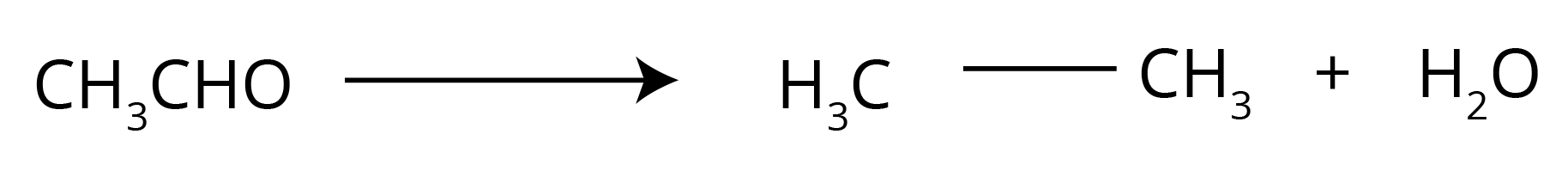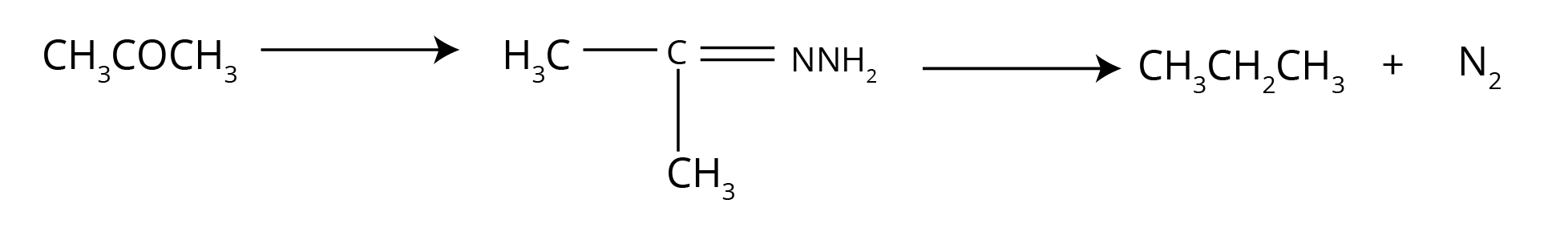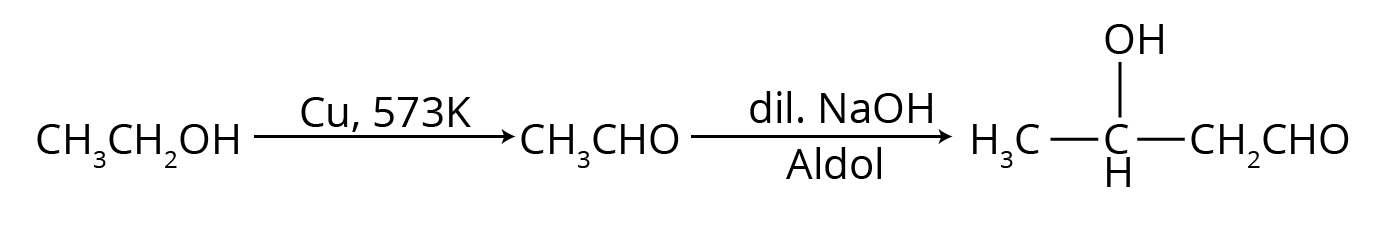Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 extra questions and answers Free PDF Download


FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - 2025-26
1. What are the most important topics and reactions to focus on from Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids for the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2025-26 board exams?
For the CBSE 2025-26 board exams, students should prioritise the following high-yield topics and reactions:
- Nomenclature and Structure: Basic understanding of the carbonyl group.
