




An Introduction to the 2008 Market Crash
The 2008 market crash, also known as the financial crisis of 2008, was the most serious economic crisis that happened in the early 21st century. It is considered to be the worst financial disaster since the Great Depression of the 1930s. This began in 2007 and grew into a full-blown international crisis.
Immoderate risk-taking by financial institutions, housing bubble, and predatory lending targeting low-income groups were some factors that contributed to the market crash. This crisis began in the US and later spread to the whole world. The market crash of 2008 took only 18 months to worsen the whole economic situation. The stock market crash happened on 29 September 2008 due to the fall of the Dow Jones Industrial Average.

2008 Market Crash
2008 Market Crash Reason
The financial crisis was caused due to deregulation in the financial world. Some of the causes are listed below:
Housing Bubble - A housing bubble is when an asset's price increases above its real value. This is considered the major cause of the crisis. In 2008, average housing prices had declined which made the borrowers default to avoid higher payments.
Predatory Lending - Predatory lending means when lenders impose unfair, deceptive, and abusive loan terms on the borrowers. During 2008, various tactics were used to push homeowners into a complicated and risky state.
Risky Wall Street Behaviour - Lenders found another way to make money along with issuing mortgages. This is done through securitization. In this, subprime lenders bundled loans together and sold them to investment banks which further sold them to investors.
Bad Economic Assumptions - Before the crisis, it was assumed that home prices would never decline. This led various underwriters and investors in mortgage-backed securities on the assumption that these were risk-free.
A Broken International Monetary System - Another reason for the financial crisis was the trade imbalance between the developed and developing countries. This is done by keeping their currencies artificially depressed versus U.S dollars to accumulate massive reserves of dollars.
Effects of the Market Crash 2008
No country in the world, developed or developing, has escaped the effect of this financial crisis.
National Levels:
Indian economy began to slow down in 2007-08. The growth in GDP moved down to 5.8% from 7.8% during the global financial crisis.
Foreign institutional investors started selling the shares of Indian companies to meet the liquidity requirements. This was done to pull out capital from India.
The capital outflow by FIIs led to a drastic fall in the value of the Indian rupee. The Indian rupee depreciated to Rs. 49 in October 2008.
The foreign trade balance worsened during the 2008 market crash. Exports declined by 13% in 2008.
International Levels:
The inter-banking market froze completely due to the fear of unknown banks worldwide.
Many banks had to approach emergency funding due to the liquidity crunch.
Many central banks and governments around the globe had started coming together to prevent any further disaster.
There were high rates of unemployment which spiked to 10% by 2009.
Most of the credit facilities tightened their lending rules which makes borrowing difficult for those with financial problems.
The financial crisis also reduced the confidence of the investors in the stock market.
2008 Stock Market Crash
The stock market crash of 2008 was considered the biggest drop in the market. Many best-performing stocks fall in a single day of trading. The market crashed because of the rejection of the bank bailout bill. A bailout is when a business or government provides financial aid to a failing company. All this led to:
Widespread unemployment
The bankruptcy of various institutions
The downfall of many investment firms

