




An Overview
General equilibrium is a theory that attempts to explain the functioning of an economy's demand, supply, and price factors. It is not related to a single or specific market. This theory was developed by French economist Leon Walras in the late 19th century. This theory is also known as Walrasian General Equilibrium.
General Equilibrium Theory
General Equilibrium Macroeconomics
The economy is in general equilibrium when product prices make each demand equal to its supply. The following are some conditions in this market:
All the consumers maximise their satisfaction.
All the producers maximise their profit.
The total amount demanded equals the total amount supplied in the markets.
Assumptions of General Equilibrium Theory
The income of the consumers is constant.
The tastes and preferences of the consumers are constant.
Returns to scale are constant.
All the firms operate under similar cost conditions.
The production techniques are the same.
How does General Equilibrium Theory Work?
The general equilibrium theory is the same as economic equilibrium. Both theories are used to study economics. According to these theories, the interaction of demand and supply will lead to a whole general equilibrium.
Walras explained the concept of general equilibrium theory by describing the simple economy. In the economy, two goods could be exchanged. Everyone in the economy is assumed to be a buyer of one product and a seller of another.
Under this model, demand and supply would be interdependent as goods consumption will depend on the income derived from selling the goods. The price of the goods would be decided according to the bidding process. He explained this in terms of individual sellers. According to him, there can be no exchange of goods until the equilibrium price is reached.
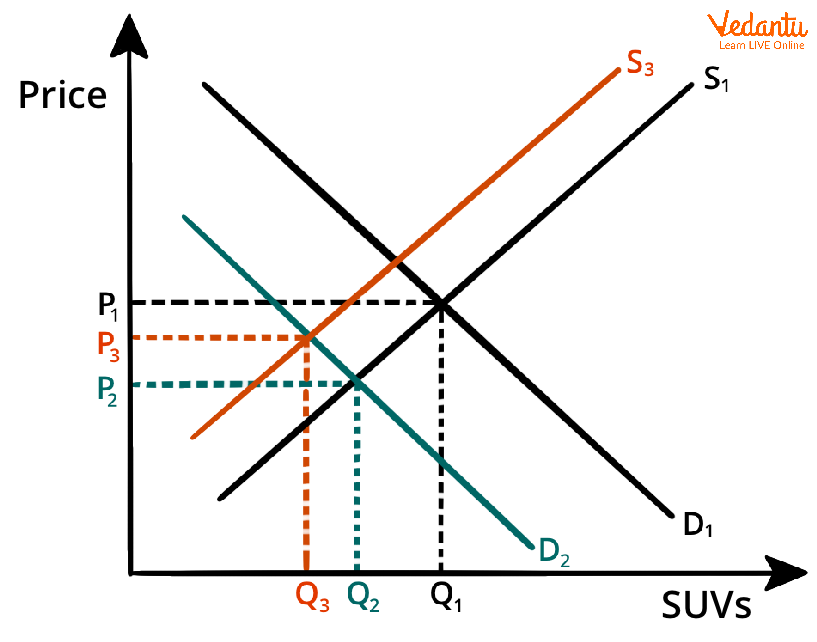
How General Equilibrium Theory Works
General Equilibrium Analysis
General equilibrium analysis is concerned with determining prices and quantities in interconnected markets.
Objectives of General Equilibrium Analysis
It provides a theoretical tool to understand an economy's working, structure, and major contributors.
This theory also analyses the inter-relationship among various sectors of an economy.
This theory is also applied to determine the effects of economic disturbances.
Uses of General Equilibrium Analysis
This theory is used in the development of various programs in economics.
Monetary theory and policy have been transformed with the introduction of this theory.
Limitations of General Economic Analysis
This theory is based on unrealistic assumptions which are contrary to real situations in an economy.
This theory is based on the assumption that producers and consumers produce and consume the same products. But in reality, they have different opinions.
The Power Equilibrium Theory
Power equilibrium theory, also known as balance of power, is an equilibrium theory. It means equilibrium between the states and should prevent any one of them from becoming strong to impose powers on the rest.
Assumptions of Power Equilibrium Theory
According to this theory, states are determined to protect their rights and interests.
The power position of the states can be measured with a degree of accuracy.
The statesmen can make important decisions based on power considerations.

Power Equilibrium Theory
Conclusion
From the above discussion, general equilibrium can be achieved only when the demand for the product is equal to the supply of the product. Moreover, the consumer's decision regarding the product and the producer regarding the production of each product should be skilful. General equilibrium theory is considered the most complete existing model of economics. This theory views the economy as a vast system of mutually interdependent markets and makes one aware of the complexity of the real world. Moreover, this theory also leads to the optimal allocation of resources.
FAQs on General Equilibrium Theory
1. What is the General Equilibrium Theory in economics?
General Equilibrium Theory is a core concept in macroeconomics that examines how supply and demand interact across an entire economy, considering all markets simultaneously. Unlike partial equilibrium, which studies a single market in isolation, this theory provides a holistic view, showing how different markets are interconnected and tend towards a state of balance, or 'general equilibrium'.
2. How does General Equilibrium analysis differ from Partial Equilibrium analysis?
The main difference lies in their scope. Partial Equilibrium analysis focuses on a single market, assuming everything else in the economy remains constant (ceteris paribus). For example, it would only look at the market for cars. In contrast, General Equilibrium analysis studies the interconnectedness of all markets at once. It analyses how a change in the car market (e.g., a new tax) would affect the steel market, the labour market, the fuel market, and consumer spending power, providing a complete picture of the economic impact.
3. Who is credited with developing the General Equilibrium Theory?
The foundational concept of General Equilibrium Theory is credited to the French economist Léon Walras. In his work, he mathematically demonstrated how a set of prices could exist that would lead to a 'market clearing' state across all markets in an economy. This framework is often referred to as the Walrasian general equilibrium. Later economists like Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu further refined the theory.
4. What are the core assumptions for a General Equilibrium to exist?
For the theoretical model of General Equilibrium to hold, several key assumptions are made:
Perfect Competition: No single buyer or seller can influence market prices.
Rational Agents: Consumers aim to maximise utility, and producers aim to maximise profits.
Complete Information: All participants have full knowledge of prices and quality.
Flexible Prices: Prices can freely adjust based on supply and demand without any friction.
No Transaction Costs: There are no costs associated with buying or selling goods.
5. Why is the concept of General Equilibrium important for economic policy-making?
The concept of General Equilibrium is crucial for policymakers because it helps them understand the wide-ranging, ripple effects of their decisions. For instance, when a government imposes a tariff on imported steel, a general equilibrium analysis can predict its impact not just on the steel industry but also on car manufacturing, construction costs, employment levels in related sectors, and overall consumer prices. It provides a comprehensive framework for assessing the total economic consequences of a policy.
6. How is a state of 'market clearing' achieved in General Equilibrium?
A state of market clearing is achieved when a specific set of prices is established for all goods and services in the economy, such that the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied in every single market. At this point, there are no shortages or surpluses anywhere in the system. The economy is in a stable state where all resources are efficiently allocated based on the collective actions of all producers and consumers.
7. What are the main limitations or criticisms of the General Equilibrium Theory?
While powerful, the theory has significant limitations. The primary criticism is that its assumptions are unrealistic. Real-world markets are rarely perfectly competitive, information is not complete, and prices can be 'sticky'. Furthermore, solving for general equilibrium in a large, complex economy is practically impossible due to the immense amount of data and computational power required. Therefore, it is often viewed more as a theoretical benchmark for economic efficiency rather than a practical tool for prediction.





