- Preparation Methods: Key methods like Rosenmund reduction, Stephen reaction, Gattermann-Koch reaction, and Friedel-Crafts acylation.
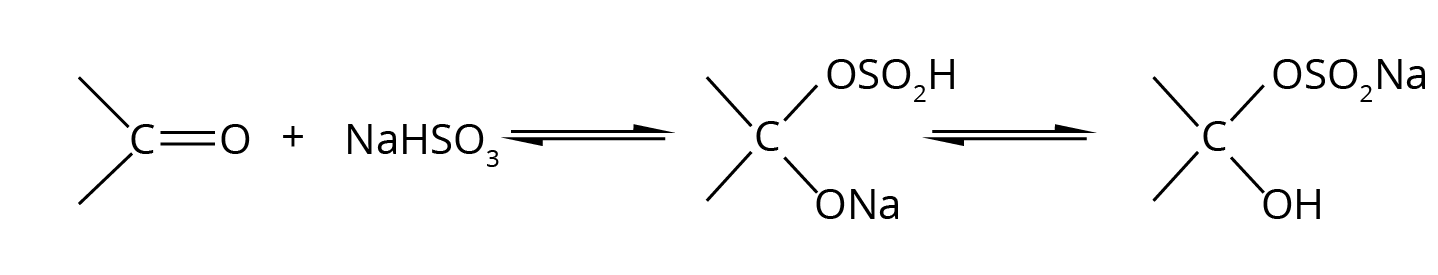
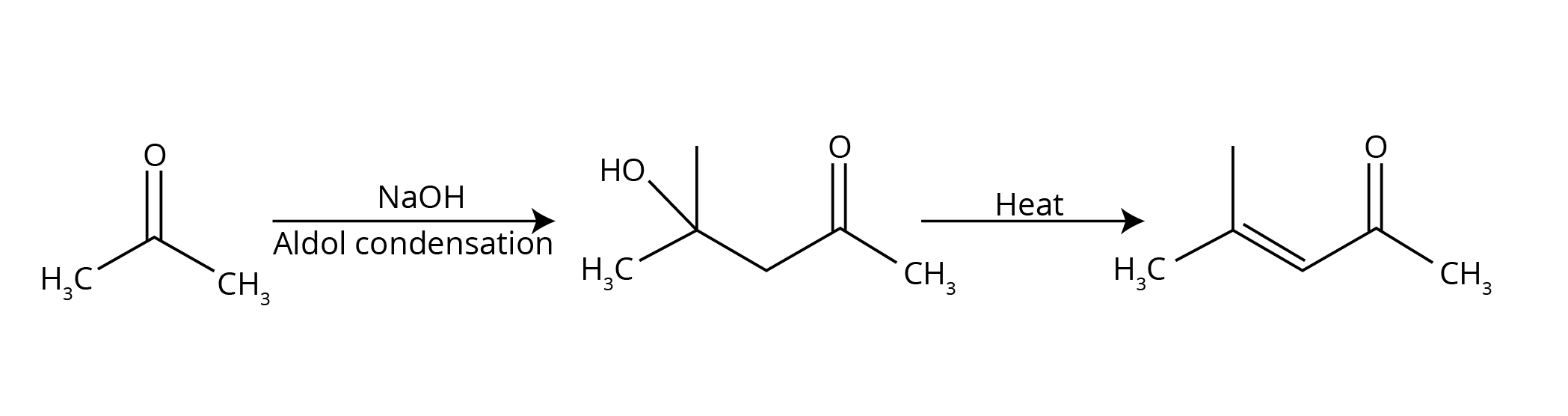
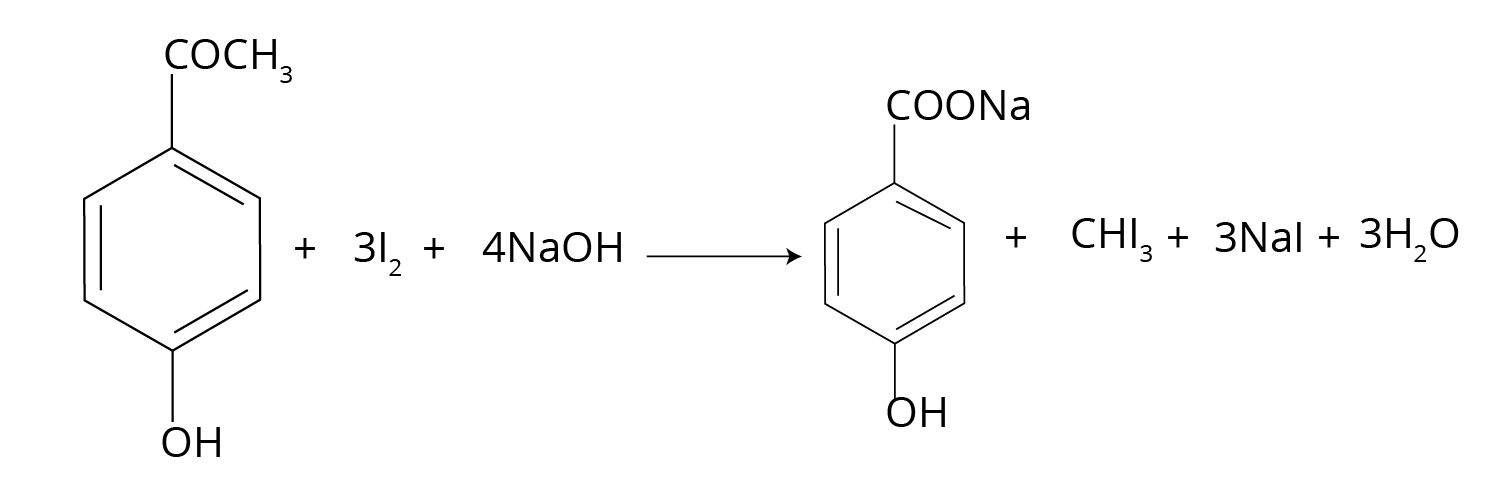
- Named Reactions: This is the most crucial area. Focus on Aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction, Clemmensen reduction, Wolff–Kishner reduction, and the Haloform (Iodoform) test.
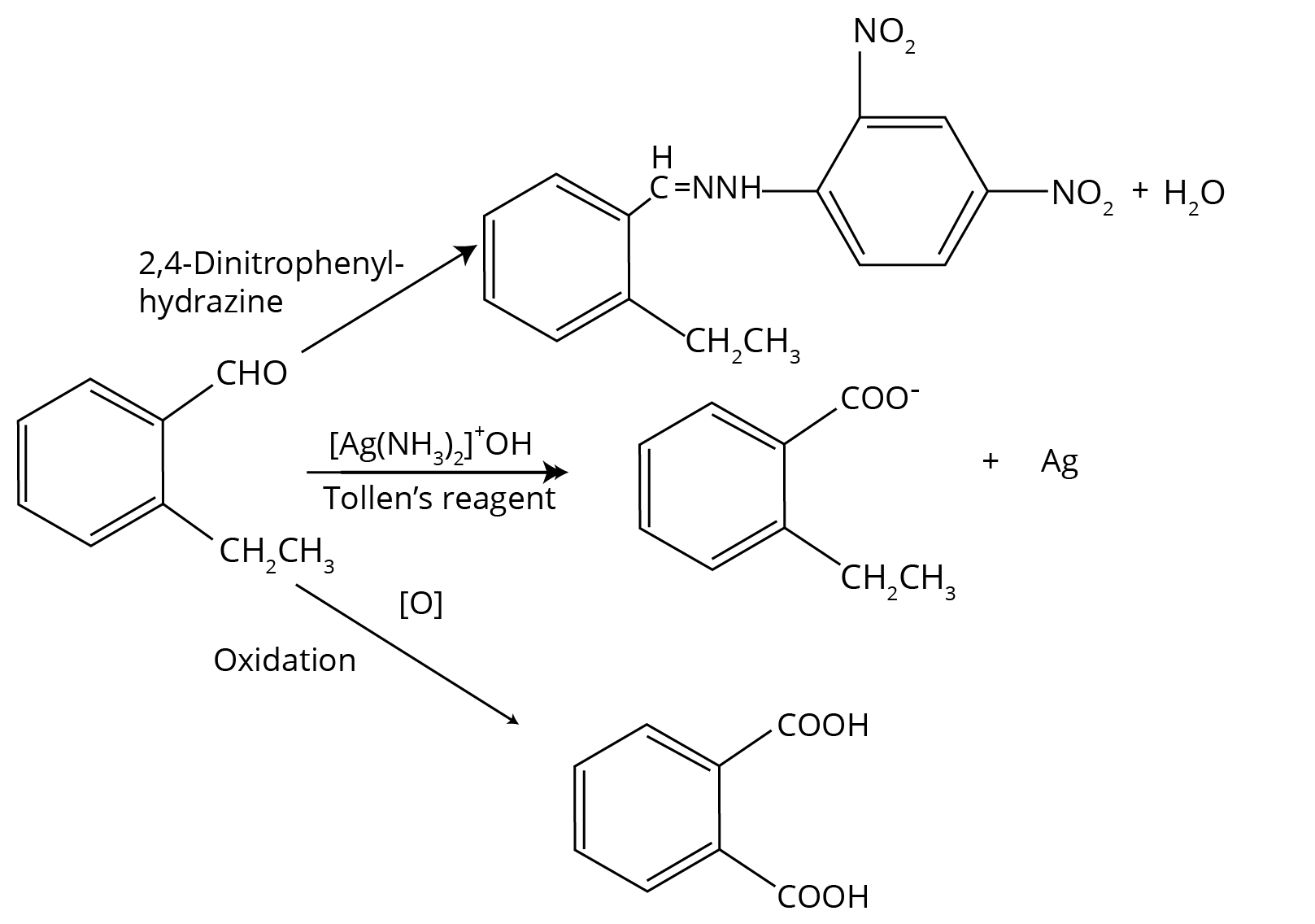
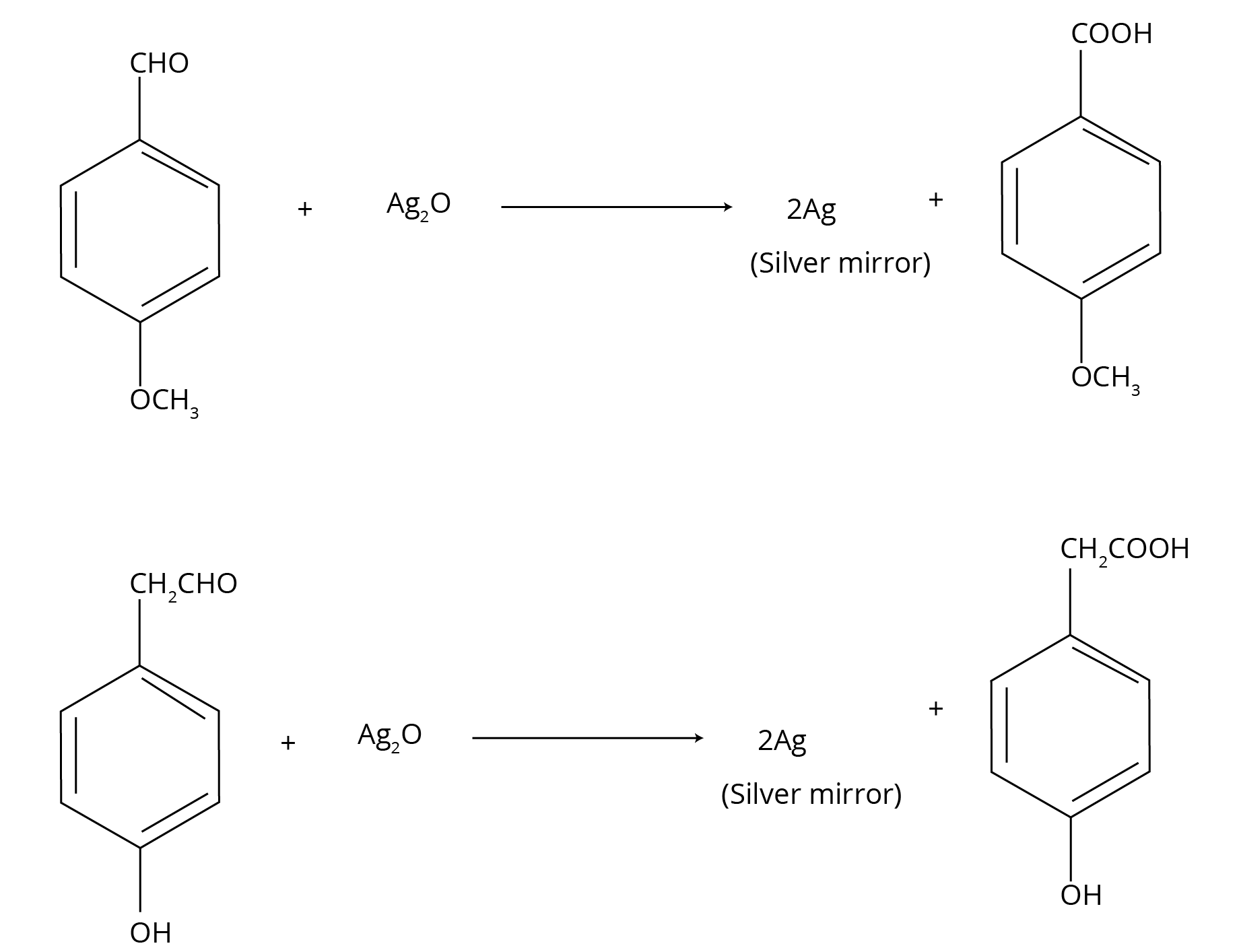
- Distinguishing Tests: Chemical tests to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones (Tollens' and Fehling's test) and specific types of carbonyl compounds.
