Data Handling and Representation Class 6 important questions with answers PDF download
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 6 Maths Data Handling and Representation - 2025-26
1. What is data handling in Class 6 Maths Chapter 4?
Data handling means collecting, organizing, and presenting information in a way that makes it easy to understand. In Vedantu’s explanation, this includes tally marks, bar graphs, pictographs, and more.
2. Why is learning data handling in maths important for Class 6 students?
It helps students understand how to organise numbers and represent them visually, which is useful for making sense of real-life situations like surveys or analysing scores.
3. What is the difference between raw data and organised data in Class 6 Chapter 4?
Raw data is unorganised information collected as it is, while organised data is arranged neatly in tables or charts for better understanding.
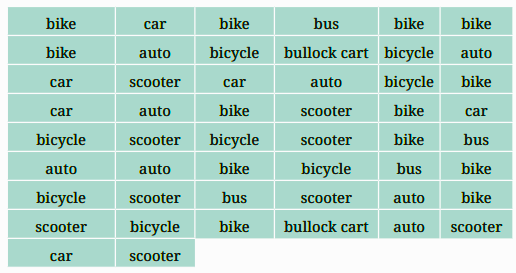
4. How do tally marks help in Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Data Handling?
Tally marks make counting easy by grouping data into sets of 5, which saves time and avoids errors during calculations.
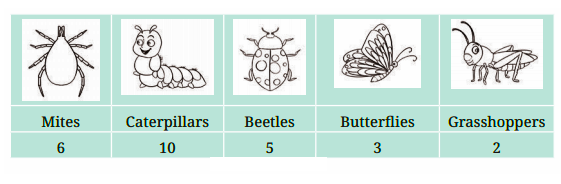
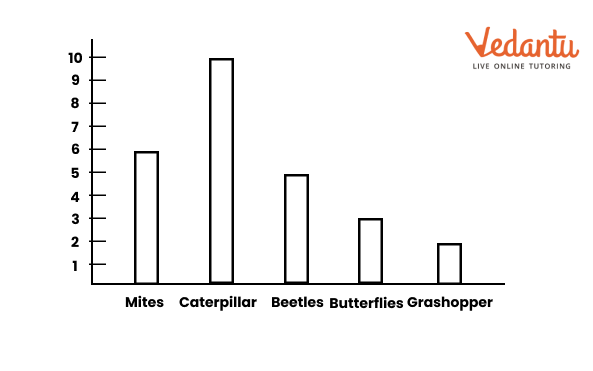
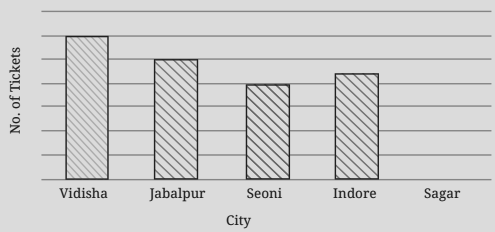
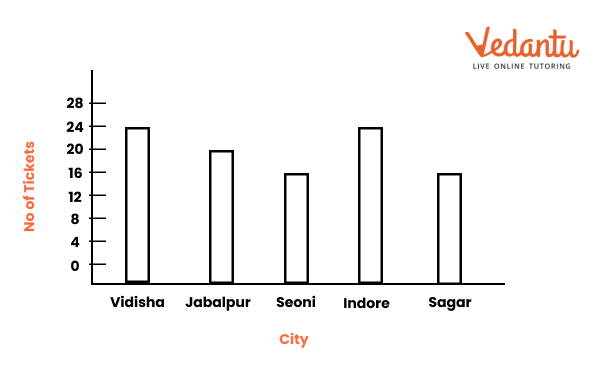
5. What is a bar graph, and why is it important in Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Data Representation?
A bar graph is a chart that uses bars to show data. It is important because it makes comparing categories (like marks or sales) simple and visually appealing.
6. What is the role of frequency tables in Class 6 Maths Chapter 4?
Frequency tables organise data by showing how often each number or category appears, making the data easy to analyse.
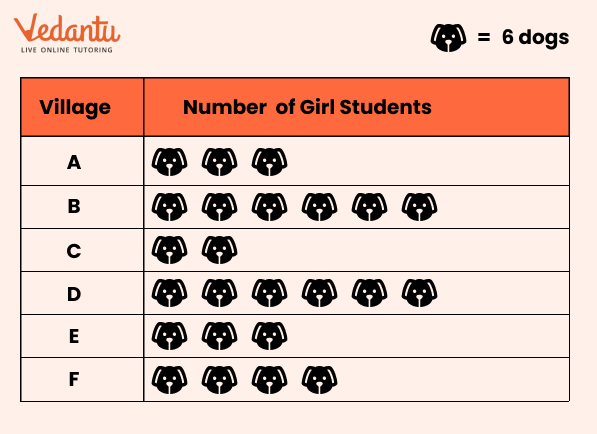
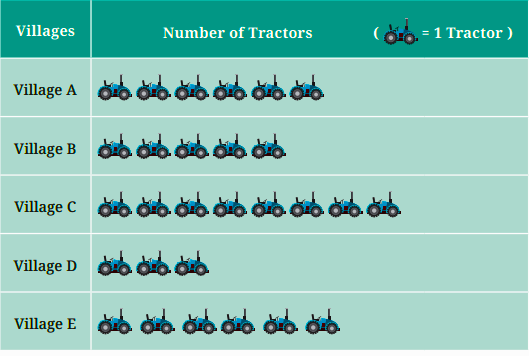
7. How is a pictograph different from a bar graph in Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Data Representation?
A pictograph uses pictures or symbols to represent data, while a bar graph uses bars. Pictographs are more colourful and fun, but bar graphs are better for precise data.
8. Can you explain the term ‘range’ in Class 6 Maths Chapter 4?
The range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a data set. It tells us how spread out the data is.
9. What are the most important questions from Vedantu’s Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 for exams?
Focus on questions about drawing bar graphs, creating frequency tables, and calculating range. These topics are the most asked in exams.
10. How does Vedantu make Maths Chapter 4 Data Handling easier for Class 6 students?
Vedantu simplifies the chapter with clear explanations, solved examples, and fun practice questions that build confidence and clarity in data handling.