




An Overview of Class 11 Physics To Observe And Explain The Effect Of Heating On A Bimetallic Strip Experiment
Thermal Expansion - An Introduction
The expansion of an object on heating is called the thermal expansion of that object. This phenomenon can be observed in solids, liquids and gases. Thermal expansion is minimum in solids and maximum in gases because intermolecular forces are maximum in solids and minimum in gases. There are three types of thermal expansion of solids: Linear expansion, Area expansion and Volume expansion. In this article, we will study the effect of heating on a bimetallic strip.
Table of Contents:
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Observations
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To observe and explain the effect of heating on a bimetallic strip.
Apparatus Required
A iron-brass bimetallic strip with an insulating handle
Heater or burner
Theory
A bimetallic strip is made of two strips of different metals but of the same dimensions. When we heat it uniformly, it tends to form an arc. The metal with a greater linear expansion coefficient lies on the convex side. In simple words, we can say that riveting two metal strips make a bimetallic strip of different materials and the same length. A bimetallic strip is generally used as a thermostat in electrical appliances like Geyser, Refrigerator, Fire alarms and Electric iron.
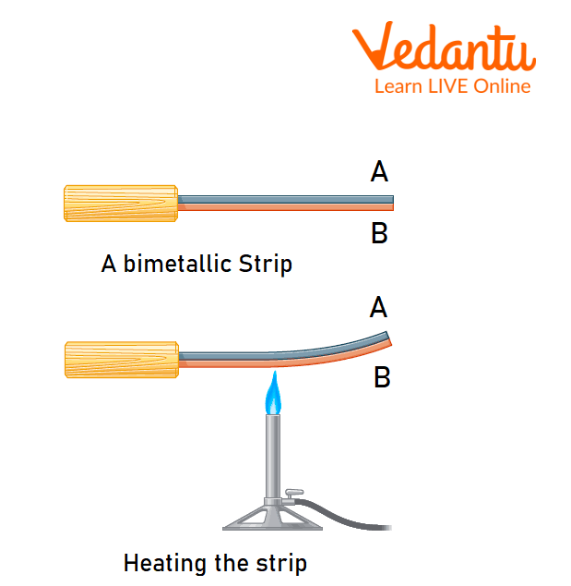
Bimetallic Strip In Straight And Bent Positions
As we can see from the figure, the bimetallic strip is straight at room temperature. When we heat it, both metallic pieces expand to different extents because of their different linear thermal expansivities and because of that, the bimetallic strip appears to bend.
When a solid is heated, it increases in thickness, length and breadth. The increase in length depends on the coefficient of linear thermal expansion, the original length and the temperature rise.
Consider a bimetallic strip of two different metals. Let ${L_1}$ be the length of a strip at temperature ${t_1}^\circ C$
Let ${L_2}$ be the length of a strip at ${t_2}^\circ C$
Here, consider that ${t_2}$ > ${t_1}$
The change in length ${L_2} - {L_1}$ is directly proportional to the original length ${L_1}$ and the rise in temperature ${t_2} - {t_1}$
So, ${L_2} - {L_1} = \alpha {L_1}\left( {{t_2} - {t_1}} \right)$
Therefore, ${L_2} = {L_1}[1 + \alpha \left( {{t_2} - {t_1}} \right)]$
and $\alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {{L_2} - {L_1}} \right)}}{{\left( {{t_2} - {t_1}} \right)}}$
Where, $\alpha $ is the coefficient of linear thermal expansion of the metal of the strip. The SI unit of the coefficient of linear thermal expansion is ${K^{ - 1}}$
Procedure
First of all, place the bimetallic strip on a horizontal surface to check whether the strip is straight or not in the beginning.
Now, suspend the bimetallic strip in a clamp stand from its one end and light a burner. Heat the bimetallic strip with the help of a burner and observe the bending of the strip.
We need to note down which side of the bimetallic strip is in direct contact with the heat source.
Now, observe the effect of heating the bimetallic strip and carefully note the direction of the bending of the free end of the bimetallic strip, whether it is upwards or downwards.
Now, identify the metal on the convex side of the bimetallic strip and the one on its concave side.
We can observe that the one on the convex side of the bimetallic strip will expand more, and hence it will have larger linear thermal expansion.
Now, note the temperature after each rise of temperature by 2 $^\circ C$ and the position of the upper edge at that temperature.
Record the observations as given below.
Now, take the bimetallic strip away from the heat source and allow the bimetallic strip to cool to room temperature.
Observations
Room temperature $\theta $ = _____ $^\circ C$
Least Count Of Vernier Scale = $1mm$
Result
The bending of a bimetallic strip on heating is because of the difference in coefficient of linear expansion of the two metals of the strip and it is found from the experiment that bimetallic strip bends more and more as its temperature rises.
Precautions
The two strips we use to perform this experiment should be firmly riveted near their ends.
One end of the bimetallic strip should be clamped rigidly, and the heating of the whole bimetallic strip should be uniform.
The length of the bimetallic strip should be large as compared to its width or thickness.
Lab Manual Questions
1. Suppose a bimetallic strip is made of brass and silver. Can we use this bimetallic strip in the thermostat?
Ans: This type of bimetallic strip can not be used in the thermostat because they have a negligible difference in thermal expansion properties. The thermostat is a device used to maintain a desired temperature in a system like an air-conditioner, refrigerator and electric iron. It works on the principle of thermal expansion of solid materials.
2. Why is mercury used in thermometers?
Ans: Mercury is a metal in a liquid state at room temperature. It is used in thermometers because it has higher boiling and lower freezing points and expands on heating due to the high thermal coefficient of linear expansion. The other reason is that it does not stick to the glass tube and is a shining metal.
3. State one disadvantage of bimetallic strips.
Ans: There will be a change in the quality of metal if we use it regularly, which may lead to an error while measuring.
