




Explanation of Building Blocks of The Body
Living organisms are constructed from biological building blocks. The building block of the body is a cell. A biological building block is the smallest element that contributes to the creation of an organism. If the organism is made up of one cell it is known as unicellular and if the organism is made up of more cells it is known as multicellular.
The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. Cells provide structure to our body and perform different functions like healing and repairing wounds. A group of cells join together and form tissue. There are four types of tissue epithelial, muscle, nervous and connective tissue. In this article, we will learn in detail about tissue and cells.
What are Cells?
Cells are a component of life, these are also called structural and functional units of life. Simple bacteria and more complex organisms like people and animals are made from these tiny building blocks. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are among the various types of cells based on complexity:
Prokaryotic: Bacteria and other single-celled, simplest organisms fall under this category. These cells are small with an internal nucleus and compartments.
Eukaryotic: Plant and animal cells are more complicated and are categorised as eukaryotic because they have recognized internal components as well as a real nucleus. One kind of eukaryotic single-celled organism is yeast. Others are typically multicellular.
What are the Main Building Blocks of Tissues and Organs?
Cells are the main building blocks of tissues and organs of the body which are mainly made up of proteins such as:
Tendon and ligament cartilage (collagen and elastin)
The element of muscles that contract (actin and myosin)
nails, hair, and skin (keratin)
Blood proteins (haemoglobin transferrin albumin and globulins)
Enzymes
Hormones
Facts About Cells
The fundamental building blocks of all living things are cells. There are many trillions of cells in the human body, and each one serves a specific purpose.
All living things have cells as their fundamental building blocks.
Cells give the body structure, absorb nutrients from food, and perform critical tasks.
Tissues are made up of a combination of cells that come together to form organs like the heart and brain.
Organelles are a class of useful structures found in our cells.
These organelles perform functions like producing proteins, processing chemicals, and giving the cell energy.
The nucleus, which is located in the centre of the cell, serves as the cell's "control room."
Within the nucleus DNA is present.
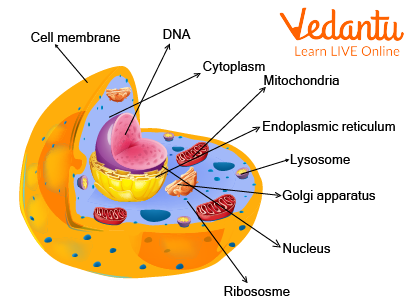
Structures of an Animal Cell
Facts About Tissues
A tissue is a component of an organ in both plants and animals. They are a collection of cells that share the same origins, composition, and purpose. Cells assemble into tissues, which the body uses to carry out specific tasks. The cells have an identical appearance, or nearly so. A tissue's cells perform the same or nearly the same tasks.
The four main kinds are:
Connective tissue
Muscles
Nerves
Epithelial tissue
Organs are composed of various types of tissue. An organ is a heart. It is composed of various tissues. Its myocardium is a type of muscle tissue. It has connective tissue on the outside and inside (endocardium) (pericardium). The heart has valves that ensure the blood flows through the heart in the proper direction. Consequently, the heart is an organ made of various tissues.
Types of Tissues in the Human Body
The four fundamental types of tissue are connective, epithelial, muscular, and nervous.
Connective Tissue:- Other tissues are supported by and bound together by connective tissue. Examples- bone, blood, and lymph tissues. It helps in binding organs and provides support.
Epithelial Tissue:- These are formed by cells that cover the external part of the body. An example is skin. It protects internal organs.
Muscle Tissue:- Muscle tissue is involved in movements like pumping blood, and maintaining a posture.
Nervous Tissue:- It is also known as neural tissue. It helps transmit information inside the body.

Four Types of Tissue
Summary
The cell is the smallest unit. It forms all living organisms. Single-celled organisms are known as unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. Cells provide structure and support to the body. There are two types of cells based on cellular structure prokaryotic and eukaryotic. A group of cells that have similar shapes and functions is known as tissue. They provide protection and support to the body. The four types of tissues are connective, epithelial, nervous, and muscle tissue. Hope this article is beneficial for you.
FAQs on Know About Building Blocks of The Body
1. What are the main 'building blocks' of the human body?
The main building blocks of our body are tiny living parts called cells. To create and maintain these cells, our body needs key nutrients from food, especially proteins. Therefore, proteins are often called the building blocks that help our body grow and repair itself.
2. Why are proteins known as the building blocks for the body?
Proteins are called 'building blocks' because they are essential for growth and repair. Just as bricks are used to build a house, your body uses proteins from food to build new cells, make muscles stronger, repair tissues when you get hurt, and help you grow taller.
3. Which foods are good sources of these building blocks?
Foods rich in protein provide the best building blocks for the body. Some common examples include:
- Milk, curd (dahi), and cheese (paneer)
- Pulses (dals) like moong and chana
- Eggs, fish, and chicken
- Soybeans and nuts
4. What are cells, and where are they found in our body?
A cell is the smallest, basic unit of life. They are so small that they can only be seen through a microscope. Cells are found everywhere in your body, making up your skin, bones, muscles, blood, and every organ like your heart and brain.
5. How do these building blocks help us when we get injured?
When you get a cut or a bruise, your body uses proteins as building blocks to repair the damaged area. They help create new skin cells and tissues to heal the wound, which is why eating healthy is very important for a quick recovery.
6. What happens if we don't eat enough foods with building blocks like protein?
If your diet lacks enough protein, your body won't have the necessary materials for proper growth and repair. This can lead to weak muscles, feeling tired often, and it might take longer for your body to heal from injuries. It can also affect your overall growth.









