error in the result of the experiment.
9. Which solution is used for cleaning a glass apparatus?
Ans. Generally, we use water to clean any type of glass apparatus, but sometimes we rinse the apparatus with the con. HCl or Con HNO3.
10. What happens when a metallic disc is heated?
Ans. When a metallic disc is being heated, which contains a hole, its size increases due to thermal expansion.
Practical Questions
1. Which chemical is used for cleaning glass wares in the chemistry laboratory?
Chloroform
Chromic acid
Benzene
Benzaldehyde
Ans. Chromic acid is used for cleaning glass wares in the laboratory. It is a mixture of the con. Sulphuric acid and dichromate.
2. Which glass apparatus is used in the volumetric analysis experiment?
Standard Flask
Beaker
Test tube
Erlenmeyer Flask
Ans. Erlenmeyer Flask, which is also known as a conical flask is used in volumetric analysis.
3. Which apparatus is used for the filtration of a solution?
Funnel
Wash Bottle
Watch Glass
Test Tube
Ans. A funnel is used for the filtration of the solution.
4. Which apparatus is used for the weighing technique in chemistry laboratories in schools?
Chemical Balance
Physical Balance
Top Loading Precision Balance
Digital Balance
Ans. Chemical balance is used for weighing techniques in schools.
5. Which jar is best for measuring liquid solutions in laboratories?
Test Tube
Weighing Balance
RB Flask
Measuring Jar
Ans. Measuring jars are used for measuring liquids in laboratories.
6. The plastic wash bottles used in laboratories are made up of?
Polyvinyl Chloride
Polystyrene
Polyethylene
Polyacrylonitrile
Ans. Polyethylene which is also known as polythene, is used for manufacturing wash bottles.
7. How much maximum weight can be measured in an analytical balance?
100 g
500 g
50 g
700 g
Ans. We can measure up to 100 g in an analytical balance.
8. How the weight of the solute is calculated while preparing a solution?
Using the Molarity formula
Using the Normality formula
Using the Molality formula
None of the above.
Ans. The weight of the solute is calculated using the molarity formula.
9. Soda-lime glass is made up of which chemicals?
Soda-Limestone-Silica
Limestone-Silica
Limestone-Borosilicate
Borosilicate
Ans. Soda-lime glass is made by heating soda with limestone and silica.
10. What are the precautions taken while bending a glass rod?
Avoid using the glass rod on one side.
Rotate the glass while heating.
Keep your hand safe while heating the rod.
All of the above.
Ans. Avoid using the glass rod on the side, keep rotating the glass rod during heating, and keep your hands safe.
Conclusion
In this above experiment, we have learned basic chemistry laboratory techniques used in chemistry. We have learned how to cut a glass rod. How to measure the volume of the liquids, and measure weights of the compounds. We have also learned to prepare an oxalic acid solution, etc.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Basic Chemistry Laboratory Techniques Experiment
1. What are some fundamental laboratory techniques that are considered important for the CBSE Class 11 Chemistry practical exam 2025-26?
For the CBSE Class 11 Chemistry practical exams, students are expected to master several core techniques. The most important ones include:
- Cutting and Bending Glass Tubes: Essential for setting up apparatus.
- Handling a Bunsen Burner: Knowing how to produce and control oxidising and reducing flames.
- Purification Techniques: Understanding the principles behind crystallisation, simple distillation, and paper chromatography.
- Measurement Skills: Accurately measuring mass using a weighing balance and volume using pipettes, burettes, and measuring cylinders.
- Determining Physical Constants: Finding the melting point of a solid and the boiling point of a liquid.
2. Why is mastering basic laboratory techniques crucial for scoring well in the Class 11 Chemistry practicals?
Mastering basic laboratory techniques is crucial because evaluation in practical exams is based on the accuracy and precision of your results. Proper technique, such as reading the meniscus correctly or heating a substance uniformly, directly impacts the outcome of an experiment. Examiners also assess your procedural skills and confidence during the experiment. Furthermore, a strong grasp of these techniques is essential for answering viva-voce questions, which carry significant marks.
3. What are some frequently asked viva-voce questions related to handling glass apparatus like cutting and bending glass tubes?
During viva-voce for the 2025-26 practicals, you can expect questions like:
- Why do we fire-polish the sharp edges of a cut glass tube? To make them smooth and prevent injury, and to avoid scratching other glassware or cutting rubber stoppers.