- Acidity of Carboxylic Acids: Questions based on the effect of substituents on acidity are very common.
2. Which reactions from this chapter are frequently asked as 3-mark or 5-mark questions in the CBSE board exams?
Based on previous years' trends, the following named reactions are frequently featured in long-answer questions:
- Aldol Condensation: Often asked with its complete mechanism or as part of a conversion problem.
- Cannizzaro Reaction: Especially its application for aldehydes without α-hydrogen.
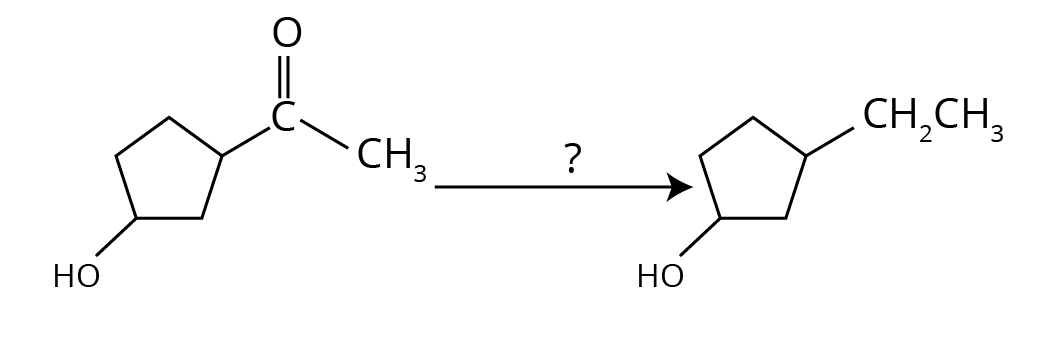
- Clemmensen and Wolff–Kishner Reductions: A comparative question on their reagents, conditions (acidic vs. basic), and applications is a board favourite.
