




Overview of DNA
What makes DNA so crucial or so important to get knowledge about? Simply said, DNA holds the instructions required for life. For most other organisms, in addition to humans, DNA is an essential chemical. Our genes and genetic material, which give us our individuality, are both found in our DNA. Our DNA contains instructions on how to build the proteins necessary for our growth, development, and general health. Discover more about what is DNA?, its functions, DNA structure facts, and much more by reading this article till the end.
What is DNA?
Humans and nearly all other species carry genetic information in DNA, also known as deoxyribonucleic acid. An individual's DNA can be found in almost all of their cells. The majority of DNA is found in the cell nucleus (where it is known as nuclear DNA), but there is also a tiny quantity of DNA in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA ). Cellular organelles called mitochondria transform the food energy into a state that cells can utilise.
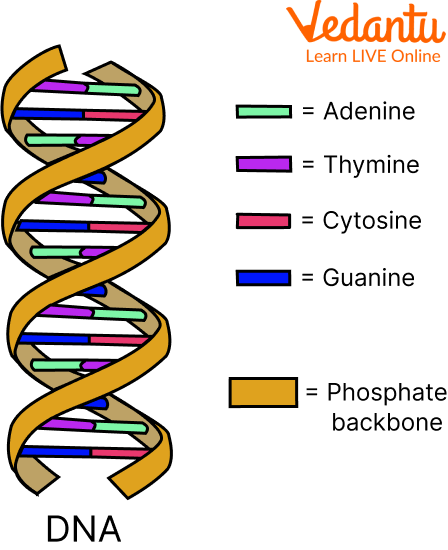
DNA
DNA Structure
DNA bases link up to form units referred to as base pairs, A, which stands for Adenine with T which stands for Thymine and C which is Cytosine with G which denotes Guanine. Adenine and Thymine form 2 hydrogen bonds, whereas Cytosine forms 3 hydrogen bonds with Guanine. A sugar and phosphate molecule are also joined to each base. A nucleotide is made up of a base, a sugar, and a phosphate. The double helix is a spiral formed by two long strands of nucleotides. The base pairs serve as the ladder's rungs, while the sugar and phosphate molecules serve as the ladder's vertical side rails in the double helix shape.
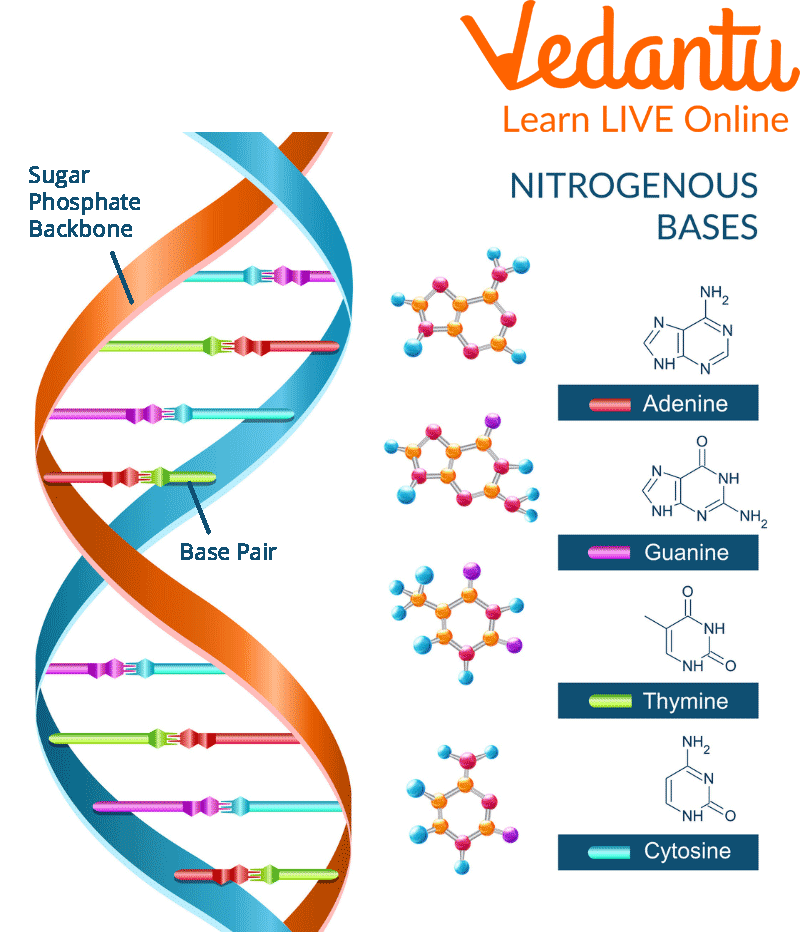
Structure of the DNA
Discovery of DNA
James Watson and Francis Crick's discovery of the double helix, or the twisted-ladder structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), in 1953. It helps in understanding how gene function takes place inside cells. Thus it helped in understanding the genetic code and protein production.
Double Helix Structure of DNA
Functions of DNA
DNA consists of genetic information that contains all of the hereditary information. Genes are short pieces of DNA that typically have between 250 and 2 million base pairs.