- What is the role of the air hole in a Bunsen burner? To control the amount of air mixing with the gas, which determines the type of flame (luminous or non-luminous).
- Why should a glass tube be rotated while heating it for bending? To ensure uniform heating and prevent it from sagging or breaking at one point.
- What is borosilicate glass (Pyrex)? A type of glass with low thermal expansion, making it resistant to thermal shock and suitable for heating chemicals.
4. How does the principle of 'like dissolves like' apply to the technique of crystallisation when purifying an impure solid?
The principle 'like dissolves like' is the foundation for choosing a suitable solvent in crystallisation. For an effective purification, you need a solvent in which the desired compound is sparingly soluble at room temperature but highly soluble at a higher temperature. Conversely, the impurities should either be completely soluble at room temperature (so they remain in the mother liquor upon cooling) or completely insoluble (so they can be filtered off from the hot solution). This selective solubility, based on the polarity of the solute and solvent, allows for the separation and formation of pure crystals.
5. What is a common mistake students make while determining the melting point of a solid, and how does it affect the final result?
A very common and critical mistake is heating the apparatus too rapidly. If the temperature rises too fast, the thermometer reading will lag behind the actual temperature of the heating bath and the sample. This leads to an observed melting point range that is both inaccurate (usually higher than the true value) and artificially broad. For a correct determination, the temperature should be raised slowly and steadily, especially near the expected melting point, to ensure thermal equilibrium.
6. What is the fundamental difference between distillation and crystallisation as purification techniques?
The fundamental difference lies in the physical properties they exploit for separation:
- Distillation separates components of a liquid mixture based on differences in their boiling points. The more volatile component (lower boiling point) vaporises first, is condensed, and then collected separately.
- Crystallisation separates a solid from a solution or a mixture of solids based on differences in their solubility in a particular solvent at different temperatures. The desired compound is crystallised out from the solution upon cooling, leaving impurities behind.
7. From an examination perspective, why is paper chromatography considered an important technique?
Paper chromatography is an important technique in exams because it demonstrates a key separation principle: differential partitioning. It separates components of a mixture (like ink) based on their differing affinities for the stationary phase (the paper) and the mobile phase (the solvent). Questions often focus on the calculation and significance of the Retardation Factor (Rf value), which is a characteristic constant for a compound under specific conditions. Understanding this helps in identifying components in a mixture, making it a frequently tested concept.
8. What key safety precautions are mandatory to follow in a chemistry lab and are often asked in viva?
Following safety rules is non-negotiable and a key aspect of evaluation. The most important precautions include:
- Always wear a lab coat and safety goggles to protect yourself from chemical splashes.
- Never taste or smell chemicals directly. To smell a substance, waft the vapours towards your nose.
- Always add acid to water, never the other way around, to prevent the solution from splashing out.
- Handle flammable liquids with care and keep them away from open flames.
- Know the location of safety equipment like fire extinguishers, fire blankets, and first-aid kits.
9. How do you correctly measure the volume of a liquid using a pipette versus a measuring cylinder to ensure accuracy in an experiment?
The accuracy of measurement differs significantly between a pipette and a measuring cylinder.
- Using a Pipette (for high accuracy): A pipette is designed to deliver a precise, fixed volume. You draw the liquid up past the calibration mark, then carefully release it until the bottom of the meniscus touches the mark. The reading must be taken at eye level to avoid parallax error.
- Using a Measuring Cylinder (for approximate volumes): A measuring cylinder is used for less precise measurements. You pour the liquid in and read the volume at the bottom of the meniscus, again at eye level. It is used when an approximate volume is sufficient for the experiment.
10. In a chemistry lab, what is the function of a 'fume hood,' and for which types of experiments is its use considered essential?
A fume hood is a critical piece of safety equipment designed to limit exposure to hazardous or toxic fumes, vapours, or dust. It is a ventilated enclosure that pulls air (and any airborne contaminants) away from the user and vents it outside the building. Its use is essential for experiments that involve:
- Volatile and toxic organic solvents (e.g., chloroform, benzene).
- Reactions that produce poisonous gases (e.g., chlorine, hydrogen sulfide).
- Working with concentrated acids and bases that release corrosive fumes (e.g., concentrated HCl, HNO₃, and ammonia).
