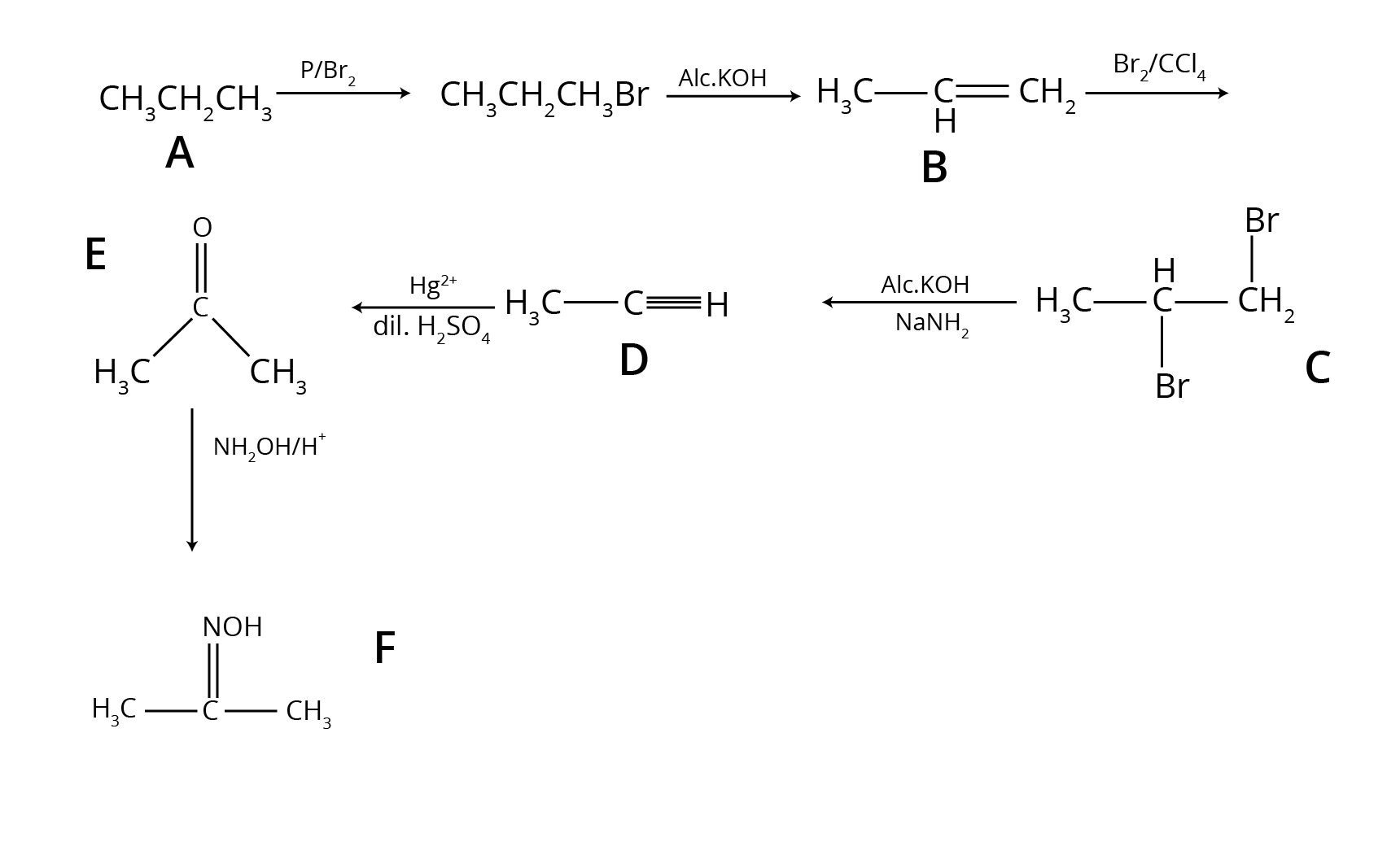
- Multi-step Conversions: Problems that require using a sequence of reactions, such as converting benzene to benzoic acid or ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal.
Practising these with their mechanisms and conditions is vital for scoring well.
3. How should a student answer a question on distinguishing between an aldehyde and a ketone for full marks in the board exam?
To secure full marks for a distinguishing test question as per the CBSE 2025-26 marking scheme, your answer must include three parts for each test:
- Test Name: Clearly state the test used, e.g., Tollens' Test (Silver Mirror Test).
- Observation: Describe what is visually observed. For example, with an aldehyde, state that a bright silver mirror is formed on the inner side of the test tube. With a ketone, state there is no change.
- Inference/Reaction: Write the balanced chemical equation showing the oxidation of the aldehyde and reduction of the Tollen's reagent.
A common alternative is Fehling's Test, where aliphatic aldehydes give a red-brown precipitate of Copper(I) oxide, while ketones and aromatic aldehydes do not.
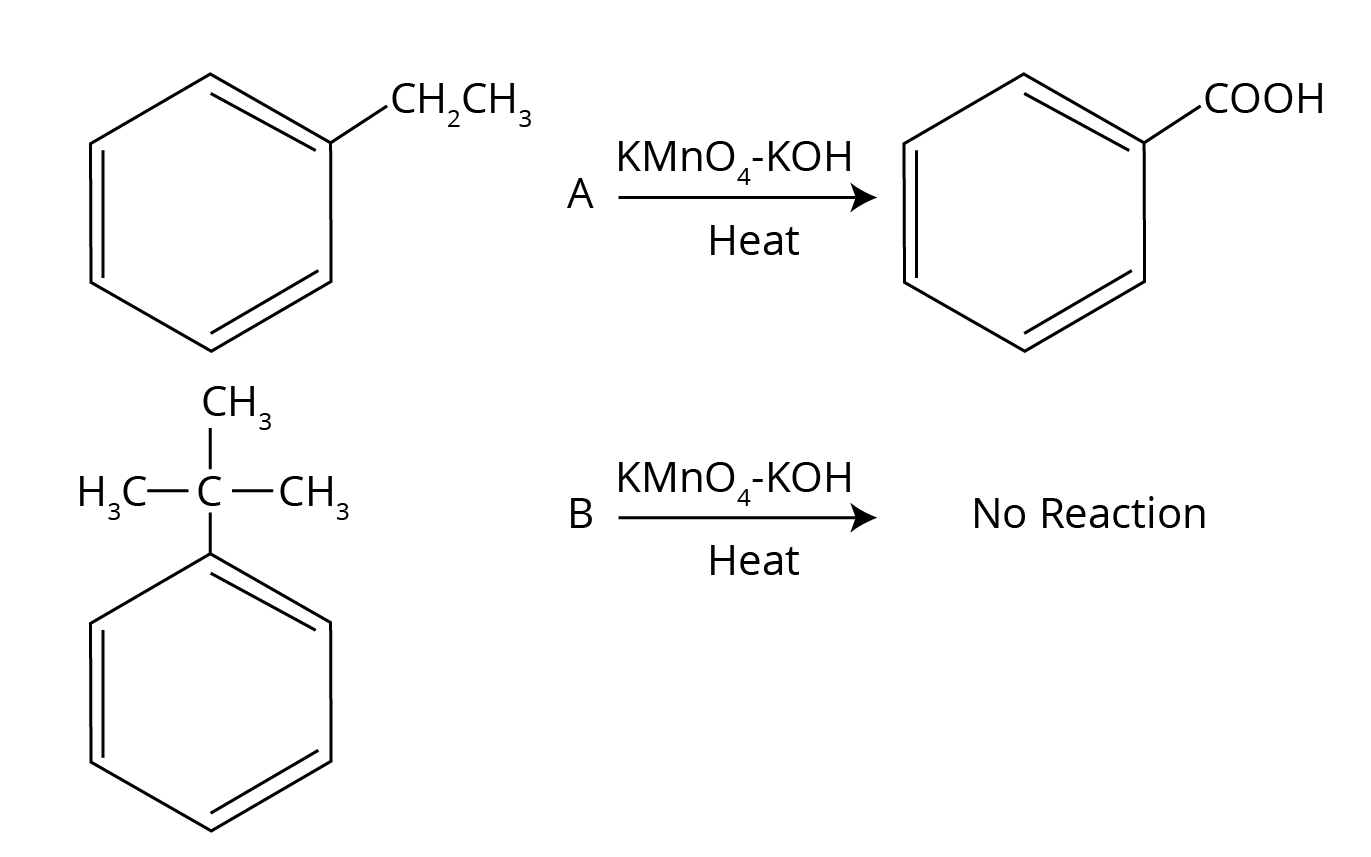
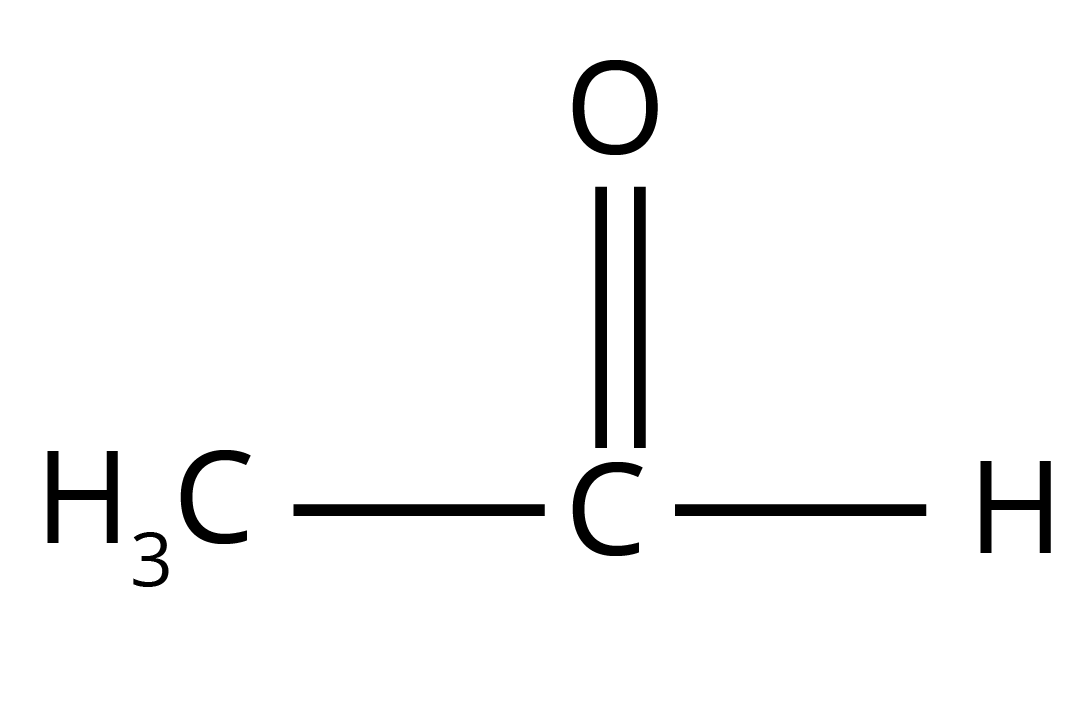