Stock Market Crash 2008
Housing Crisis 2008
Many banks in the US were providing loans with low-interest rates to boost the economy. This encouraged the individuals to take more loans. Banks also introduced asset-backed securities, also known as mortgage-backed securities. Afterwards, banks also started lending to borrowers with higher chances of fraud. The credit was given without assessing the ability of the borrower to pay the instalments. Then, borrowers started defaulting. There were several houses in the market, and it became difficult to detect the fraudsters. Thus, all this led to a sudden downfall in the prices of houses.
2008 Subprime Crisis
The subprime mortgage crisis had a terrible impact on the international markets. This was caused by a large decline in US house prices. This occurred when credits were given to borrowers without assessing their financial strength. The mortgage-backed securities were sold to third parties. Lehman Brothers were one of the largest investment banks which became bankrupt during this financial crisis. Some of the causes are as follows:
The inability of the house owners to pay mortgage payments.
Risky mortgage securities.
Inappropriate government policies.
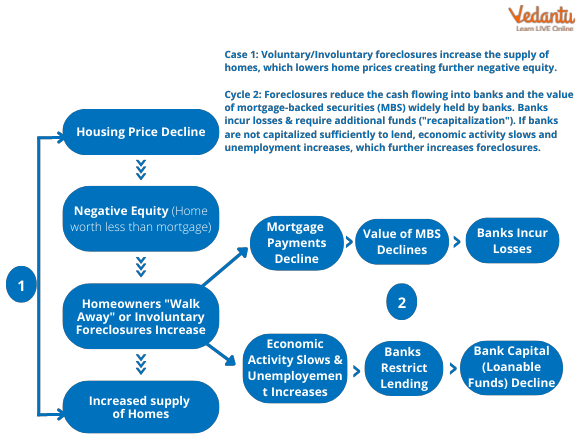
2008 Subprime Crisis
Conclusion
The 2008 Market Crash was the biggest financial disaster that impacted the overall world. This also had a severe impact on the investors. This has changed the lives of people. Some lost their homes as well as their savings. Some had to face long-term unemployment. Banks and financial institutions were equally affected.
FAQs on Stock Market Crash of 2008: The Global Financial Crisis
1. What were the primary causes of the 2008 Stock Market Crash and Global Financial Crisis?
The crisis stemmed from a combination of factors that created a systemic failure. The key causes include:
- The collapse of the U.S. housing bubble, which had been fuelled by years of excessive speculation and rising property values.
- Widespread issuance of subprime mortgages, which were high-risk loans given to borrowers with poor credit histories.
- The creation of complex financial products like Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs), which bundled these risky mortgages together and were sold to investors as seemingly safe assets.
- A significant lack of financial regulation and oversight, allowing banks to take on excessive risk.
- Inaccurate credit ratings from agencies that failed to represent the true risk associated with these mortgage-backed securities.
2. How significantly did the stock market fall during the 2008 crash?
The 2008 crash resulted in a severe and prolonged decline in global stock markets. The U.S. bear market, a key indicator, lasted for about 17 months. Major indices experienced massive drops; for example, the S&P 500 fell by nearly 57% from its peak in October 2007 to its lowest point in March 2009. The bankruptcy of major financial institutions, most notably Lehman Brothers in September 2008, acted as a major catalyst that accelerated the market's decline and spread panic globally.
3. What exactly is a 'subprime mortgage' and how did it trigger a global crisis?
A subprime mortgage is a home loan extended to individuals with poor credit scores who do not qualify for conventional, 'prime' rate loans. These loans typically carry higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk of default. They triggered the global crisis in two main ways:
- Mass Defaults: When the U.S. housing market stalled and interest rates on these mortgages reset to higher levels, a vast number of subprime borrowers could no longer afford their payments and defaulted on their loans.
- Spread of Risk: These risky loans were not held by the original lenders. Instead, they were packaged into complex financial instruments called Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) and sold to banks, pension funds, and investors worldwide. When the defaults occurred, the value of these securities collapsed, causing catastrophic losses for financial institutions globally and freezing the credit system.
4. How did some investors manage to profit from the 2008 market crash?
While the majority of investors suffered huge losses, a small group of individuals and hedge funds profited by correctly predicting the collapse of the housing market. They used financial strategies to bet against the market's health. The primary methods were:
- Short-selling: This involves borrowing and selling stocks of companies that were heavily exposed to the risky mortgage market, with the plan to buy them back at a much lower price after the crash.
- Credit Default Swaps (CDS): They purchased CDSs, which act like insurance policies on mortgage-backed securities. When these securities failed, the holders of the CDSs received massive payouts from their counter-parties. This strategy allowed them to generate enormous profits from the financial collapse.
5. What were the major long-term effects of the 2008 financial crisis on the world economy?
The long-term effects of the 2008 crisis were profound and reshaped the global financial landscape. The key consequences include:
- The Great Recession, which was the most severe economic downturn since the Great Depression of the 1930s, resulting in millions of job losses and a slow, prolonged recovery.
- Sweeping regulatory reforms worldwide, such as the Dodd-Frank Act in the U.S., designed to increase transparency and reduce excessive risk-taking in the financial sector.
- A deep and lasting loss of public trust in banks and other financial institutions.
- The emergence of the European sovereign debt crisis, as several governments had to take on massive debts to bail out their failing banking systems.
6. How was the 2008 financial crisis fundamentally different from the dot-com bubble of 2000?
The two crises were different in their origin and impact. The dot-com bubble of 2000 was primarily an equity bubble, confined to the technology and internet-related stocks on the NASDAQ exchange. When it burst, the losses were mostly contained within the stock market. In contrast, the 2008 crisis was a credit crisis that originated in the housing and banking sectors. Its failure was systemic, as it crippled the global credit system, making it nearly impossible for businesses and individuals to get loans. This credit freeze had a far more devastating and widespread impact on the real economy across the globe.
7. How was the Indian economy affected by the 2008 Global Financial Crisis?
Although India's banking system was largely insulated from direct exposure to subprime assets, the interconnected nature of the global economy meant it was still impacted. The main effects on India were:
- Capital Outflow: Panicked Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) pulled a significant amount of money out of the Indian stock market, leading to a sharp decline in key indices like the Sensex and Nifty.
- Currency Depreciation: The large-scale withdrawal of foreign capital caused the Indian Rupee to depreciate sharply against the U.S. dollar.
- Economic Slowdown: A decrease in global demand led to a slowdown in India's export growth and, consequently, its overall GDP growth rate. However, the impact was less severe than in developed countries due to India's strong domestic consumption and conservative banking regulations by the RBI.























