




Nitrogen: Atomic Structure, Properties, and Everyday Examples
Have you ever listened to nitrogen gas? You have definitely played with air balloons. What gas is filled in those balloons? You will be able to learn and clear all your doubts related to nitrogen in this learning material. So, let's start with the basic knowledge of nitrogen gas.
Nitrogen is an element on the periodic table. It is a colourless, odourless, and tasteless gas. It Is a part of all living things.

The Element Symbol of Nitrogen
Nitrogen makes up 78.1% of our planet earth’s atmosphere. Nitrogen gas is not a metal. It is an inert gas. The atomic number of Nitrogen is 7. It can also be found in various minerals. Also known to be the seventh most common element in our universe. It can be found in human DNA, stars, and animals. This gas also helps plants grow.
What is the Chemical Symbol of Nitrogen Gas?
Nitrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 7. N is the chemical symbol of Nitrogen gas. It is non-metal. It is used in the chemical industry for many purposes as it is one of the lightest gas in all elements.
The Cycle of Nitrogen Gas
Bacteria play a vital role in the process. When the soil absorbs the bacteria, different bacteria help it change its states so that it can be absorbed by the plants later. Plants are an important source in providing nitrogen to the animals when animals feed on the plants.
Different Stages of the “Nitrogen Cycle” Process are
Fixation
During this stage, the bacteria change nitrogen into ammonium. It is the primary stage of the cycle.
Nitrification
This is the method by which ammonium gets turned into nitrates by bacteria. Nitrates are what the plants can then absorb.
Assimilation
This is how plants get nitrogen. They absorb nitrates from the soil into their roots. Then the nitrogen gets utilised in amino acids, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll.
Ammonification
This is a part of the decaying process. When a plant or animal dies, decomposers like fungi and bacteria turn the nitrogen back to ammonium so it can re-enter the organic process.
Denitrification
Extra nitrogen within the soil gets replaced out into the air. There are special bacteria that perform this task similarly.
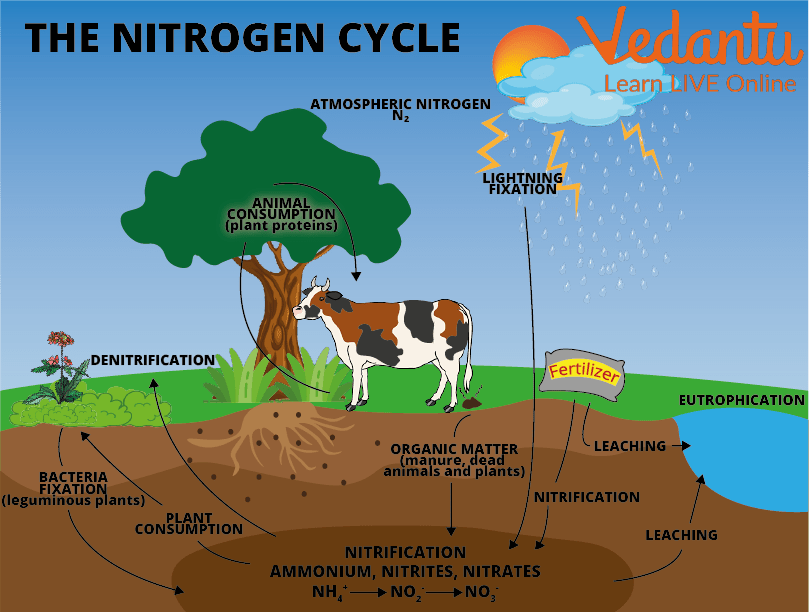
The Nitrogen Cycle
Features and Uses of Nitrogen Gas
Nitrogen must be combined in compounds to be utilised by living things. Nitrogen compounds help plants grow and structure protein in animals.
Nitrogen becomes a liquid at very low temperatures. in this state, it's useful for freeze-drying food and keeping foods cold once they are transported over long distances. The human body contains almost 3% of Nitrogen Gas.
The two most significant compounds of nitrogen that are utilised in factories or businesses are ammonia and aqua fortis. Ammonia may be a gas that's used to prepare many other nitrogen compounds. aqua fortis may be a liquid that's used to produce fertilisers, dyes, drugs, and explosives.
Properties of Chemical Symbol of Nitrogen Gas
Nitrogen Gas turns into a liquid at -195.8°C and turns into a solid at -210°C. If it's compressed, it will be changed into a liquid without making it cold.
It usually doesn't combine with other atoms thanks to its strong bond. The bond prevents it from reacting. Lithium is one of the sole chemical elements that react with nitrogen without being heated. Magnesium can burn in nitrogen. Nitrogen also makes blue electric sparks. The blue colour is caused by the atoms being excited. once they get normal again, they release light. When nitrogen is worked up, it reacts with many things that it doesn't normally react with.
Where is Nitrogen Gas Found? What Are Its Uses?
The primary industrial use of nitrogen is to form ammonia. The method by which nitrogen is used to form ammonia is termed the Haber process, where nitrogen and hydrogen are combined to create NH3 (ammonia). Ammonia is then used in factories to create fertilisers, acid, and explosives.

Factory that Produces Nitrogen Gas
Many explosives contain nitrogen like TNT, nitroglycerin, and gunpowder. Some applications of nitrogen gas include the preservation of fresh food, the manufacturing of chrome steel, reducing fire hazards, and as a part of the gas in incandescent light bulbs.
Liquid nitrogen is employed as a refrigerant to keep things cold. it's also employed in the cryopreservation of biological samples and blood.
Scientists often use atomic number 7 when performing coldness science experiments. Even though there's most nitrogen within the air, there's little within the crust. It may be found in some fairly rare minerals like saltpetre.
Nitrogen can even be found in all living organisms on the earth including plants and animals. It plays a vital role in proteins and nucleic acids.
Summary
The chemical element with the atomic number 7 and the letter N is known as nitrogen. The lightest element in group 15 of the periodic table, often known as the pnictogens, nitrogen is a nonmetal. It is a typical element in the cosmos, believed to be eighth in the Milky Way and the Solar System in terms of overall abundance. Although nitrogen has the chemical formula N, it only exists as a molecule of two ions, which is why the chemical symbol for nitrogen gas is written as N2.
FAQs on What Is the Symbol of Nitrogen in Chemistry?
1. What are the three main properties of nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a component of all biological tissues and makes up 78 percent of the atmosphere of the earth. Since it is a component of DNA, a part of the genetic code, nitrogen is a necessary element for life. Most nitrogen molecules are found in the air. Nitrogen is present as nitrates and nitrites in soil and water. The nitrogen cycle involves each of these elements, and they are all interrelated. Its three main properties are colourless, odourless, and tasteless gas. It is a part of all living things.
2. Name the different stages of the nitrogen cycle. What are the common explosives in which nitrogen is found?
Nitrogen is a common normally colourless, odourless, tasteless, and mostly diatomic nonmetal gas. It has five electrons in its outer shell, so it is trivalent in most compounds. The different stages of the nitrogen cycle are Fixation, Nitrification, Immobilisation, and Denitrification.
Simply put, nitrogen is an essential component of an explosive because when ignited, its very unstable molecules will quickly disintegrate into nitrogen gas, an absurdly stable compound. The common explosives in which nitrogen is found are TNT, nitroglycerin, and gunpowder.