4. Why are aldehydes generally more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic addition reactions? How should this be explained in an exam?
This is a very common 'Give Reason' question. Your explanation should cover two key factors:
- Steric Factor: The carbonyl carbon in an aldehyde is bonded to a hydrogen atom and one alkyl group, making it less crowded. In a ketone, it is bonded to two bulkier alkyl groups, which sterically hinder the approach of a nucleophile.
- Electronic Factor: Alkyl groups are electron-donating (+I effect). In ketones, two such groups decrease the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon, making it less electrophilic. Aldehydes have only one such group, so their carbonyl carbon is more electrophilic and readily attacked by nucleophiles.
Therefore, due to both lesser steric hindrance and greater electrophilicity, aldehydes are more reactive.
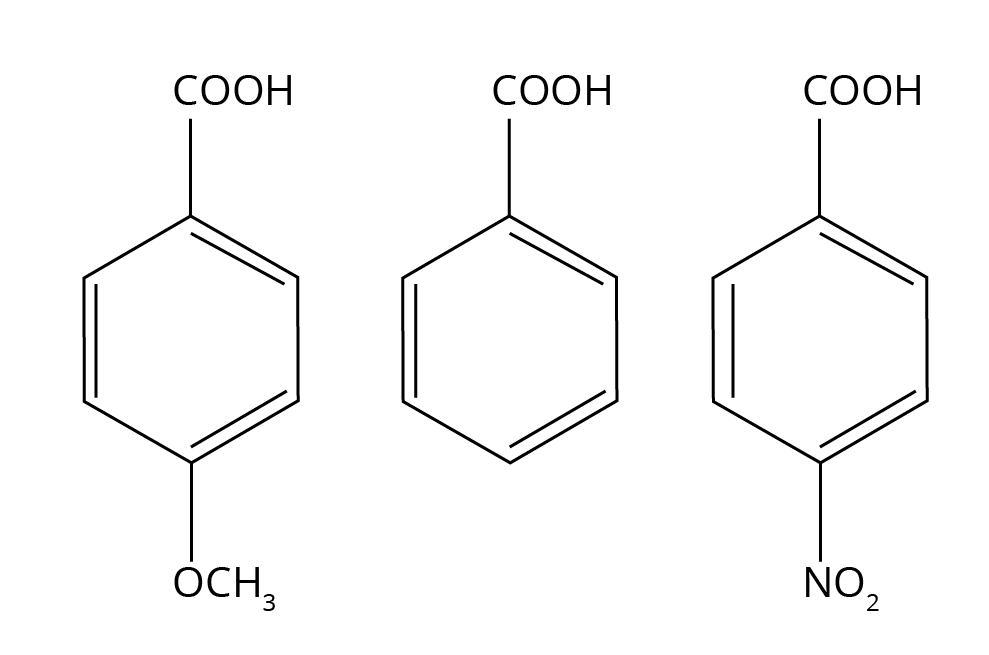
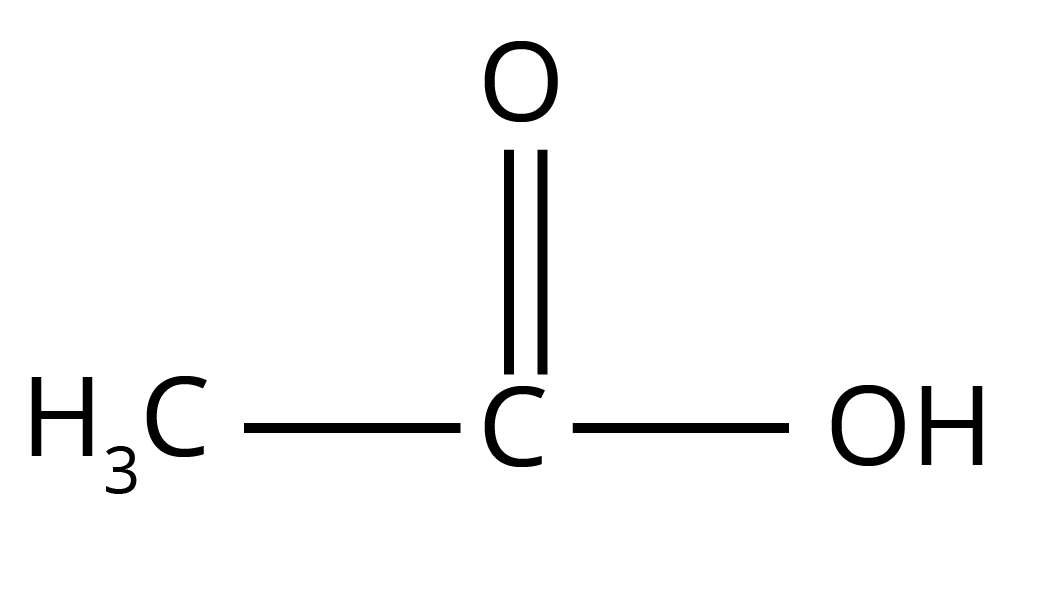
5. How do electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups affect the acidity of carboxylic acids? Explain with an example.
The acidity of a carboxylic acid depends on the stability of its conjugate base (carboxylate ion) after donating a proton.
