




Fun Everyday Uses of Water: Easy Examples for Kids
Before we learn about where freshwater comes from, it’s important to know what it is. Freshwater is different from seawater and brackish water because it has very little salt. Brackish water has more salt than freshwater but less than seawater.
Freshwater comes from rivers, lakes, ponds, wetlands, glaciers, icebergs, ice caps, aquifers, and groundwater. These sources have very low salt levels, usually less than 500 parts per million (ppm).
Even though most of the Earth’s water—about 70%—is salty ocean water, there are many natural places where we can find fresh water. Freshwater is very important in our daily lives. It gives us drinking water and is used for cooking, cleaning, and growing crops.
Knowing the uses of water for kids helps them understand how water is part of their everyday lives. We use it to drink, bathe, brush our teeth, water plants, and wash clothes. Water also helps animals survive and keeps nature healthy.
By learning about where freshwater comes from and how we use it, kids can understand how important it is. Since only a small part of the Earth’s water is freshwater, it’s important to use it carefully.
Also Read Water - A Wonder Liquid
The Four Sources of Freshwater
The main sources of water are rain, groundwater, ice, rivers, lakes, streams, and natural reservoirs. We derive water for daily use through these sources. Let us now learn about each of these sources of water in detail.
Rain
An important source of freshwater that is often overlooked is stormwater. This is the product of earth's water that has evaporated into the atmosphere and turned into rain. Making the most of an unlimited supply of freshwater that is sometimes taken for granted, rainwater harvesting is a technology that was employed by ancient civilizations and is currently commonly used in many rural places.

A Girl Enjoying the Rain
Groundwater
Beneath the surface of the earth lies a great source of freshwater. Groundwater is the largest source of freshwater on the planet and the second largest source of water, along with that present in the oceans. Like the salt water of the sea, most of it cannot be consumed by people or animals. However, a percentage of the groundwater is fresh and can be desalinated and refined in order to provide safe drinking water for the population.
Ice
A major topic of debate surrounding the earth's climate change issues is the melting of the polar ice caps and the shrinking of ice shelves throughout the Arctic. Along with groundwater, ice makes up the second largest source of freshwater on the planet, accounting for just under 2 percent of earth's water. Some of the freshwater preserved in ice, especially in the Antarctic ice sheets, is thousands of years old. As with groundwater and seawater, it is also difficult to use ice water as a source of drinking water, but it is possible.
Rivers, Lakes, Streams, and Natural Springs
As the only natural source of freshwater on earth, rivers, lakes, streams, and natural springs are referred to as surface water sources (0.0014 per cent). Despite the fact that there are millions of freshwater lakes and many kilometres of rivers and streams on the planet, these water sources represent an almost insignificant amount of freshwater. However, they remain vitally important: A large amount of our drinking water comes from them.
You can see the main water sources images below:

Sources of Water
Uses of Water Chart for Kids
The importance of water for human beings is not only in its daily use such as washing dishes, personal hygiene, watering plants, etc. There are activities in which water plays a very important role and also becomes an economic and industrial resource. These various uses of water reflect its importance in the development and growth of the human being in all its areas. The below image shows the uses of water for kids to learn.
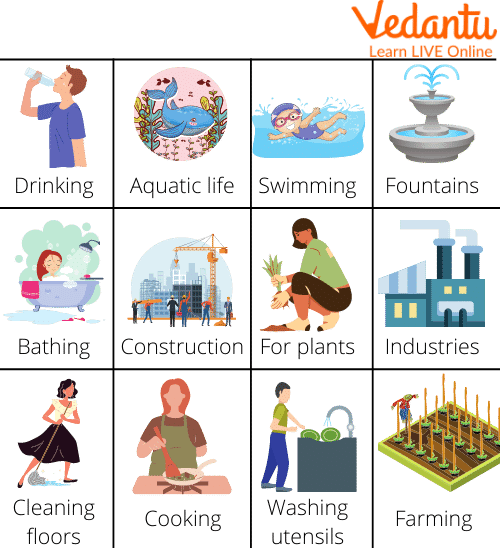
Uses of Water
Human consumption: Water is used for drinking, to make the different beverages that man consumes, to prepare food, and in factories where food is processed.
Personal hygiene: Personal hygiene activities are where water is most wasted: people tend to waste thousands of litres of water when bathing and brushing their teeth. Pisciculture: This is an activity that refers to the cultivation of fish, that is, their breeding and reproduction. In it are also shellfish and, in general, any aquatic animal.
Agriculture: The importance of water for this set of activities created by man is fundamental, it is where fruits, vegetables, and grains are grown for human consumption. The land is treated so that it is fertile and can provide food for people and animals.
Industry: There are different sectors in which the function of water is important. It can be from a technological point to the textile sector that is responsible for the creation of fabrics.
Summary
Although most of the earth is water (1,386 million km3 of water), only 2.5% of this water is freshwater. Of this percentage, only 0.01% is found in rivers and lakes and 0.5% in underground deposits. Of all this amount of water that the planet has, only 0.007% is drinking water and due to environmental pollution, reserves are reduced year after year. We hope you have learnt about the importance and uses of water in this article and will practise saving it rather than wasting it.
FAQs on Uses of Water for Kids: Why Water Matters Every Day
1. What are 5 main uses of water for kids?
For kids, water is used every day in many ways. Here are five main uses:
- Drinking: To stay healthy and hydrated.
- Bathing: To keep our bodies clean.
- Cooking: To help prepare our food.
- Washing: For cleaning hands, clothes, and dishes.
- Watering Plants: To help flowers and trees grow.
2. Why is water so important for us to live?
Water is essential for life because it keeps our bodies working properly. It helps digest the food we eat, carries nutrients to all parts of our body, and helps control our body temperature. Without enough water, we would feel tired and sick, which is why it is the most important element for survival.
3. What are some easy ways for kids to save water every day?
Saving water is very important, and kids can help too! Here are some easy ways:
- Turn off the tap while brushing your teeth.
- Take shorter showers.
- Tell a grown-up if you see a leaky tap.
- Use a bucket and mug for bathing instead of a shower.
- Use leftover water from your bottle to water a plant.
4. How does water help plants and animals?
Just like us, plants and animals need water to survive. Plants use water to make their own food through a process called photosynthesis and to stand up straight. Animals need water for drinking to stay hydrated and for living in, like fish who live in rivers and oceans.
5. Where does the water we use at home come from?
The water we use in our taps, showers, and kitchens comes from different natural sources. The main sources of freshwater are rain, rivers, lakes, and underground wells. This water is collected, cleaned to make it safe, and then sent to our homes through pipes.
6. How does water help in keeping things clean?
Water is excellent for cleaning because it can dissolve dirt and germs. When we wash our hands with soap and water, the water helps rinse away the dirt. It is also used to wash our clothes, clean our dishes, and mop the floors, keeping our homes and ourselves hygienic and clean.
7. What would happen if there was no water on Earth?
If there were no water on Earth, life could not exist. Plants would wither and die, animals would have nothing to drink, and humans would not be able to survive. Our planet would become a dry, empty desert. This shows why water is the most precious resource we have.
8. Why can't we drink water from the sea or ocean?
We cannot drink water from the sea because it is saltwater. It contains a very high amount of salt, which is harmful to our bodies. Drinking it would actually make us more thirsty and sick. The water we drink must be freshwater, which has very little salt and is safe for us.
9. How much water should a child drink in a day?
The amount of water a child should drink depends on their age and how active they are. A general good habit is to drink about 6 to 8 small glasses of water throughout the day. It's especially important to drink more water when it's hot outside or after playing and running around.