A gene codes for a polypeptide molecule in which a sequence of three nitrogenous bases represents each amino acid.
Since every creature has a large number of genes in its DNA, various kinds of proteins can be created.
The primary structural and functional molecules in the majority of organisms are proteins.
It also helps in the analysis of DNA fingerprinting.
Interesting Facts of DNA
We looked at all the basic information about the history and structure of DNA, let us now glance at a few interesting facts about human DNA.
A single chromosome can contain about 50 million to 250 million base pairs!
DNA analysis can help understand the genetic disease pattern and provide appropriate treatment.
No other human has the same genetic code as you! Unless you have an identical twin. Identical twins have the same DNA makeup as they are developed from the same fertilised zygote.
Although no two humans (except identical twins) on the face of the earth have the same genetic makeup, 9% of our DNA is the same as other humans.
Forensic DNA testing to determine the Questioned blood sample and the suspect's blood sample look at specific 13 segments.
In 2001, scientists made a map of all the genes that make a person - this complete DNA sequence is known as the human genome. About 99.9% of the DNA of every person on the planet is the same - it’s the 0.1% that makes us unique.
Summary
In this article about DNA, the genetic material, we have learnt about DNA, its function and much more. The DNA's linear nucleotide sequence contains genetic information. A hydrogen bond between the G-C and A-T base pairs holds the complementary strands of nucleotides that make up each DNA molecule's double helix. An organism's future protein synthesis will be governed by the genetic information encoded in its DNA. DNA is located in the cell nucleus of eukaryotes. We hope you enjoyed reading this article. In case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on DNA Structure Facts
1. What are the three main components that make up a DNA nucleotide?
A DNA nucleotide, the basic building block of DNA, is made up of three main components: a deoxyribose sugar (a five-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar and phosphate groups form the backbone of the DNA strand, while the nitrogenous base determines the genetic code.
2. What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA and what are their pairing rules?
DNA contains four nitrogenous bases which are essential for storing genetic information. These are:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T)
These bases follow a specific pairing rule known as Chargaff's rule, where Adenine always pairs with Thymine (A-T) via two hydrogen bonds, and Guanine always pairs with Cytosine (G-C) via three hydrogen bonds. This is called complementary base pairing.
3. What are the key features of the Watson and Crick model of DNA structure?
The Watson and Crick model describes DNA as a right-handed double helix. Its key features include:
- Two polynucleotide chains coiled around a central axis.
- The backbone is formed by sugar-phosphate, and the bases project inwards.
- The two chains have antiparallel polarity, meaning one runs in the 5' to 3' direction and the other in the 3' to 5' direction.
- The bases in the two strands are paired through hydrogen bonds (A with T, and G with C).
4. How does the structure of DNA allow it to be copied so accurately during cell division?
The unique structure of DNA is central to its ability to replicate with high fidelity. The double helix can unwind, and each of the two single strands acts as a template for creating a new, complementary strand. Because of the strict base-pairing rules (A with T, G with C), the sequence of the new strand is precisely determined by the sequence of the template strand, resulting in two identical DNA molecules from one original.
5. If the DNA in a single human cell is about 1.8 metres long, how does it fit inside a microscopic nucleus?
This incredible feat is possible due to a highly efficient packaging system. The long DNA molecule is wrapped tightly around proteins called histones. This DNA-histone complex, known as chromatin, is then further coiled and supercoiled into a compact structure called a chromosome. This multi-level compaction allows metres of DNA to be stored within the tiny confines of a cell's nucleus.
6. What does it mean for the two strands of a DNA molecule to be 'antiparallel'?
The term 'antiparallel' refers to the orientation of the two sugar-phosphate backbones in the DNA double helix. They run in opposite directions. One strand is oriented in the 5' to 3' direction, while the complementary strand runs in the 3' to 5' direction. This orientation is crucial for both DNA replication and the process of reading the genetic code to synthesise proteins.
7. What are the primary structural differences between DNA and RNA?
While both are nucleic acids, DNA and RNA have three primary structural differences:
- Sugar: DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, whereas RNA contains ribose sugar.
- Bases: DNA uses the base Thymine (T), while RNA uses Uracil (U) in its place. Adenine pairs with Uracil in RNA.
- Structure: DNA is typically a double-stranded helix, whereas RNA is usually a single-stranded molecule.
8. Is it true that DNA can store information like a computer's hard drive?
Yes, this is one of the most amazing facts about DNA. Due to its incredibly dense and stable structure, DNA is a fantastic medium for information storage. Scientists have successfully encoded digital data, including text, images, and audio, into synthetic DNA sequences. It is estimated that just a few grams of DNA could theoretically store all the digital data in the entire world.
9. How does DNA's structure explain the genetic similarity between humans and other species like chimpanzees?
The sequence of the nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G) in DNA acts as a genetic blueprint for an organism. By comparing these sequences between different species, scientists can determine how closely they are related. For example, human DNA and chimpanzee DNA have a sequence similarity of over 98%. This high degree of similarity in their fundamental DNA structure and code is powerful evidence of a recent common ancestor.