- Electron-Withdrawing Groups (EWGs): Groups like -NO₂, -CN, or halogens (-Cl, -F) increase acidity. They pull electron density away from the carboxyl group, dispersing the negative charge and stabilising the carboxylate ion. This makes the release of a proton (H⁺) easier. For example, Trichloroacetic acid (Cl₃CCOOH) is a much stronger acid than acetic acid (CH₃COOH).
- Electron-Donating Groups (EDGs): Groups like alkyl groups (-CH₃, -C₂H₅) decrease acidity. They push electron density towards the carboxyl group, intensifying the negative charge and destabilising the carboxylate ion. This makes proton release more difficult. For example, Formic acid (HCOOH) is stronger than acetic acid (CH₃COOH).
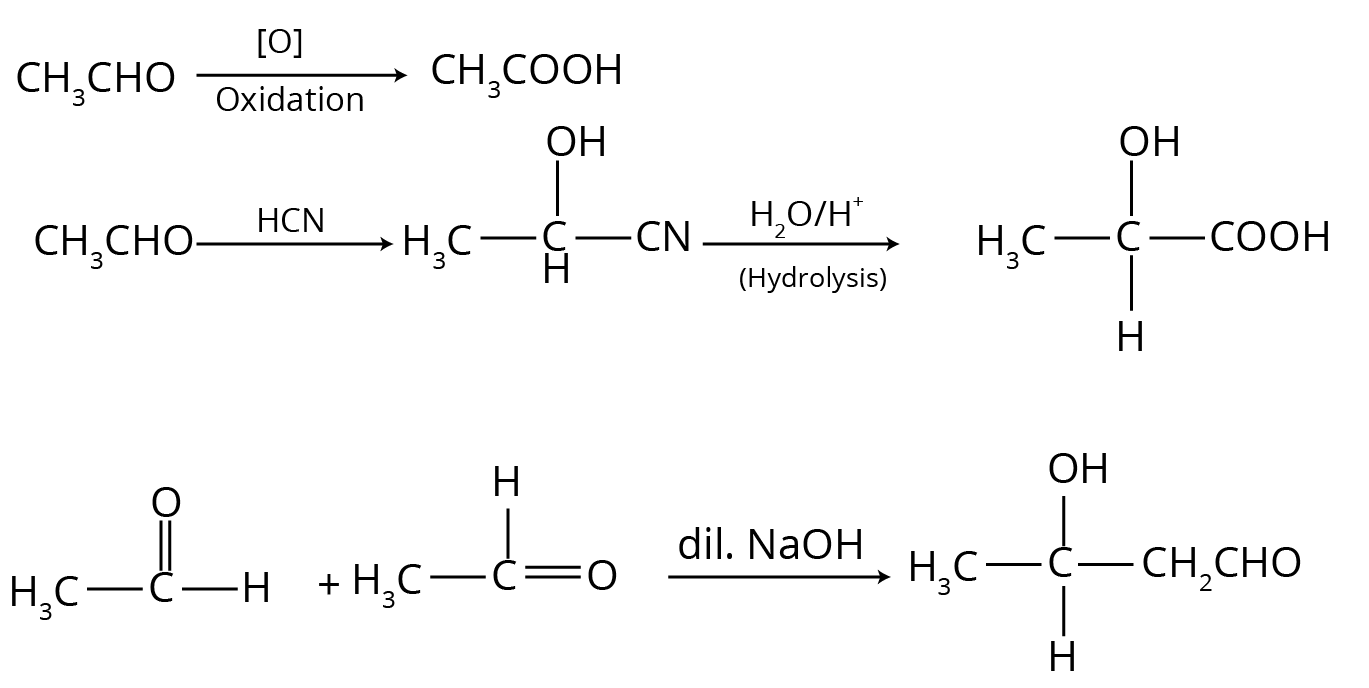
6. What is the fundamental difference between the Aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction?
The key difference lies in the presence or absence of an α-hydrogen atom (alpha-hydrogen) in the aldehyde:
- Aldol Condensation: Occurs in aldehydes and ketones that possess at least one α-hydrogen. In the presence of a dilute base (like NaOH), these compounds undergo self-condensation to form β-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones (aldols).