Viva Questions
1. Name one device which uses a bimetallic strip.
Ans: A fire alarm is a device which uses a bimetallic strip.
2. State two different types of bimetallic strips.
Ans: Spiral strip type and helical type are the two different types of bimetallic strips.
3. Can we use bimetallic strips in fans?
Ans: Yes, we can use bimetallic strips in fans to convert temperature into mechanical displacement.
4. State two advantages of the bimetallic thermometer.
Ans: The bimetallic thermometer can easily be installed, and wide temperature ranges are available. Another advantage is that its cost is meagre.
5. Define linear thermal expansion.
Ans: The change in length due to heat at constant pressure is known as linear thermal expansion.
6. Which device is used to measure the hotness or coldness of an object?
Ans: A thermometer is a device used to measure an object's hotness or coldness.
7. Give two applications of bimetallic strips.
Ans: Bimetallic strip is used in iron box, heat engines and in thermistors also.
8. Name one device which works on the principle of thermal expansion.
Ans: Bimetallic thermostat works on the principle of thermal expansion.
Practical Based Questions
We can measure temperature in
Second
Newton
Kelvin
Tesla
Ans: Option C - Kelvin
S.I. unit of heat is
Ampere
Joule
Tesla
Second
Ans: Option B - Joule
_____ should be filled in the bulb of a thermometer.
Lead
Silver
Gold
Mercury
Ans: Option D - Mercury
1 cal = _____ joule
9.9
7.9
4.2
1.0
Ans: Option C - 4.2
We can measure heat by _____
Galvanometer
Thermometer
Calorimeter
None of the above
Ans: Option C - Calorimeter
Bimetallic strip is used in _____
Fire alarms
galvanometer
Ammeter
None of the above
Ans: Option A - Fire alarms
In solids, transfer of heat takes place by the process of _____
Radiation
Conduction
Convection
None of the above
Ans: Option B - Conduction
Bimetallic strip is made up of _____
Metals with different linear expansion coefficients
More than two metals with the same linear expansion coefficient
More than two metals with different lengths
None of the above
Ans: Option A - Metals with different linear expansion coefficient
Thermometer works on the _____
Faraday’s law of induction
Ampere’s circuital law
Principle of thermal expansion
Coulomb’s law
Ans: Option C - Principle of thermal expansion
A device which is used to measure temperature is called _____
Telescope
Galvanometer
Thermometer
Micrometer
Ans: Option C - Thermometer
Conclusion
We can conclude from this experiment that
With the increase in temperature the bimetallic strip bends more. Bimetallic strip bends due to the metal thermal expansion property.
When the temperature increases, the bimetallic strip expands towards the metal which has a lower value of temperature coefficient and when the temperature decreases, the bimetallic strip expands towards the metal which has a higher value of temperature coefficient.
FAQs on Class 11 Physics To Observe And Explain The Effect Of Heating On A Bimetallic Strip Experiment
1. What is a bimetallic strip and on what fundamental principle of physics does it operate?
A bimetallic strip is a composite beam made by bonding two different metals with significantly different coefficients of thermal expansion. Its operation is based on the principle of differential thermal expansion. When heated, the metal with the higher coefficient of expansion expands more than the other, forcing the strip to bend.
2. What is the main observation from the experiment on heating a bimetallic strip, and why does this happen?
The main observation is that upon heating, the bimetallic strip bends into an arc. This happens because the two metals bonded together have different coefficients of linear expansion (α). The metal with the higher α expands more for the same temperature rise, becoming longer than the other metal. To accommodate this difference in length, the strip is forced to curve.
3. A bimetallic strip is made of steel (α ≈ 12 x 10⁻⁶ /°C) and brass (α ≈ 19 x 10⁻⁶ /°C). In which direction will the strip bend when heated?
When heated, the bimetallic strip will bend with the brass on the outer side of the curve and the steel on the inner side. This is because brass has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion and will expand more than steel. To occupy a longer path, the brass strip must form the outer edge (convex side) of the arc.
4. State two important practical applications of bimetallic strips that are relevant for the CBSE Class 11 Physics syllabus 2025-26.
Two important applications of bimetallic strips are:
Thermostats: They are used as switches in temperature-regulating devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, and electric irons. The bending of the strip at a preset temperature makes or breaks an electrical circuit.
Thermal Switches: They are used in fire alarms. When the ambient temperature rises significantly due to a fire, the strip bends to complete an electrical circuit, which then triggers an alarm bell.
5. Why is it an important design consideration for the metals in a bimetallic strip to have a large difference in their coefficients of thermal expansion?
It is crucial to have a large difference in the coefficients of thermal expansion because the amount of bending is directly proportional to this difference. A larger difference results in a more pronounced and sensitive bending action for a given temperature change, making the device more effective as a switch or sensor. If the coefficients were nearly identical, the strip would barely bend, rendering it useless for most applications.
6. How is the principle demonstrated by a heated bimetallic strip applied when fitting a metal rim onto a wooden cartwheel?
This is a classic application of thermal expansion. The metal rim is manufactured with a slightly smaller diameter than the wooden wheel. To fit it, the rim is heated uniformly. This causes it to expand (increase in diameter) enough to be easily slipped over the wheel. As the rim cools down, it contracts and grips the wooden wheel very tightly, ensuring a secure fit. This process is known as shrink-fitting.
7. What would happen if a bimetallic strip, after being heated, is then cooled to a temperature well below its initial room temperature?
If a bimetallic strip is cooled below room temperature, it will bend in the opposite direction to which it bent when heated. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion (which expanded more when heated) will also contract more when cooled. This greater contraction forces it to become the shorter, inner side of the curve.
