- Cannizzaro Reaction: Occurs in aldehydes that do not have any α-hydrogen (e.g., formaldehyde, benzaldehyde). In the presence of a concentrated base, these aldehydes undergo a self-oxidation-reduction (disproportionation) reaction to produce a molecule of alcohol and a molecule of the salt of a carboxylic acid.
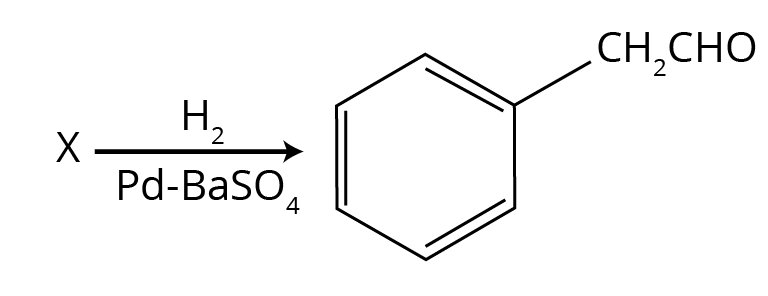
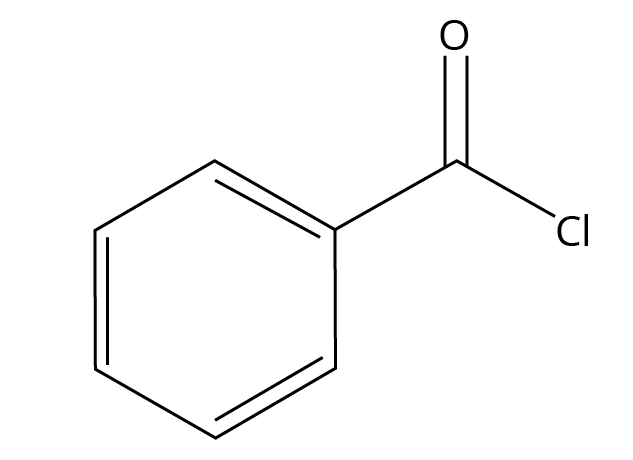
7. For the CBSE exam, what is the role of BaSO₄ in Rosenmund reduction?
In the Rosenmund reduction, where an acid chloride is reduced to an aldehyde using H₂ gas and a Palladium catalyst, Barium Sulphate (BaSO₄) acts as a catalytic poison. Its role is to partially deactivate or 'poison' the palladium catalyst. This is critical because it prevents the over-reduction of the aldehyde formed into a primary alcohol. Without BaSO₄, the reaction would proceed all the way to the alcohol, failing to isolate the desired aldehyde product.
8. What are some expected 'Give Reason' type questions from this chapter for the board exams?
Apart from the reactivity of aldehydes vs. ketones, some high-probability 'Give Reason' questions are:
- Why is the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones lower than corresponding alcohols but higher than hydrocarbons? (Answer relates to dipole-dipole interactions vs. hydrogen bonding).
- Why is p-chlorobenzoic acid a stronger acid than benzoic acid? (Answer relates to the -I effect of chlorine).
- Why does benzaldehyde not give a positive Fehling's test? (Answer: Fehling's is a milder oxidising agent than Tollens' reagent).
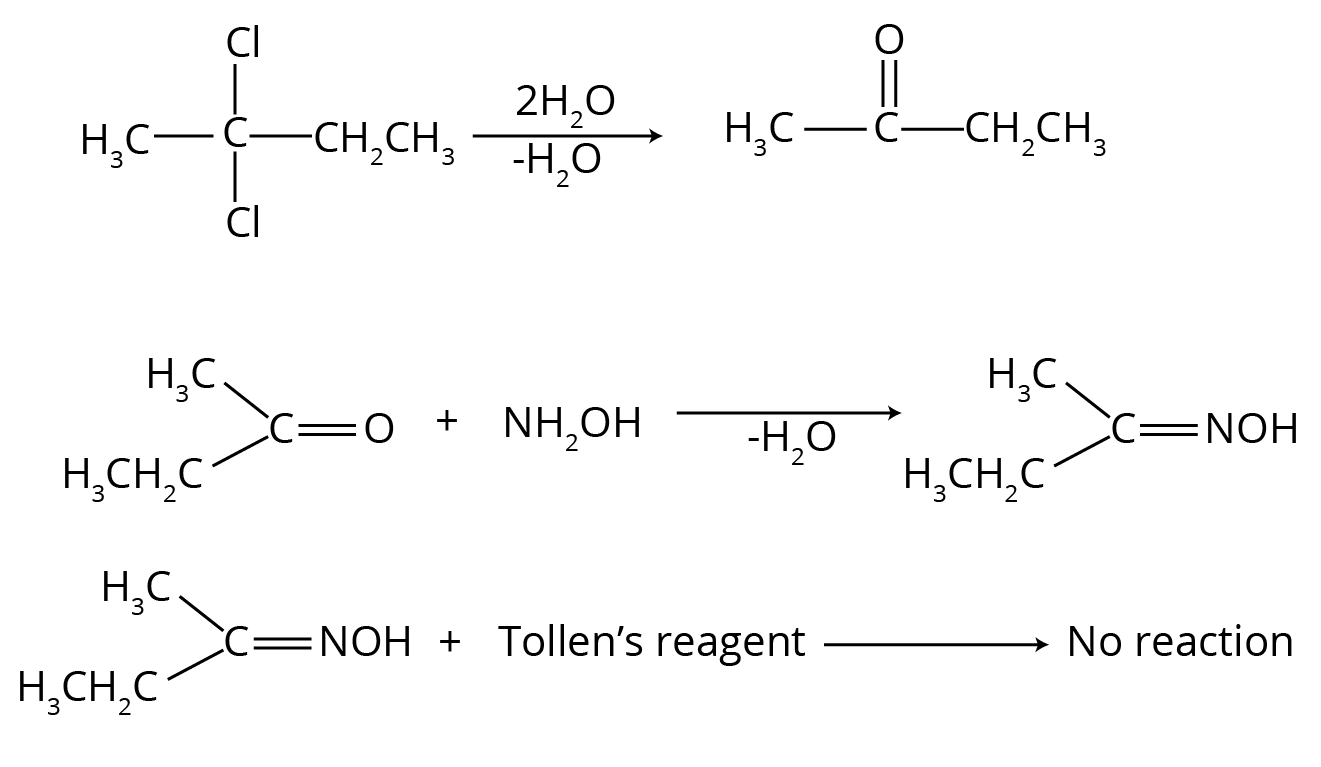
- Why are hydrazones of aldehydes prepared in a weakly acidic medium, not a strongly acidic one? (Answer: In strong acid, hydrazine gets protonated and loses its nucleophilicity).
9. How can a student strategically prepare for the important conversion questions from this chapter?
To master conversions from Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids, follow this strategy:
- Map the Reactions: Create a chart connecting different functional groups. For example, how to get from an alkyne to an aldehyde, or from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid.
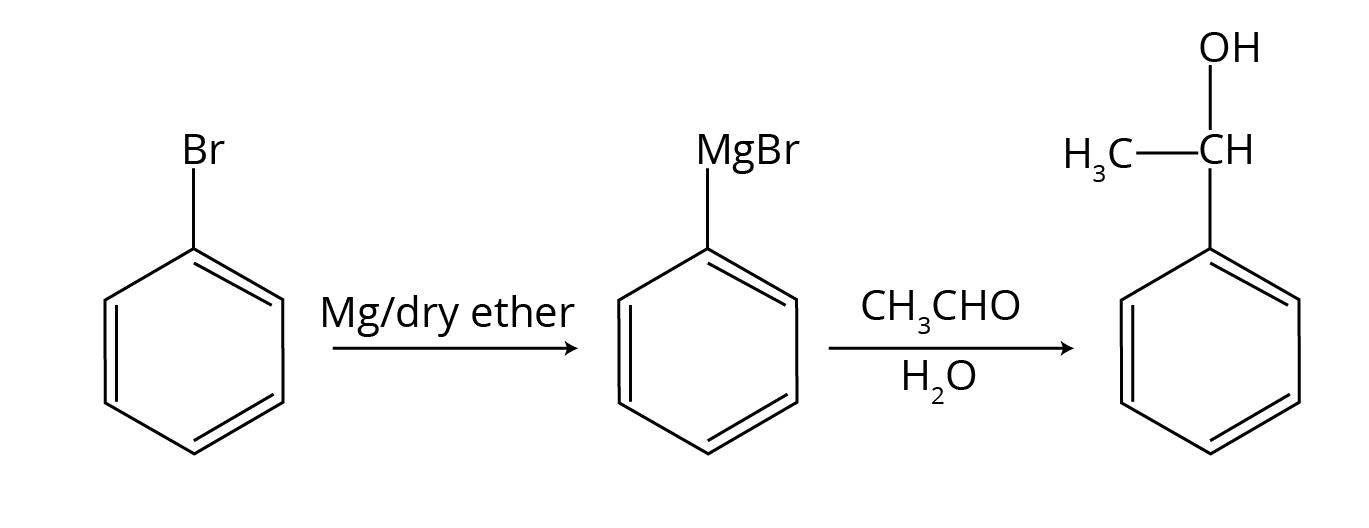
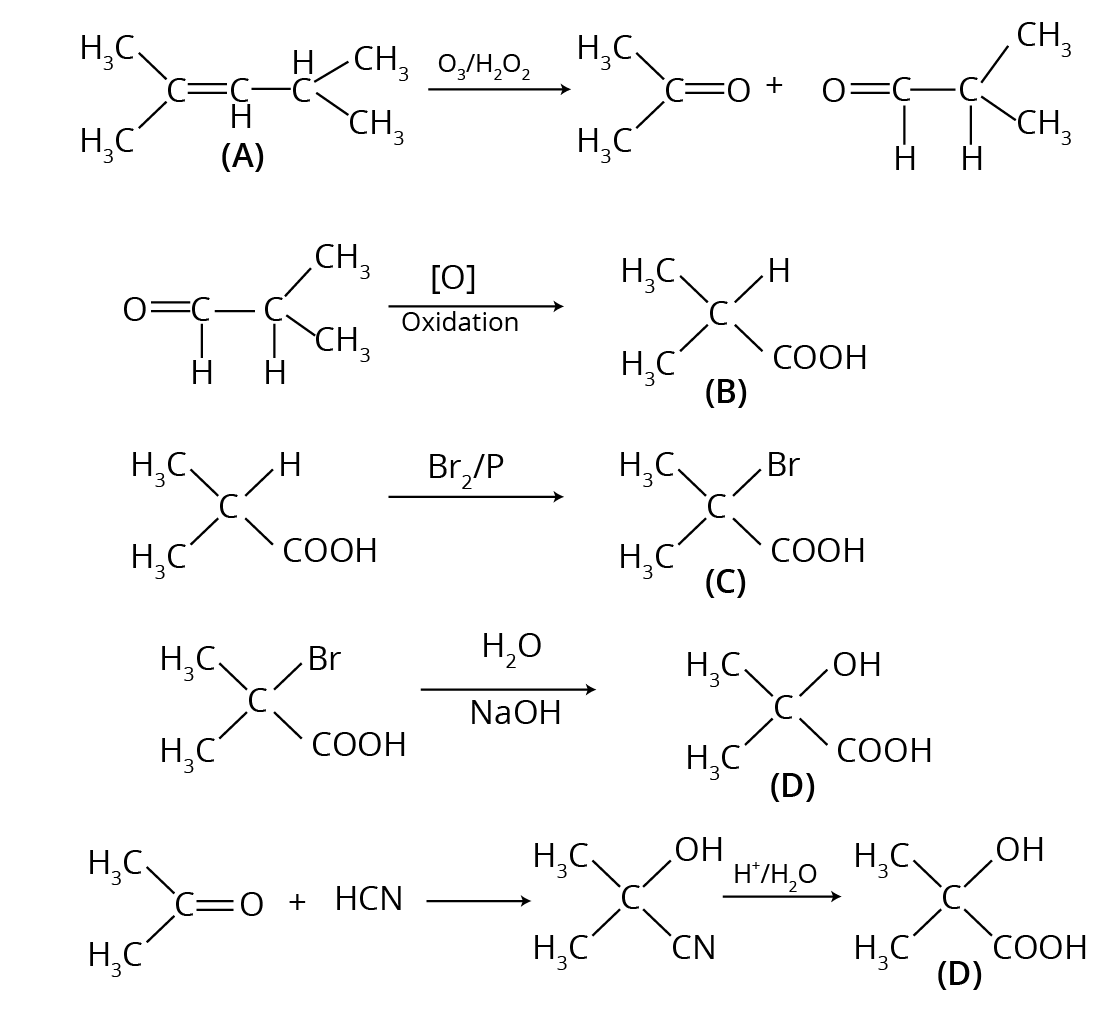
- Focus on Step-up/Step-down Reactions: Understand which reactions increase the carbon chain length (like using Grignard reagent) and which decrease it (like haloform reaction or decarboxylation).
- Practise Named Reactions as Tools: View reactions like Rosenmund, Stephen, and Clemmensen not just as definitions but as specific tools to achieve a certain conversion (e.g., acid chloride to aldehyde).
- Solve PYQs: Work through the last 5-7 years of CBSE papers to understand the patterns and common conversion pathways asked in exams.